By: Poojitha Nagishetti, Department of Computer Science & Engineering (Data Science), Student of Computer Science & Engineering, Madanapalle Institute of Technology and Science, Angallu(517325), Andhra Pradesh.
Abstract –
Hypertension, a major, and common risk factor for both cardiovascular diseases and kidney ailments, requires early detection and efficient treatment to prevent it from having its negative effects felt. Advanced technology such as Artificial Intelligence or AI has now been integrated in hypertension care modifying the models used in hypertension, diagnosis, and treatment plans. In this article, the author focused on the following subtopics; how machine learning is used to predict hypertension, how diagnosis of hypertension is enhanced by Artificial Intelligence, AI in hypertension treatment through mapping and genomic data. Nevertheless, data privacy, and algorithmic bias present limitations of AI. However, the chance to transform hypertension care and enhance patients’ quality of life and cost efficiency of health care services is enormous.
Keywords – Hypertension Management, Artificial Intelligence, Predictive Models, Real-Time Monitoring, Personalized Treatment.
Introduction –
High blood pressure or commonly referred to as hypertension is among the most crucial health issues affecting a considerable number of individuals across the globe. It affects approximately 1. 2 billion adults globally and a significant number of them have no clue they are infected[1]. Hypertension is a potent risk factor for cardiovascular diseases, stroke, and kidney failure and needs adequate control to minimize the dangers of the diseases globally. The earlier practice in hypertensive management has been considered to comprise of routine measurement of blood pressure, lifestyle changes and the use of drugs. However, these methods are not efficient in coping with the issue, which is often polyacetal by its nature and manifests itself as hypertension. The relations between genetic factors, environmental factors, and the patient’s life and habits are still complex and cannot be described by using the conventional means.
Thus, Artificial Intelligence (AI) has become a revolutionary tool in the healthcare sector through improved ways of early estimation, probable diagnosis, and prevention of chronic diseases such as hypertension[2]. It can process large amounts of data from various sources such as EHRs, wearable devices, genetic data, and more to deliver more precise and individualized recommendations or outputs. When AI is applied to hypertension management, healthcare practitioners will be one step closer to a timelier and more personalized model of care that can result in better early diagnostics, effective approaches to treatment, and overall quality of patient’s lives[3]. This article tries to show where and how hypertension management could be benefited from the use of AI, particularly, the possibility of AI in constructing accurate risk prediction model, how the use of AI increases the possibility of the accuracy of diagnoses of hypertension, and how an intelligence-guided hypertension treatment plan could be created. In this way, the AI solutions can change the treatment and management of hypertension as more efficient, effective, and personalized.
Overview of Hypertension –
Hypertension also referred to as high blood pressure, is a prevalent primary cardiovascular disease which greatly raise chances of developing diseases of the heart and blood vessels, stroke, and kidney failure. It is prevalent in one-third of the adult population, which locates in first line of morbidity and mortality in the world. Companion diseases that are often called “the silent killer,” hypertension, can be masked for years and manifested only when the final stage and possible heart attack or stroke is reached. The condition is one that results from both the genetic makeup of the individual as well as the environment in which the person finds him or herself; other factors include poor diet, obesity, sedentary lifestyle, chronic stress, among others. With the developing tendency towards an aggravated age structure of the global population with the tendency towards worsening of hypertension and the constantly growing level of unhealthy lifestyles, the burden of hypertension as a disease on health care facilities will continue to increase.
Standard care of patients with hypertension usually entails a combination of dietary changes including taking low cholesterol diet, change in diet more physical activity, reduction in the use of salt, and the pharmacological management that encompasses the use of drugs such as ACE inhibitors, beta-blockers, and diuretics[4]. These approaches in general can be useful to reduce blood pressure, but they do not comprise all the multifactorial aspects of this condition, and individual differences in its development and management. Daily measurements of a patient’s blood pressure may not be feasible; therefore, accepting periodically checked blood pressure values as satisfactory can be insufficient. Therefore, the public requires new, better, and individual solutions in managing this vital condition. This is where AI comes in because, with its ability to provide solutions that make this prediction, diagnosis, and treatment more efficient, improved hypertension management is possible.
