By: Dadapeer Agraharam Shaik, Department of Computer Science and Technology, Student of Computer Science and technology, Madanapalle Institute of Technology and Science, Angallu,517325, Andhra Pradesh.
Abstract:
Even as the threats rodents become more advanced, the same goes for the specialization of Cyber forensics. Thus, it is clear that shift is taking place with AI at the heart of the change, which is affecting how cyber forensics is done. In this article, the impacts of AI on the field of cyber forensic with regards to the identification, monitoring, and preventing of cyber threats are discussed. Through the implementation of AI-based tools, the area of cyber forensics can analyse larger amounts of information, as well as state and recognize various trends and abnormalities, which in turn will allow for better understanding of cyber incidents.
Keywords: Artificial Intelligence , cyber security , Digital Forensics.
1.Introduction
Digital technology refers to the effective change that has occurred in societies because of the provision of connection and convenience. But this process has also had a critical downside, namely, the increase in risks and threats stemming from the sphere of cybersecurity – threats that have become both more numerous and more complex. Computer criminality is also one of the present threat [sic] and concerns the everyday life of many people, companies, and states, which requires more complex tools for investigation and protection. In this regard, cyber forensics, which is the study of the methodology of the collection, examination, and preservation of the digital evidence, is a very important matter. Conventionally, cyber forensics has been a domain that involved manual analysis and examination of the digital content along with the help of skilled professionals who have the ability to analyse and infer from the digital evidence related to cybercrimes. In spite of this, these traditional approaches have been found to be quite useful though they fall short of meeting the dynamic nature of the cyber threats.
The nature of the contemporary cyberviolence, merged with the volume of daily generated information, exceeds the possibilities of traditional approaches to digital forensics. For instance, while analysing a gigabyte of data from a series of events that involve a major data leak or a complex ransomware attack, understanding the specifics of malicious code, and tracking hackers’ movement across regions or countries. These tasks are time consuming and can be resource intensive and when human beings are involved the possibility of error is always an issue. Enter artificial intelligence an innovative technology that is revolutionizing many fields among them being cyber forensics. AI’s capability to handle vast amounts of data, transform it into insights, analyse, predict with optimal accuracy necessary to solve the issues troubling cyber forensic investigators.
2.TRADITIONAL FORENSIC ANALYSIS METHODS
Conventional investigation approaches represent the foundation of CS practice as a set of fundamental principles on the identification, containment, and attribution of cyber threats, a bundle of methods and procedures. The initial and most fundamental method of digital forensics, disk imaging copies the data files stored in a digital media and later reviews the items during the digital forensics undertaking. These approaches allow the forensic team to work with the disk image as a separate copy, which will allow preserving all the original information and then search for viruses, file traces, and other malicious activities. Another common and obligatory step in the forensic examination is the analysis of volatile memory (RAM) in the living system or in the dump. Speaking of the memories’ contents, one may find specifics of the operating sessions, the connected networks, and the presence of malware as evidence of active dangerous work and indications of a compromise. In addition, it will be easier to analyze the memory to understand the adversary TTPs, which will subsequently lead to identifying the proper measures or ways on how to address them[1].
The third challenge is the analysis of the log file; where logs of the system and applications used in the system are processed in order to reconstruct the sequence of events before and after the particular cyber incident. Thus, based on log files, the analysis of the investigators may find the time and scope of the specific suspicious activities, intrusion attempts, and information security breaches for the benefited organizations to affect the issue to the level and power. Furthermore, the use of log files goes hand in hand with identity and tracking of cyber attacks since the latter can be used in the tracing of the origin and flow of the malicious activities in the network.[2]
3.Forensics of Internet of Things
DF is considered as a subset/cross-over of the classical forensic, which only deals with the identification and examination of digital/computerized information. The DF specialists are responsible for the identification, collection, storage, review, interpretation, and management of the digital evidence found in a number of gadgets.
