By: Pinaki Sahu, International Center for AI and Cyber Security Research and Innovations (CCRI), Asia University, Taiwan, 0000pinaki1234.kv@gmail.com
Abstract
In the world of cyber threats becomes serious, protecting our digital identities and sensitive information is essential. As a strong defence, two-step authentication (2FA) adds another level of protection to our online interactions. This article delves into the concept of 2FA,its importance and how it can improve security in the digital platforms and services. It explores the challenges faced during user interaction by referring from the statistics of cybercrimes and as a conclusion, the article gives a detailed flow diagram of the 2FA procedure and solution using 2FA and looks ahead to future works for the incorporation of chatbots in cybersecurity, a sign of a hopeful advancement in the defence of our digital world.

Introduction
Internet security plays an important role in the fast moving digital world . It enables unlimited websites and platforms access to our private data, financial accounts, and digital identities as we travel the wide virtual universe[1]. However, the digital environment is not a peaceful refuge but a dynamic battleground full of enemies who are always looking to exploit weaknesses. Identity theft, data breaches, and persistent cyber threats serve as chilling reminders of our online presence’s inherent vulnerability. Passwords, our digital keys, are frequently the first line of defence against malicious attackers in today’s society. [2].
However, the challenges to the digital environment change along with it. The effectiveness of passwords alone in securing our digital domains has come under investigation in an era of more sophisticated intrusions. Passwords, our digital keys, may no longer be the only line of defence against today’s digital marauders, it has become clear.
The Essence of Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
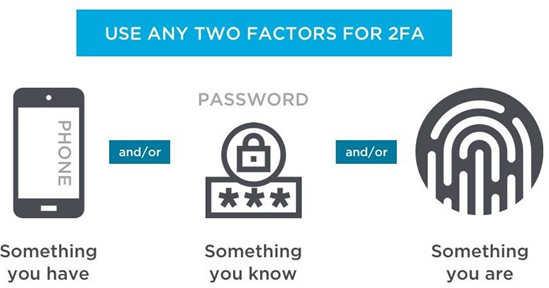
Enter Two-Step Authentication (2FA), a security procedure created to strengthen our online defences. By requesting two types of authentications before giving access to an account or system, 2FA stands as a sentinel that guards the gates of digital access. For better of understanding the 2FA,these factors typically fall into three categories:
The first one is knowledge factor which involves anything the user is aware of, like a password or a personal identification number (PIN).The second one is ownership factor which focuses on something the person physically possesses. This might be a smart card, a mobile device, or even a specialised hardware token. The last one is biometric factor that identifies the person, such as a fingerprint, facial recognition technology, or retina scan.
2FA combines any two of these factors to create a robust authentication process. For instance, when you log in to an online site that uses 2FA, you might first enter your password (knowledge factor), and then as a second step, you might receive a one-time code on your mobile phone (ownership factor)[3].
The Authentication Challenge
Although 2FA offers a significant defence against online risks, it is important to recognise the ongoing difficulties with authentication. The vulnerability of traditional authentication methods to man-in-the-middle attacks is one of the main issues. These covert assaults take place when malicious people eavesdrop on and maybe tamper with user and authentication system communications. The constant risk of token theft is one of the key issues. Traditional authentication techniques frequently rely on tokens or physical objects that users own, like hardware tokens or mobile phones. In such situations, attackers may use these stolen tokens to
access user accounts and systems without authorization, potentially resulting in data breaches and security breaches[4]. Additionally attackers may exploit users by manipulating their trust during a conversation, potentially leading to the theft of user identification.
High incidence of identity theft is about one-third of Americans have experienced identity theft, more than double the global average. Phishing and related attacks are over 300,000 Americans fall victim to phishing, vishing, and smishing attacks annually, as reported by the FBI. Every year, the U.S. witnesses over 50,000 individual personal data breaches. Online exposure: Alarmingly, 87% of people leave personal information exposed online[5].
Table1:Statistics of cybercrimes happened in USA in 2021[5]
| Rank | Cybercrime | US Victims (2021) |
| 1 | Phishing/Vishing/Smishing | 323,972 |
| 2 | Identity Theft | 51,629 |
| 3 | Personal Data Breach | 51,829 |
| 4 | Confidence/Romance Fraud | 24,299 |
| 5 | Tech Support | 23,903 |

Implementing Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) during User Interaction