Risk Factors –
Hypertension being polygenic has predisposing factors that are endogenous and exogenous, as well as, genetic and acquired. Other risk factors include genetic factors this is, there is a tendency to inherit hypertension since those, whose parents or other close relatives have the disease, are at greater risk. Age can also be expressed as a risk factor because the likelihood of hypertension raises with age because of changes in the blood vessels and other structures of the cardiovascular system. Gender is also involved because it is observed that men develop hypertension at an earlier age than women though the risk in women rises during menopause.
Lifestyle characteristics are significant causes of hypertension. Obesity is a significant cause since excess body mass puts extra pressure on the heart, and thus, raises the blood pressure. Lifestyle factors such as high sodium intake and high salt intake cause edema and raise blood pressure respectively. Lack of physical exercise enhances the condition since the muscles are progressively negated and the heart and blood vessels are weakened. Alcohol consumption and tobacco use are some of the factors that cause a person’s blood pressure to rise and consequently raise his/her risk of developing hypertension. Furthermore, chronic stress can lead to the temporary increase in the blood pressure level and, therefore, if frequent, it results to pressure level in hypertension. Further, coexisting diseases like diabetes, chronic kidney diseases and sleep apnea are recognized as risk factors for hypertension as such diseases complicate the cardiovascular profile of a patient.
Predictive Models for Hypertension –
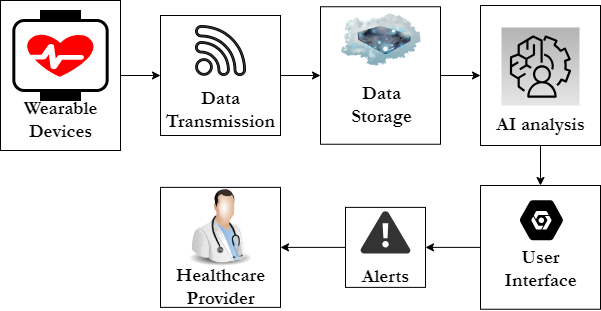
Predictive models that use AI involve machine learning (ML) techniques to look for high risk groups/individuals for hypertension by using big data analyses comprising of factors such as age, gender, BMI, genetics, lifestyle, and other aspects of the personal and family history. These models, built with the help of such tools as decision trees, SVM, and artificial neural networks, can detect pre-hypertensive states and forecast the further condition of a patient with hypertension with high efficiency. Feature engineering is critical here because AI picks and optimizes the features with great efficiency to increase the prediction power of the models. Moreover, the wearable technology in the form of clothing, gadgets, and mobile applications can monitor the patient’s biometrics including the heart rate and blood pressure and constantly analyze this information to give the alerts and the levels of risk to respond quickly. Figure 1 it shows the flow of data and interactions within a real-time monitoring system for hypertension.
AI-Driven Diagnostics for Hypertension –
Consequently, based on data obtained during the early diagnosis as well as during hypertension management, new unique opportunities of accurate, timely and personal diagnostics are implemented benefiting from the AI-based diagnostics. Essential concepts of many traditional models of the patient-management paradigm include rarely measured blood pressure and periodic examinations that do not depict emerging or nascent conditions. AI for example has the added advantage of being able to process clinical record data, imaging data and even a patient’s genotypes hence giving a biopsy for the diagnosis. For example, using the data of ECG and echocardiography concerning hypertension, AI algorithms can determine such relative changes in cardiovascular system as, for example, thickening of the left ventricle or arterial stiffness, which cannot be detected during a standard examination. Besides, it may use genomics and get to discover other bio markers that are related to a particular disease like hypertension and the probability of having this disease[5]. The integration of genetic data with clinical and lifestyle features produces a treatment strategy which is much more personalized, so that one professional can meet another patient’s risk or need in a much more global way than before. However, the actualization of new data relating to diagnostic models occasionally enhances the precision and help clinicians to view diseases progression or effect of treatment over time. AI-based diagnostics are leading to enhancing detection and continuous evaluation of hypertension in patients; this in turn enhances the patient’s health and the structure of the health care delivery system.
