By: Vanna karthik; Vel Tech University, Chennai, India
Abstract
One of the most dangerous risks to network security is DDoS, which can cause interruptions, significant financial losses, and permanent harm to one’s reputation. Due to a single point of failure and its inability to expand, traditional centralized defense against such threats has not been effective. Blockchain will provide a better way for maintaining network security in terms of preventing DDoS attacks because of its decentralization, transparency, and immutability qualities. The current architectural trends, benefits, and drawbacks of blockchain-enabled distributed systems for DDoS mitigation are covered in this study. The study also outlines the future course of research on combining AI and ML for proactive threat mitigation. This study concludes that blockchain-based systems will greatly improve network security and resilience, opening the door for stronger and expandable defenses.
Introduction
Everything is getting digital, and, as a result, the security of a network has become a concern for any organization around the world. Of the most pervasive threats, one includes the DDoS attacks that overwhelm target systems with malicious traffic, making them unreachable for legitimate users. Most of the traditional defense mechanisms, such as firewalls and intrusion detection systems, are often helpless while mitigating these attacks because of their centralized nature, single point failures, and scalability issues.
The blockchain itself-developed to plug a hole in network security for digital cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin-is one of the biggest game-changers. Immutable Ledger, cryptographic security, and decentralized design-these are what blockchain assurances are all about to support the creation of a distributed system that is resistant to DDoS attacks. Blockchain enables organizations to build tamper-proof, transparent, and highly scalable defense mechanisms resistant to manipulation and single points of failure[1].
The purpose of this paper is to highlight current trends in blockchain-enabled distributed systems developed for securing networks against DDoS attacks, together with the challenges and limitations of such systems and future directions in research and development. It presents an integration of emerging technologies like AI and ML that further extends the effectiveness of blockchain-based defense mechanisms.
Current Trends in Blockchain-Enabled DDoS Defense
Decentralized Architecture : Traditional DDoS defense mechanisms are based on centralized servers, which can easily become the target of an attacker. Blockchain’s decentralized architecture eliminates single points of failure, distributing the workload across multiple nodes. This makes it significantly harder for attackers to disrupt the system[2].
Immutable Blockchain Log : The immutable logs of blockchain make all the activities over the network, apart from attack attempts, transparent and indelible. It offers a very reliable record of activity for forensic analysis and assists organizations with identifying and mitigating any attacks more effectively.
Autonomous Defense using Smart Contracts : DDoS can be detected and mitigated using smart contracts, which are self-executing programs on the blockchain. For example, smart contracts may automatically initiate mitigation actions if certain suspicious traffic patterns are observed, like blocking malicious IP addresses or rerouting traffic[2], [3].
Integration with Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning : Blockchain integrated with AI and machine learning is an emerging trend for DDoS defense. These AI/ML algorithms analyze network traffic anomalies in real time, while blockchain ensures data integrity and transparency that they are trained on. This results in better precision and speed during attack detection.
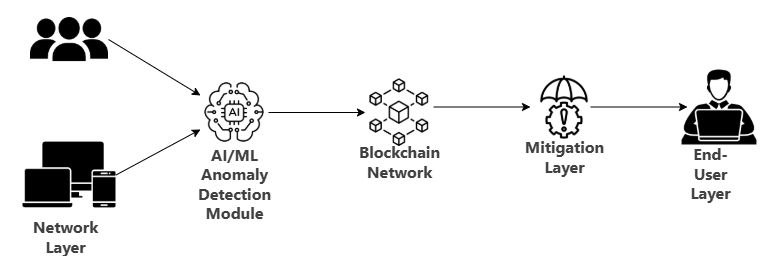
Network Layer : Represents the incoming traffic from users and devices. Includes both legitimate users and potential attackers.
AI/ML Anomaly Detection Module : A module that utilizes machine learning algorithms to detect unusual patterns of traffic. Constantly learn from previous data for better accuracy.
Blockchain Network : a decentralized ledger where attack records and traffic data are kept.
The blockchain network’s nodes confirm and validate transactions.
Mitigation layer : consists of traffic filters, firewalls, and honeypots to stop or reroute harmful traffic. collaborates with the blockchain network to implement security regulations.
End Users Layer : represents the authorized users who gain access to the network following the filtering of traffic.
Conclusion
Blockchain-enabled distributed systems are considered one more leap forward in combating DDoS attacks. Blockchain technology ensures that there are no single points of failure, and it is a transparent, immutable ledger that adds to the resilience and security of the network. The integration of blockchain with AI and ML is attracting attention in current trends for proactive threat detection and response.
In securing systems from DDoS attacks, blockchain-based approaches create a really promising approach; in its continuous development, this technology is sure to play a very important function in the ways of developing more robust and highly scalable defense mechanisms.
References
- D. Saveetha, G. Maragatham, V. Ponnusamy, and N. Zdravković, “An Integrated Federated Machine Learning and Blockchain Framework With Optimal Miner Selection for Reliable DDOS Attack Detection,” IEEE Access, vol. 12, pp. 127903–127915, 2024, doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2024.3413076.
- M. Younas, I. Awan, S. Benbernou, and D. Petcu, Eds., The 4th Joint International Conference on Deep Learning, Big Data and Blockchain (DBB 2023), vol. 768. in Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems, vol. 768. Cham: Springer Nature Switzerland, 2023. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-42317-8.
- D. Dhillon, A. K. Vashist, Diksha, V. Mariaprecilla, and D. Mehrotra, “A Framework for Blockchain-Enabled Smart Contract Management System of Arms and Ammunition for Defence Industry,” in 2024 11th International Conference on Reliability, Infocom Technologies and Optimization (Trends and Future Directions) (ICRITO), Noida, India: IEEE, Mar. 2024, pp. 1–6. doi: 10.1109/ICRITO61523.2024.10522135.
- Wang, H., Li, Z., Li, Y., Gupta, B. B., & Choi, C. (2020). Visual saliency guided complex image retrieval. Pattern recognition letters, 130, 64-72.
- Plageras, A. P., Psannis, K. E., Stergiou, C., Wang, H., & Gupta, B. B. (2018). Efficient IoT-based sensor BIG Data collection–processing and analysis in smart buildings. Future Generation Computer Systems, 82, 349-357.
- Gupta, B. B., Gaurav, A., & Arya, V. (2023). Secure and privacy-preserving decentralized federated learning for personalized recommendations in consumer electronics using blockchain and homomorphic encryption. IEEE Transactions on Consumer Electronics, 70(1), 2546-2556.
- Ali S.R. (2024) AI IN IDENTITY VERIFICATION AND ACCESS CONTROL, Insights2Techinfo, pp.1
Cite As
Karthik V. (2025) Blockchain Enabled Distributed System for Securing Network Against DDoS Attacks Current Trends, Insights2techinfo pp.1