By: Vanna karthik; Vel Tech University, Chennai, India
Abstract
People can benefit from the convenient nature of Quick Response (QR) codes to both instantly obtain information and use them for payments and authentication verification processes. Because cybercrime operators evolved this commonly adopted technology into Quishing (QR code phishing) it has become a new phishing vector. The article evaluates how attackers exploit QR technology to execute their malicious purposes while examining established security protocols for risk reduction. User awareness about QR code risks in daily transactions will help advance cyber security protections because these codes have become standard for everyday payments. The adoption of user ignorance and technical advancement of cyber attackers has turned Quishing into a major security concern. People and organizations need to implement strong security protocols together with awareness about security risks to protect themselves against these harmful attacks.
Introduction
Users today easily perform rapid website and payment gateway and login page scans through QR codes embedded in their daily lives. Technology provides businesses with three key uses which simplify both business transactions and access points and help improve their marketing capabilities. QR codes have become popular targets for cyber-criminals because of their increased use. The cyber threat known as Quishing involves attackers embedding harmful website links into QR codes to trick users into relinquishing data or downloading harmful software. The ongoing development of technology brings better phishing techniques to hackers which complicates user ability to recognize genuine from fake QR codes[1]. Security concerns must receive immediate attention since QR codes are used extensively in banking services alongside retail operations and healthcare facilities and government institutions. Users lacking necessary awareness about QR code safety end up giving away precious data which results in identity theft as well as financial fraud incidents.
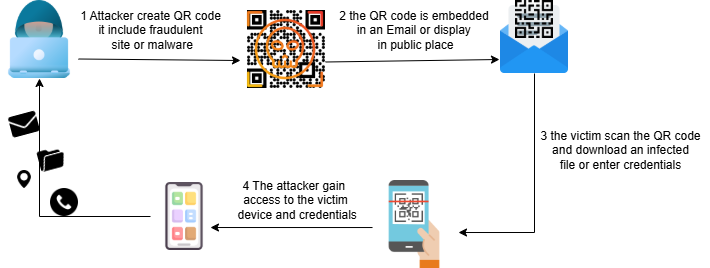
How QR Code Phishing Works
Human beliefs in others together with convenient technology enable quishing attacks to take place. The basic attack methods include:
1. Malicious URL Embedding: Cyber attackers place deceptive QR codes in place of authentic ones which point users toward dangerous phishing websites. Fraudulent websites use copied designs from real login pages to mislead users into giving up their account information[2].
2. Crooks distribute counterfeited QR payment links which make users mistake for valid financial connections that lead to illegitimate account transfers[2].
3. Email and SMS Phishing: Attackers place bogus QR codes inside fraudulent emails and messages which pretend to come from established financial institutions and government departments and public service agencies to push people into scanning them immediately.
4. Physical QR Code Manipulation: Attackers place counterfeit QR codes on actual ones which appear at dining spots, parking facilities and marketing displays to route users toward fake fraudulent pages rather than real business pages[3].
5. Corporate Attacks: The practice of sending deceptive QR codes through business emails to personnel represents a favored tactic by attackers for stealing organization credentials or placing destructive malware on company systems[3].
Case Studies and Real-World Attacks[4]
The dangers of QR code phishing become evident through major hacking events that have occurred.
Scammers put fake QR codes on parking meters throughout major cities which directed users to phish payment portals that obtained their payment information.
Corporate employees fell victim to phishing attacks when they scanned malware-infused QR codes that appeared in their email inboxes thus allowing cybercriminals to steal their credentials and deploy ransomware.
How to Protect Against QR Code Phishing
The prevention of QR code phishing requires users and organizations to implement these security practices:
1. Verify QR Code Authenticity: Users should check both the source legitimacy and physical state of QR codes before making a scan[5].
2. Users should scan QR codes using security-enabled tools because they help block malicious content. Mobile security applications include safe scanning capabilities through their ability to identify dangerous URLs contained in QR codes[5].