Comparing Traditional and AI-Driven Approaches in Hypertension Management –
The previous approaches to the control of hypertension include random blood pressure check on a particular subject, assessment of the client’s behavior, and employing the protocol drugs. While these approaches, to a certain extent, are operating rather effectively, they mainly rely on data assessment in time intervals and general principles of treatment having no regard to several factors such as risk factors, course of disease, or therapeutic efficiency in patients who are different from each other. However, in the modern approaches toward the AI field and the business applications, the situation is opposite. AI based models can handle big and diverse streaming data including real-time data from wearable, genetics, or complete records of the patients to assess their risk of developing hypertension; they can diagnose better and offer a better care plan for every patient. As opposed to the paper-based information which can be gathered only at a certain time interval and might only present intermittent views on the patient’s status, AI can potentially analyze constant data flows and detect early signs of deterioration, as well as such things as real-time trends and specific treatment plans adjusted to the evolution in a patient’s condition. Essentially, this transition of screening uneven approximation of population hypertension patients to methods that are developed from solving individual patient data analytic computations is a level up from the traditional management and treatment of hypertension patients and a step towards improved and efficient health care system. Table 1 shows the key differences between traditional and modern AI methods in managing hypertension, showcasing how AI advances offer more continuous, precise, and personalized care.
Table 1: Traditional methods and modern AI methods for managing hypertension
Aspect | Traditional Methods | Modern AI Methods |
Monitoring | Periodic blood pressure measurements during clinical visits | Continuous real-time monitoring via wearable devices and apps |
Predictive Analytics | Basic statistical methods, limited data analysis | Advanced machine learning algorithms analyzing large datasets |
Diagnostic Tools | Manual or semi-automated tools like sphygmomanometers, standard imaging (e.g., ECGs) | AI-enhanced imaging analysis, including automated ECG and echocardiogram interpretation |
Data Analysis | Manual or basic statistical analysis | Automated and complex analysis integrating diverse data sources |
Treatment Personalization | General lifestyle and pharmacological interventions | Tailored treatment recommendations based on individual data, including medication optimization |
Early Detection | Detection based on periodic visits and symptomatic assessment | Early prediction using AI models that identify risk factors and patterns before symptoms arise |
Integration | Data from various sources is often separate and manually integrated | Seamless integration of data from multiple sources for comprehensive analysis |
Adaptability | Adjustments to treatment based on periodic assessments | Dynamic and real-time adjustments to treatment plans based on ongoing data analysis |
Integrating AI with Traditional Methods –
The solution lies in integrating AI-driven approaches with traditional methods to create a hybrid model that leverages the strengths of both. By incorporating AI into routine hypertension management, healthcare providers can enhance traditional practices with advanced predictive analytics, personalized treatment plans, and continuous monitoring. AI can be used to analyze data from wearable devices, genetic tests, and comprehensive health records, providing real-time insights and early warnings that complement the periodic monitoring and lifestyle interventions of traditional care[6]. This hybrid approach allows for more precise and timely interventions, improving patient outcomes by addressing the unique needs of each individual and adapting to changes in their condition over time. Additionally, this integration can help optimize healthcare resources by identifying high-risk patients early, enabling more targeted and effective treatments, and potentially reducing the long-term costs associated with unmanaged hypertension.
Future Trends in AI-Driven Hypertension Management –
If the development scenario exists, the shared area is adaptable to new innovations in the fight against hypertension employing the AI technology. Former, one of the reported specific advancements is the separation of improved models that allow using deep learning and neural networks. These models will work with the more prefetched datasets such as genetics and multi-omics to predict better prognosis of hypertension risk factors[7-11]. Thirdly, finer integration of the artificial intelligence with wearable devices that shall lead to constant monitoring of pressure and other important indicators. Real-time data will assist into providing accurate health advice to the patients thus boosting them into better management of their status.