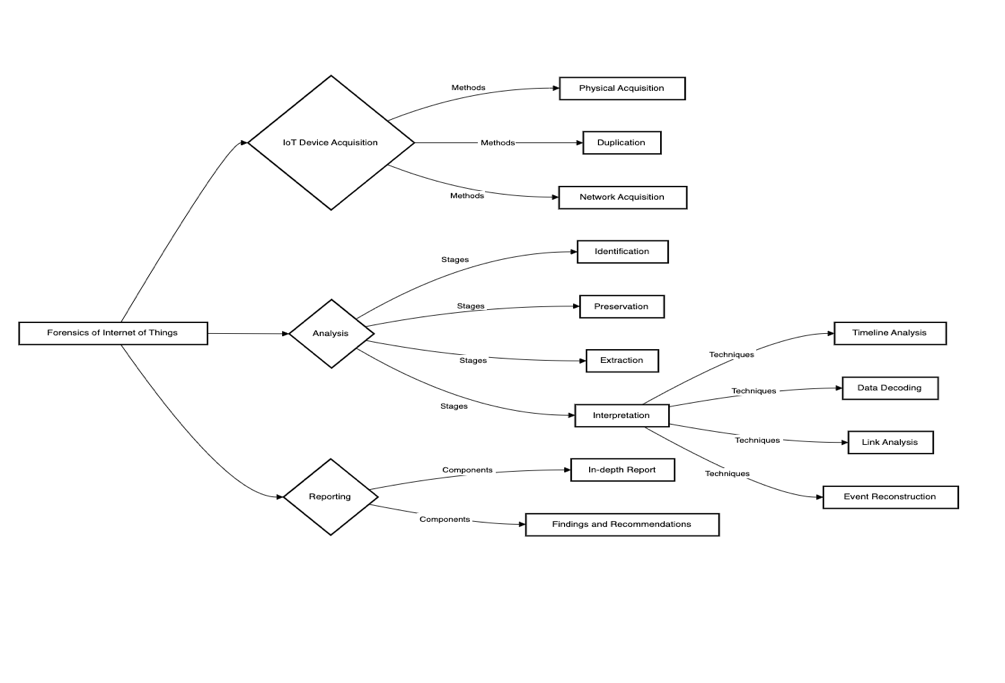
IoT has become a vital aspect in the civilization of human individuals; thus, any investigation, civilian or criminal or even internal inquiries, ought to consider IoT. The vulnerabilities which can be experienced in IoT systems relate to attacks, which can be used to gain remote control of the systems, for example, it is possible to unsuccessfully control the braking system of a vehicle leading to an accident. Thus, the IoT system realizing an emergent need for carrying out more research on IoT forensics to help determine the who, what, where, when, and how in cases. From this digital forensic perspective, IoT environment contains an abundance of objects that may potentially be helpful to investigations, further, characteristics of IoT have led to the concept of ‘IoT Forensics,’ newly defined for investigative needs in the IoT framework[3].
Based on these two approaches, a basic but significant difference between IoT Forensics and conventional digital forensics lies on the sources of evidence. Unlike regular digital enforcement in which the laptops, computers, smartphones, smartwatches, the cloud servers are used as a regular item of investigation, the proofs pertaining to IoT Forensics may be much more invasive and include the implantations of medical instruments into animals, newborn incubation systems, traffic signals, and In-Vehicle Infotainment syria. In essence, maintaining the security of all IoT devices, an IoT network and information and communication storage practically becomes problematic, if not totally unfeasible within the various layers of the IoT network. Sometimes an event occurs and when it does, the initial function, that forensics workers perform is to identify the extent of the breach. However, it is different from the conventional procedures of securing internet of things.[4]
3.Benefits of Integrating AI in Forensic Accounting
AI in forensic accounting practices has many advantages, which develop the sector and equip the experts with the tools for the more effective identification, investigation, and prevention of the financial fraud. There are significant benefits for forensic accountants resulting from the synergy that exists between the application of AI and the traditional investigatory processes of this profession in the contemporary complex economic environments.
1.Increased Efficiency and Speed of Investigations
- Data Processing: Originally, forensic accountants used to take a longer time to analyze large datasets but with the implementation and arrival of AI this process gets much faster. This enhances the quality as well as the efficiency of investigation processes.
- Real-time Monitoring: This makes the work of monitoring for the possible fraudulent activities done automatically hence helping in the identification of any of the activities as they occur.
2.Enhanced Accuracy in Identifying Suspicious Patterns
- Pattern Recognition: The use of the algorithm makes it easy for the identification of patterns in the data that may not be identifiable using other methods hence being an added advantage of the machine learning algorithms.
- Automated Detection: An automation of patterns improves the classification and detection of the irregularities as well as signs of fraud.
3. Improved Risk Management and Proactive Fraud Prevention
- Predictive Analytics: Instead of presenting findings that are a posteriori analysis, predictive analytics shall ensure that forensic accountants are able to formulate an outright approach of preventing it by analyzing historical records and future trends.
- Risk Assessments: Risk assessments made easy through artificial intelligence help the professionals to act proactively before the fraudsters can go to the next level.
4. Streamlined Data Analysis for Large Datasets
- Efficient Processing: AI technologies help in analyzing and sorting out mass data at a much faster and efficient rate and is not impaired as the manual analysis.
- Insight Interpretation: Criminology experts can work on consulting about the insights rather than being enclosed by the quantity of information.
5. Cost-Effectiveness and Resource Optimization
- Automation: As operations are integrated with AI, a lot of mundane work is done away with hence reducing the amount of work to be done by hand.
- Productivity Gains: This in turn leads to cost saving with regards to time and resources required in the investigations.
6.Continuous Monitoring and Adaptive Learning
- Constant Surveillance: Integration of AI systems makes it possible to monitor financial activities, and if the status malfunctions, forensic accountants will be put on notice that there is something wrong at that stage.
- Adaptive Learning: Another advantage of using AI in detecting fraud is that the learning process is constantly adjusted to ensure its applicability in the identification of the new trends in fraud schemes.
7.Early Detection of Emerging Fraud Schemes
- Historical Analysis: AI can use the previous fraud scenarios to deduce and recognize new fraudulent activities before they go viral.