3. Manually Enter URLs: Users should type web addresses manually instead of scanning QR codes when such codes direct to website visits because it ensures better security evaluation.
4. Always verify the source as well as the authenticity of QR Codes before performing a scan. Handle all QR code transmissions with skepticisms because they arrive as suspicious attachments from either emails or messaging platforms from unidentified senders[6].
5. Enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): MFA functions as an extra protective measure which stops unauthorized access when credentials get exposed[6].
6. Educate and Train Employees: To help employees detect and deflect QR code phishing attacks educational cybersecurity programs should run on a regular basis within organizations[6].
Conclusion
Using QR codes provides wonderful convenience to users while simultaneously presenting novel security threats to their digital systems. People and organizations need to maintain continuous vigilance alongside adopting preventive measures because cyber criminals will persist in exploiting common technology. Ads and informed precaution augment users’ defense against threats connected to Quishing attacks. Businesses need to establish security protocols and users must adopt a step which involves checking QR code origin information prior to scanning. Anti-Quishing efforts can be protected through security tool deployment and public education campaigns along with threat updates about new cyberattack techniques. To protect themselves, users need to educate themselves about Quishing methods and execute preventive security measures which allow them to perform digital activity securely.
References
- K. Im-Erb, “Understanding and Mitigating Phishing Attacks in the Digital Era,” 2024, doi: 10.13140/RG.2.2.19619.98085.
- A. S. Rafsanjani, N. B. Kamaruddin, H. M. Rusli, and M. Dabbagh, “QsecR: Secure QR Code Scanner According to a Novel Malicious URL Detection Framework,” IEEE Access, vol. 11, pp. 92523–92539, 2023, doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3291811.
- Y. Li et al., “ScreenID: Enhancing QRCode Security by Fingerprinting Screens,” in IEEE INFOCOM 2021 – IEEE Conference on Computer Communications, May 2021, pp. 1–10. doi: 10.1109/INFOCOM42981.2021.9488859.
- “(PDF) Hooked: A Real-World Study on QR Code Phishing,” ResearchGate. Accessed: Feb. 10, 2025. [Online]. Available: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/382492608_Hooked_A_Real-World_Study_on_QR_Code_Phishing
- M. Taraka Rama Mokshagna Teja and K. Praveen, “Prevention of Phishing Attacks Using QR Code Safe Authentication,” in Inventive Computation and Information Technologies, S. Smys, V. E. Balas, and R. Palanisamy, Eds., Singapore: Springer Nature, 2022, pp. 361–372. doi: 10.1007/978-981-16-6723-7_27.
- G. A. Amoah and H.-A. J.B., “QR Code Security: Mitigating the Issue of Quishing (QR Code Phishing),” Int. J. Comput. Appl., vol. 184, no. 33, pp. 34–39, Oct. 2022, doi: 10.5120/ijca2022922425.
- Infrastructure and Network Security,M Rahaman, SS Bakkireddygari, S Chattopadhyay… – Metaverse Security Paradigms, 2024
- Zheng, Q., Wang, X., Khan, M. K., Zhang, W., Gupta, B. B., & Guo, W. (2017). A lightweight authenticated encryption scheme based on chaotic scml for railway cloud service. IEEE Access, 6, 711-722.
- Hammad, M., Abd El-Latif, A. A., Hussain, A., Abd El-Samie, F. E., Gupta, B. B., Ugail, H., & Sedik, A. (2022). Deep learning models for arrhythmia detection in IoT healthcare applications. Computers and Electrical Engineering, 100, 108011.
- Sravanthi B.S. (2024) Identified Cyber Attacks and How to Protect Yourself from Spear Phishing, Insights2Techinfo, pp.1
Cite As
Karthik V. (2025) QR Code Phishing : how Cybercriminals are Exploiting Everyday Tech, Insights2techinfo pp.1