By: Soo Nee Kee1,2
1Universiti Malaya, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia.
2International Center for AI and Cyber Security Research and Innovations, Asia University, Taiwan Email: nee.kee2001.nks@gmail.com
Abstract
Cloud-based and IoT technologies are widely adopted in education sectors to support resource sharing, seamless management process and collaboration between students and educators. IoT and cloud services provide seamless access to educational resources, ensuring data sharing across all devices and platforms in real time and improving academic performance. Through these services, educational institutions can conduct remote learning, automate menial administrative tasks and develop smart campus. However, it faces security challenges like phishing and unauthorized access due to the increasingly interconnected devices. To enhance security and provide a safe learning environment for students, blockchain technology is brought to the table.
Keywords: blockchain, IoT, cloud, authentication, access control
Introduction
Blockchain technology provides a robust solution to address security vulnerabilities in cloud and IoT ecosystems. Its decentralized, immutable, transparent and traceable nature ensures that data store in a secure manner, avoiding any malicious changes and data deletion. [1] It is used in a smart campus to provide decentralized access control to all educators, students and researchers, enhancing privacy and security. By using blockchain and smart contracts, only authorized users have the ability to access educational resources like students’ personal information and research data, effectively preventing phishing attacks and unauthorized access. For example, only researchers can access research libraries provided by institutions. Students are not allowed to view educators’ personal information and access school management system.
Technologies
Blockchain provides decentralized access control mechanism in the smart school environment due to its immutability and traceability. It can verify identity of every user and any malicious changes in the access permissions can be tracked. Most traditional access control management systems are centralized and all data is stored on a single server, making it vulnerable to many security threats. By utilising blockchain-based access control management system, educational institutions can enhance security against various cybersecurity threats. In blockchain, access permissions are stored in distributed manner rather than being stored on a single server, effectively avoiding single point of failure.
In this system, all users including teachers, students or clerks are assigned unique identities and these identities are stored on blockchain, making it immutable. [2] When users want to access resources, such as administrative dashboard, system will check their credentials based on the stored data on blockchain to ensure that only users with appropriate access permission can access the dashboard. In addition, any changes on access permissions will be recorded on blockchain which provides a transparent and traceable history of all access control permissions, protecting systems from unauthorized access. The use of smart contracts can specify conditions for accessing certain resources and ensure only permissions comply with institutional policies. For example, smart contract provides automated process to grant access to research databases only to computer science students.
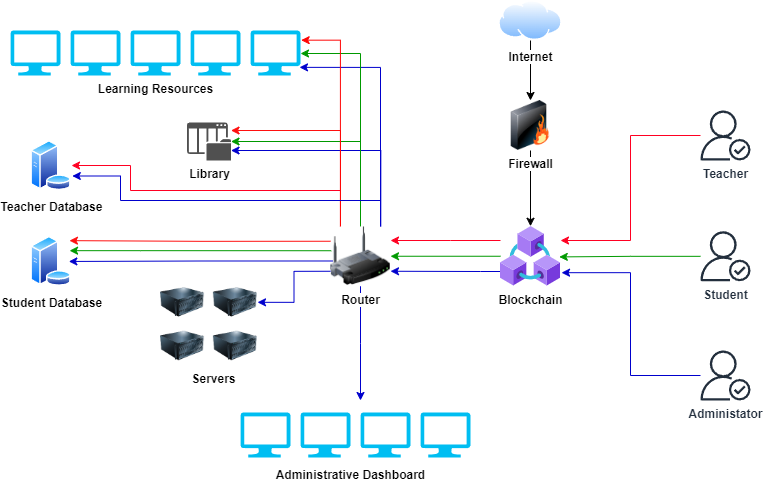
Figure 1: Integration of blockchain as Authentication System in IoT and Cloud-based Smart School
Conclusion
In conclusion, smart institutions can utilize blockchain-based access control management system to build a more secure and reliable environment in order to protect privacy data from unauthorized access and foster users’ trust. This innovative approach not only mitigates limitations faced by traditional access control management system, but also provides a safe environment for students, researchers and educators to learn and adsorb knowledge without any worries.
Reference
- “Exploring the integration of edge computing and blockchain IoT: Principles, architectures, security, and applications – ScienceDirect.” Accessed: Oct. 04, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1084804524000614
- V. Aanandaram and P. Deepalakshmi, “Blockchain-based Digital Identity for Secure Authentication of IoT Devices In 5G Networks,” in 2024 Third International Conference on Intelligent Techniques in Control, Optimization and Signal Processing (INCOS), Mar. 2024, pp. 1–6. doi: 10.1109/INCOS59338.2024.10527739.
- Law, K. M., Ip, A. W., Gupta, B. B., & Geng, S. (Eds.). (2021). Managing IoT and mobile technologies with innovation, trust, and sustainable computing. CRC Press.
- Li, K. C., Gupta, B. B., & Agrawal, D. P. (Eds.). (2020). Recent advances in security, privacy, and trust for internet of things (IoT) and cyber-physical systems (CPS). CRC Press.
- Mourelle, L. M. (2022). Robotics and AI for Cybersecurity and Critical Infrastructure in Smart Cities. N. Nedjah, A. A. Abd El-Latif, & B. B. Gupta (Eds.). Springer.
- Gupta, B. B., & Srinivasagopalan, S. (Eds.). (2020). Handbook of research on intrusion detection systems. IGI Global.
Cite As
KEE S.N. (2024) Blockchain-Enhanced Security Models for Cloud and IoT-Based Services, Insights2Techinfo, pp.1