If a user starts the conversation while the attacker tries to trick them. In order to increase security, the user uses two-step authentication (2FA). Their username and password are initially entered, and the system verifies them. The attacker tries to deflect the 2FA challenge at the same time. The system then checks the user’s entry of a 2FA code. Secure access is given because the attacker is unable to obtain the 2FA code, highlighting the value of 2FA in boosting security. This approach makes it difficult for attackers to get unauthorised access since it
combines something the user has with something they know (their credentials)[6]. As part of the solution, integrating chatbots into the Two-Step Authentication (2FA) process can provide an additional layer of security and user convenience.[7][11-13]
Upcoming Directions for Future Chatbot in Cybersecurity
Undoubtedly, Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) is strengtheningcybersecurity, but there many approaches for enhancing the security if the cyber crime happens in digital platforms. The integration of chatbots looks promising for even greater security during user interactions, particularly when dealing with potential attackers.
Chatbots can act a vigilant sentinel in the digital platform for ensuring authentication procedure are carried out properly and defending against malicious intruders. These are outfitted with sophisticated algorithms and real time monitoring abilities.
- Real Time Monitoring : In order to spot the unusual behaviour duringuser interaction, chatbot will detect the attacker in real time and inform the user to leave the conversation. The Intelligent Chatbot Security Assistant (ICSA) is excellent at monitoring chat activity in real-time and examining user behaviour. It uses a Text-CNN machine learning model to quickly identify the different stages of SNS phishing assaults. ICSA quickly raises an alarm if an attacker poses as a user or manipulates the discussion, strengthening security during digital interactions[8].
- Promoting Cybersecurity awareness: Being informed is crucial in the field of cybersecurity. A chatbot that can advise users on cybersecurity facilitating user education in this important field. Users can ask the chatbot for definitions, take self- tests to gauge their knowledge of cybersecurity, and get advice on recognising and countering phishing threats[9].
Conclusion
In the ongoing struggle against cybersecurity threats, two-step authentication (2FA) has proven to be a strong ally. It erects a strong barrier against unauthorised access, password breaches, and phishing attempts by requiring two different authentication factors. Although issues like compatibility and user resistance continue, solutions like user education, standardisation, and backup techniques can help pave the way for widespread use. Adopting 2FA guarantees a safer digital experience for both individuals and organisations[10].
In an increasingly connected and dangerous digital environment, we can improve our defences against cyber-attacks by using chatbots to monitor, verify and maintain user interactions. Our methods for enhancing our online visibility and safeguarding online integrity must advance at roughly the same rapid rate as technology.
Future research in this area will examine how to seamlessly incorporate machine learning and artificial intelligence into chatbots for even more pro-active danger detection and response. A promising area for research and development is the creation of chatbots with user-friendly educational interfaces to raise cybersecurity awareness. In the constantly changing digital environment, the search for more robust, flexible, and user-centred cybersecurity measures continues.
References
- An, Q., Hong, W. C. H., Xu, X., Zhang, Y., & Kolletar-Zhu, K. (2023). How education level influences internet security knowledge, behaviour, and attitude: a comparison among undergraduates, postgraduates and working graduates. International Journal of Information Security, 22(2), 305-317.
- K. Kumar, P. C. Vashist, A. Sharma, K. Sharma and A. K. Jha, “A Real-Time Attendance Capturing System Using 2-Step Authentication,” 2023 International Conference on Disruptive Technologies (ICDT), Greater Noida, India, 2023, pp. 137 -139, doi: 10.1109/ICDT57929.2023.10151217.
- Kennedy, W., & Olmsted, A. (2017, December). Three factor authentication. In 2017 12th International Conference for Internet Technology and Secured Transactions (ICITST) (pp. 212-213). IEEE.
- H. Fujii and Y. Tsuruoka, “SV-2FA: Two-factor user authentication with SMS and voiceprint challenge response,” 8th International Conference for Internet Technology and Secured Transactions (ICITST-2013), London, UK, 2013, pp. 283-287, doi: 10.1109/ICITST.2013.6750207.
- .Howarth, J. (2023, January 19). 30+ Identity Theft Statistics for 2023. Exploding Topics.
- Fereidouni, H., Fadeitcheva, O., & Zalai, M. (2023). IoT and Man-in-the-Middle Attacks. arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.02479.
- Cho, J., Lee, G., Song, T., & Jeong, H. D. (2023). Chatbot-engaged construction daily work report using mobile messenger. Automation in Construction, 154, 105007.
- Yoo, J., & Cho, Y. (2022). ICSA: Intelligent chatbot security assistant using Text-CNN and multi-phase real-time defence against SNS phishing attacks. Expert Systems with Applications, 207, 117893.
- Fung, Y. C., & Lee, L. K. (2022). A chatbot for promoting cybersecurity awareness. In Cyber Security, Privacy and Networking: Proceedings of ICSPN 2021 (pp. 379-387). Singapore: Springer Nature Singapore.
- Balaban, D. (2021, July 27). What Is Authentication And How Does It Work? Forbes.
- Yadav, K., Gupta, B. B., Chui, K. T., & Psannis, K. (2020). Differential privacy approach to solve gradient leakage attack in a federated machine learning environment. In Computational Data and Social Networks: 9th International Conference, CSoNet 2020, Dallas, TX, USA, December 11–13, 2020, Proceedings 9 (pp. 378-385). Springer International Publishing.
- Tripathi, S., Gupta, B., Almomani, A., Mishra, A., & Veluru, S. (2013). Hadoop based defense solution to handle distributed denial of service (ddos) attacks.
- Gupta, B. B., Joshi, R. C., & Misra, M. (2012). ANN based scheme to predict number of zombies in a DDoS attack. Int. J. Netw. Secur., 14(2), 61-70.
Cite As
Sahu P. (2023) Enhancing Cybersecurity with 2FA and Future Chat-bot Integration, Insights2Techinfo, pp.1