By: Brij B. Gupta, Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering, Asia University, Taichung 413, Taiwan.
Abstract
The advent of Industry 4.0 has triggered a transformative shift across the industrial landscape, where automation, data-driven decision-making, and cyber-physical integration define the future of smart manufacturing and enterprise operations. This blog explores the convergence of emerging technologies—Artificial Intelligence (AI), Internet of Things (IoT), Edge Computing, Blockchain, and Metaverse—and their collective impact on cybersecurity, authentication, data analysis, and real-time intelligence. We highlight contemporary research that illustrates the practical deployment of these technologies, including the role of lightweight authentication protocols, facial emotion recognition in the Metaverse, and AI-enhanced digital forgery detection. By reviewing these recent advancements, this article presents a cohesive understanding of how security and intelligence are being redefined in the era of Industry 4.0.
Introduction
Industry 4.0 [1] represents the fourth industrial revolution, characterized by interconnected systems, intelligent automation, and real-time data exchange. This cyber-physical era brings substantial benefits—enhanced efficiency, predictive maintenance, and smart factories—but also introduces new challenges, particularly concerning security, trust, and data privacy. As traditional perimeters dissolve, the demand for intelligent, lightweight, and interoperable security mechanisms grows significantly.
Security in Industry 4.0 is no longer a mere protective layer; it is a strategic enabler. Technologies like edge computing, digital twins, semantic data models, and AI-based anomaly detection are being incorporated not only to enhance efficiency but also to embed trust at the system level. These innovations are shaping a new blueprint for the digital enterprise.
Emerging Tech Trends and Their Role in Industry 4.0
1. AI and Neuro-Fuzzy Systems for Real-Time Intelligence
AI is revolutionizing how data is processed and decisions are made. Neuro-fuzzy systems, which combine the adaptability of neural networks with the interpretability of fuzzy logic, are now used for stream data flux mitigation in real-time applications [3]. These systems enhance operational efficiency and resilience, especially in dynamic environments like industrial monitoring and network management.
Table 1: Comparison of AI Techniques for Industry 4.0 Applications
Technique | Application Area | Key Feature |
|---|---|---|
Deep Neural Networks | Predictive Maintenance | High accuracy, data-hungry |
Neuro-Fuzzy Systems | Real-time Stream Analysis | Interpretability and flexibility |
Knowledge-Based NLP | Multilingual Processing | Semantic-rich decision support |
Transformer Models | Cybersecurity & Vision Tasks | Parallelization, context preservation |
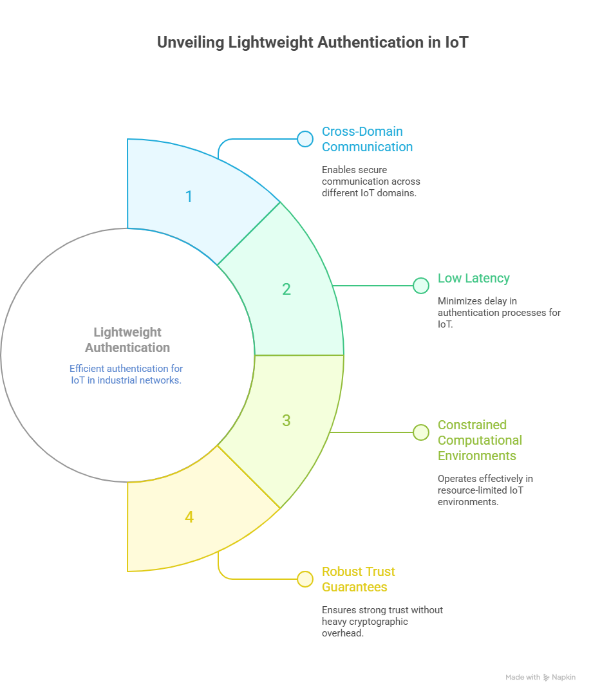
2. Lightweight Authentication and Secure Protocols in IoT
As IoT devices multiply in industrial networks, authentication mechanisms must evolve to support cross-domain communication, low latency, and constrained computational environments. Zhang et al. introduced a lightweight cross-domain authentication protocol tailored for the Industrial Internet, demonstrating robust trust guarantees without heavy cryptographic overhead [4].
This is particularly vital for edge-based DDoS detection systems in transportation and manufacturing environments where every millisecond matters [5].
3. Digital Twins and Malicious Node Detection
Digital twin technology offers real-time digital replicas of physical systems, enabling simulation, prediction, and rapid decision-making. However, it also exposes new attack surfaces. A recent study proposed a digital twin-based model for malicious node detection in VANETs (Vehicular Ad Hoc Networks), showing how twin-based feedback loops can proactively identify network anomalies [6].
4. Metaverse and Emotional AI in Industrial UX
The Metaverse extends Industry 4.0 into immersive, interactive environments. Emotion detection in virtual spaces is gaining traction for improving user experience (UX), training simulations, and mental health monitoring in smart industries. A deep learning-based system for facial emotion recognition in the Metaverse demonstrated its potential in human-machine collaboration [7].
Further, as virtual worlds blur the line between physical and digital, intellectual property rights (IPR) and legal frameworks require urgent evolution [8].