- Prompt Action: Its effectiveness increases when fraud is detected at an early stage thus decreasing the negative impact of some of the complex fraud gears that are in the market today.
8.Data Visualization for Enhanced Insights
- Visual Representation: Technology solutions provided by AI present most financial data in an easy to comprehend manner, making a much better interpretation of patterns possible.
- Improved Communication: Graphic illustrations add to the flow of information and the problem-solving part of the investigation.
9.Increased Accuracy in Unstructured Data Analysis
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): NLP enhances the assessment of qualitative sources like emails and textual documents by it enhancing the accuracy of the evaluation.
- Meaningful Insights: The ability to extract more valuable information from a greater information array of form generates more efficiency in investigation by forensic accountants.
10.Strategic Allocation of Human Resources
- Automated Operations: Demands your time for the scripting of these functions to be spared for critical analytical and decision-making tasks forensic accountants can address with AI assistance.
- Optimized Expertise: Human resources involvement is systematically scheduled, namely, perfecting the outcomes of investigative work.
Applying AI to forensic accounting removes all the barriers instigated by the new age and opens a range of opportunities that improve professionals’ productivity, reliability, and prophetic vision. This shift puts forensic accountants in the driver’s seat as regards the application of emerging advanced technological tools for analysis of financial data and business fraud.[5]
CONCLUSION:
The use of artificial intelligence (AI) therefore in the field of cyber forensics is now deepening a revolution in the field in the way that various tools and capabilities for identification, investigation and curbing of cybercrimes are being provided. The various availabilities of AI in forensic professions make processing in today’s security problems much more efficient than traditional methods.
What greatly benefits from the use of AI is the fact that computers can analyse thousands of records in hours and identify patterns that can easily remain unnoticed by ordinary people, or even experienced investigators. Integration of AI in information security makes it easier to detect risks and threats in real-time and generalize the investigational processes and responses since it automates the whole process. It also increases the efficiency of forensic investigation as well as reduces the impact of cyber threats.
Furthermore, through risk analysis, AI-led predictive analytics enhances risk prevention to avoid situations that could lead to forensic expert’s exposure. In this regard, big data and analysis that consider the historical information and the early signs of potential threats contribute toward the implementation of protective measures, thus strengthening the security position of organizations.
The identified possibilities of the optimisation of the resources can also be regarded as the evidence of the crucial importance of the AI in cyber forensics. Outsourcing routine and tedious assignments increase the value and efficiency of forensic workers’ work on substantial analysis and decision-making and the effective use of available resources to a considerable extent, bring down operational expenditure.
Therefore, AI is transforming cyber forensics by delivering potent solutions that enrich the efficacy, precision, and pre-emptive potential of forensic processes. This brief review reveals that, as the field of AI technology evolves, its function in cyber forensics will remain critical so that forensic professionals have the tools and knowledge they need to address the constantly changing and complex nature of cyber threats. This revolution sets cyber forensics as one for the most advanced technological tools of the current society, protecting the digital properties and ensuring the stability of cyberspace.
Reference:
- S. Manikandan, M. Rahaman, and Y.-L. Song, “Active Authentication Protocol for IoV Environment with Distributed Servers,” Comput. Mater. Contin., vol. 73, no. 3, pp. 5789–5808, 2022, doi: 10.32604/cmc.2022.031490.
- V. Kolluri, “A PIONEERING APPROACH TO FORENSIC INSIGHTS: UTILIZATION AI FOR CYBERSECURITY INCIDENT INVESTIGATIONS,” Int. J. Res. Anal. Rev., vol. 3, pp. 919–922, Aug. 2016.
- M. Rahaman, B. Chappu, N. Anwar, and P. K. Hadi, “Analysis of Attacks on Private Cloud Computing Services that Implicate Denial of Services (DoS),” vol. 4, 2022.
- M. Abdel-Basset, N. Moustafa, H. Hawash, and W. Ding, “Introduction Conceptualization of Security, Forensics, and Privacy of Internet of Things: An Artificial Intelligence Perspective,” in Deep Learning Techniques for IoT Security and Privacy, M. Abdel-Basset, N. Moustafa, H. Hawash, and W. Ding, Eds., Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2022, pp. 1–35. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-89025-4_1.
- F. Tuli and U. R. Thaduri, “The Integration of Artificial Intelligence in Forensic Accounting: A Game-Changer Asian Accounting and Auditing Advancement,” Asian Account. Audit. Adv., vol. 14, pp. 12–20, Oct. 2023.
- Shrivastava, G., & Gupta, B. B. (2014, October). An encapsulated approach of forensic model for digital investigation. In 2014 IEEE 3rd Global Conference on Consumer Electronics (GCCE) (pp. 280-284). IEEE.
- Gupta, B. B. (Ed.). (2021). Cloud Security: Concepts, Applications and Perspectives. CRC Press.
Cite As
Shaik D.A. (2024) How AI is Revolutionizing Cyber Forensics, Insights2Techinfo, pp.1