By: Vanna karthik; Vel Tech University, Chennai, India
Abstract
The Internet of Things (IoT), which links a variety of gadgets to improve performance and comfort, has grown to be an essential component of modern life. The spread of IoT devices has, however, also given hackers new ways to take advantage of security errors, presenting serious risks to people, businesses, and vital infrastructure. This study looks at how hackers target Internet of Things devices in a variety of ways, such as taking advantage of weak authentication procedures to use weaknesses in the hardware to launch massive attacks. It also covers efficient methods for safeguarding IoT networks, such as using cutting-edge technology like blockchain and artificial intelligence, detecting threats, and managing devices securely. The goal of this article is to support the creation of more secure IoT ecosystems through studying typical attack vectors and providing measures.
Introduction
The Internet of Things (IoT) is quickly changing daily life and entire fields. By linking items like wearable technology, smart household appliances, and industrial gear, although these gadgets offer greater automation, efficiency, and convenience, there are a number of risks associated with their integration into the larger online environment. Cybercriminals have a greater attack surface as many more gadgets connect to the internet. Unauthorized access, data theft, or even more extensive attacks like botnet-driven distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks can result from taking advantage of faults in IoT devices. This study examines the ways in which cybercriminals target Internet of Things devices, identifies critical security errors, and provides measures.
Literature Review
Cybercriminals frequently use several attack vectors to take advantage of IoT devices, according to recent studies. Weak or inadequate authentication methods are among the most common vulnerabilities. Many IoT devices have weak or default password settings that are simple for hackers to get around[1]. Furthermore, low-processing-resource devices frequently can’t include strong security measures, which leaves them vulnerable to attacks[2].
The importance of botnets in IoT-related cybercrimes is also highlighted by research. The significance of protecting connected devices was highlighted by the Mirai botnet attack, which used unprotected IoT devices to launch one of the biggest DDoS attacks ever. According to research by[3] , new technologies like artificial intelligence (AI) and block chain technology may be able to identify unusual activity in Internet of Things networks and resist these kinds of extensive attacks.
Researchers stress the significance of introducing security measures into the design process of IoT devices in order to deal with these issues of security[4] . In order to protect IoT devices from cybercriminals, it is also advised to use network segmentation, encryption, and frequent security updates.
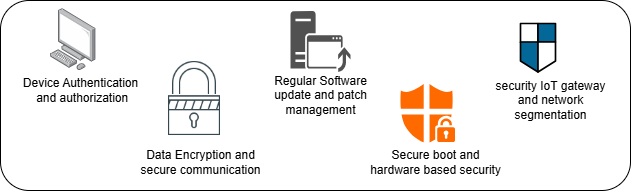
Fig : Key Components of IoT Security[5].
Methodology
This study combines a qualitative approach, integrating case studies and an extensive literature review to investigate how cybercriminals take advantage of IoT devices and pinpoint practical defense tactics.
Literature Review: To identify prevalent attack vectors, vulnerabilities, and IoT security concerns, a comprehensive examination of government publications, industry papers, and scholarly articles has been carried out.
Case Studies: These case studies provide the spotlight on the methods cybercriminals use to take advantage of IoT weaknesses and the adverse effects of such breaches.
Data Analysis: To determine the source of IOT related cybersecurity, the study examine current cybersecurity publication and attacks statistics. The information is utilized to determine IoT security trend and evaluate how well the present defense are working.
Recommendation Development: The study improves formulate suggestions for protecting IoT devices. These include developing technologies that can improve IoT security as well as best practices for both device user and manufacturer.
Conclusion
Although the internet of things (IoT) has many advantages, there are also serious security vulnerabilities due to its explosive growth, cyber security uses a variety of techniques to target IoT devices, such as taking advantage of ineffective software, unprotected network, and poor authentication. Strong cybersecurity protection is manufactured need to embrace standardize security procedure, apply frequent upgrades and give security top priority during the design stage. By creating secure passwords, turning on encryption, and dividing their networks, users can also contribute. Furthermore, by guaranteeing data integrity and identifying threats in real time, cutting-edge technologies like blockchain and artificial intelligence (AI) have the potential to enhance IoT security. We can reduce the threats posed by cybercriminals and establish a more secure IoT environment by implementing these preventative steps.
References
- M. Shafiq, Z. Gu, O. Cheikhrouhou, W. Alhakami, and H. Hamam, “The Rise of ‘Internet of Things’: Review and Open Research Issues Related to Detection and Prevention of IoT-Based Security Attacks,” Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput., vol. 2022, no. 1, p. 8669348, 2022, doi: 10.1155/2022/8669348.
- A. Khanna and S. Kaur, “Internet of Things (IoT), Applications and Challenges: A Comprehensive Review,” Wirel. Pers. Commun., vol. 114, no. 2, pp. 1687–1762, Sep. 2020, doi: 10.1007/s11277-020-07446-4.
- M. Shen et al., “Blockchains for Artificial Intelligence of Things: A Comprehensive Survey,” IEEE Internet Things J., vol. 10, no. 16, pp. 14483–14506, Aug. 2023, doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2023.3268705.
- S. N. Swamy and S. R. Kota, “An Empirical Study on System Level Aspects of Internet of Things (IoT),” IEEE Access, vol. 8, pp. 188082–188134, 2020, doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3029847.
- “Iot Security: Safeguarding Connected Devices and Data from Cyber Threats.” Accessed: Dec. 26, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/iot-security-safeguarding-connected-devices-data-from-cyber
- Zou, L., Sun, J., Gao, M., Wan, W., & Gupta, B. B. (2019). A novel coverless information hiding method based on the average pixel value of the sub-images. Multimedia tools and applications, 78, 7965-7980.
- Lu, J., Shen, J., Vijayakumar, P., & Gupta, B. B. (2021). Blockchain-based secure data storage protocol for sensors in the industrial internet of things. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 18(8), 5422-5431.
- Kee S.N. (2024) IoT Device Authentication Protocols Using Blockchain Technology, Insights2Techinfo, pp.1; https://insights2techinfo.com/iot-device-authentication-protocols-using-blockchain-technology/
Cite As
Karthik V. (2025) How Cybercriminals Target IoT Devices and Strategies for Protection, Insights2techinfo pp.1