5. AI-Driven Digital Forgery Detection and Cyber Trust
With increasing reliance on digital content and remote operations, ensuring content authenticity is critical. An AI-enabled system for digital forgery detection and interaction monitoring in smart communities offers tools for maintaining trust, compliance, and surveillance across Industry 4.0 networks [9].
6. Multilingual NLP for Enterprise Systems
As global enterprises operate in multilingual environments, semantic understanding becomes a strategic necessity. A knowledge-based multilingual NLP framework leverages low-resource language processing to extract meaning from complex datasets—supporting decision-making in enterprise systems, especially in non-English regions [10].
7. Edge AI and Low-Cost Intrusion Detection
Low-power devices like Raspberry Pi 3B+ are increasingly deployed for lightweight intrusion detection in IoT networks. A practical model integrating lightweight AI to detect network breaches in constrained environments is crucial for remote industrial operations or underfunded settings [11].
8. Big Data for Environmental Sustainability
Sustainability is a cornerstone of Industry 4.0. One study integrated big data analytics with environmental models for isotope hydrology, showing how domain-specific AI applications can enhance compliance and environmental responsibility [12].
Broader Applications and Future Outlook
The fusion of technologies explored above converges at multiple critical junctions within Industry 4.0:
- Cybersecurity is no longer reactive—it is predictive, distributed, and embedded into system design.
- AI models are transitioning from monolithic to modular and explainable, allowing seamless integration in regulated environments.
- Digital rights in virtual and augmented spaces are prompting new legal-tech ecosystems.
- Cross-domain protocols are becoming essential as digital twins and smart devices communicate across decentralized environments.
Conclusion
As we step deeper into the interconnected world of Industry 4.0, the boundaries between data, intelligence, and infrastructure are dissolving. This transformation calls for a redefinition of security, not as a gatekeeper but as an integral, intelligent component of every system. From emotional AI in the Metaverse to real-time authentication in edge environments, the synergy between AI, cybersecurity, and digital innovation is reshaping industrial futures.
Through the referenced works, it becomes evident that intelligence in Industry 4.0 is not only computational—it is contextual, adaptive, and secure. The research contributions across authentication, emotion detection, NLP, forgery analysis, and digital twins provide a rich foundation for the next phase of innovation. To fully realize Industry 4.0’s potential, enterprises must embrace these emerging technologies—not in isolation, but in an orchestrated, secure, and ethically guided manner.
References
- Ghobakhloo, M. (2020). Industry 4.0, digitization, and opportunities for sustainability. Journal of cleaner production, 252, 119869.
- Sinha, D., & Roy, R. (2020). Reviewing cyber-physical system as a part of smart factory in industry 4.0. IEEE Engineering Management Review, 48(2), 103-117.
- Goyal, S., Kumar, S., Singh, S. K., Sarin, S., Priyanshu, Gupta, B. B., … & Colace, F. (2024). Synergistic application of neuro-fuzzy mechanisms in advanced neural networks for real-time stream data flux mitigation. Soft Computing, 28(20), 12425–12437.
- Zhang, T., Zhang, Z., Zhao, K., Gupta, B. B., & Arya, V. (2023). A lightweight cross-domain authentication protocol for trusted access to industrial internet. International Journal on Semantic Web and Information Systems, 19(1), 1–25.
- Gaurav, A., Gupta, B. B., & Chui, K. T. (2022). Edge computing-based DDoS attack detection for intelligent transportation systems. In Cyber Security, Privacy and Networking (pp. 175–184). Springer.
- Arya, V., Gaurav, A., Gupta, B. B., Hsu, C. H., & Baghban, H. (2022, December). Detection of malicious node in VANETs using digital twin. In International Conference on Big Data Intelligence and Computing (pp. 204–212). Springer.
- Gupta, B. B., Gaurav, A., Chui, K. T., & Arya, V. (2024, January). Deep learning-based facial emotion detection in the Metaverse. In 2024 IEEE International Conference on Consumer Electronics (ICCE) (pp. 1–6). IEEE.
- Gupta, B. B., Gaurav, A., Arya, V., & Alhalabi, W. (2024). The evolution of intellectual property rights in metaverse-based Industry 4.0 paradigms. International Entrepreneurship and Management Journal, 20(2), 1111–1126.
- Sedik, A., Maleh, Y., El Banby, G. M., Khalaf, A. A., Abd El-Samie, F. E., Gupta, B. B., … & Abd El-Latif, A. A. (2022). AI-enabled digital forgery analysis and crucial interactions monitoring in smart communities. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 177, 121555.
- Jain, D. K., Eyre, Y. G. M., Kumar, A., Gupta, B. B., & Kotecha, K. (2024). Knowledge-based data processing for multilingual natural language analysis. ACM Transactions on Asian and Low-Resource Language Information Processing, 23(5), 1–16.
- Sai, K. M., Gupta, B. B., Hsu, C. H., & Peraković, D. (2021, December). Lightweight intrusion detection system in IoT networks using Raspberry Pi 3B+. In SysCom (pp. 43–51).
- Keesari, T., Goyal, M. K., Gupta, B., Kumar, N., Roy, A., Sinha, U. K., … & Goyal, R. K. (2021). Big data and environmental sustainability based integrated framework for isotope hydrology applications in India. Environmental Technology & Innovation, 24, 101889.
Cite As
Gupta B.B. (2025) Redefining Security and Intelligence: Emerging Tech Trends Shaping Industry 4.0, Insights2Techinfo, pp.1