The other massive-scale trend will be the creation of precision medicine where using artificial intelligence, the treatment will be personalized according to the human and Milan and diagnosis, genes, and history and, in that way, the rates of effectiveness will be higher, and the rates of the negative effects will be lower. AI usage will continue to rise with the application of automation of telemedicine for optimizing the management of hypertension with help of virtual assistants to monitor conditions and use of medications, among others[8]. Additionally, participants attributed the change of status in healthcare delivery and equitable distribution of appropriate response and treatment among the excluded categories to AI. The outlined trends indicate that in the future the technology does not only enhance the hypertension treatment, but also help to develop individual preventive measures in the healthcare system.
Conclusion –
AI is expected to enhance the technique of managing hypertension by fixing the gaps of routine approaches and providing new solutions for risks, diagnosis, and therapies. The use of artificial intelligence, diagnosis and monitoring devices also implies better risk estimation, individual treatment, and preventive management. These developments shall bring a shift from dealing with health crises and focusing on individual patients thereby creating value in the healthcare system. In future, hypertension care has a possibility of being done better, personalized, and equitably through the help of AI.
References –
- H. Kohjitani, H. Koshimizu, K. Nakamura, and Y. Okuno, “Recent developments in machine learning modeling methods for hypertension treatment,” Hypertens. Res., vol. 47, no. 3, pp. 700–707, Mar. 2024, doi: 10.1038/s41440-023-01547-w.
- S. Arefin, “Chronic Disease Management through an AI-Powered Application,” J. Serv. Sci. Manag., vol. 17, no. 4, Art. no. 4, Jul. 2024, doi: 10.4236/jssm.2024.174015.
- A. Faezi and B. Alinezhad, “AI-Enhanced Health Tools for Revolutionizing Hypertension Management and Blood Pressure Control,” Infosci. Trends, vol. 1, no. 1, pp. 67–72, Jun. 2024, doi: 10.61186/ist.202401.01.08.
- M. Rahaman, F. Tabassum, V. Arya, and R. Bansal, “Secure and sustainable food processing supply chain framework based on Hyperledger Fabric technology,” Cyber Secur. Appl., vol. 2, p. 100045, Jan. 2024, doi: 10.1016/j.csa.2024.100045.
- I. Setiawan et al., “Utilizing Random Forest Algorithm for Sentiment Prediction Based on Twitter Data,” 2022, pp. 446–456. doi: 10.2991/978-94-6463-084-8_37.
- A. Juyal, S. Bisht, and M. F. Singh, “Smart solutions in hypertension diagnosis and management: a deep dive into artificial intelligence and modern wearables for blood pressure monitoring,” Blood Press. Monit., p. 10.1097/MBP.0000000000000711, doi: 10.1097/MBP.0000000000000711.
- M. Rahaman, C.-Y. Lin, and M. Moslehpour, “SAPD: Secure Authentication Protocol Development for Smart Healthcare Management Using IoT,” in 2023 IEEE 12th Global Conference on Consumer Electronics (GCCE), Oct. 2023, pp. 1014–1018. doi: 10.1109/GCCE59613.2023.10315475.
- M. Moslehpour, A. Firman, J. Sulistiawan, P.-K. Lin, and H. T. T. Nguyen, “Unraveling the Puzzle of Turnover Intention: Exploring the Impact of Home-Work Interface and Working Conditions on Affective Commitment and Job Satisfaction,” Behav. Sci., vol. 13, no. 9, Art. no. 9, Sep. 2023, doi: 10.3390/bs13090699.
- Gupta, B. B., & Panigrahi, P. K. (2022). Analysis of the Role of Global Information Management in Advanced Decision Support Systems (DSS) for Sustainable Development. Journal of Global Information Management (JGIM), 31(2), 1-13.
- Gupta, B. B., & Narayan, S. (2021). A key-based mutual authentication framework for mobile contactless payment system using authentication server. Journal of Organizational and End User Computing (JOEUC), 33(2), 1-16.
- Gupta, B. B., & Narayan, S. (2021). A key-based mutual authentication framework for mobile contactless payment system using authentication server. Journal of Organizational and End User Computing (JOEUC), 33(2), 1-16.
Cite As
Nagishetti P. (2024) AI-Powered Approaches to Managing Hypertension: From Prediction to Treatment, Insights2Techiinfo, pp.1