Introduction
The amorphous concept that influenced the new name has been a popular topic since Facebook reopened as a meta on October 28, 2021.
This is partly due to the fact that the metaverse means various things to different individuals, but it’s also due to the fact that the boundaries between the virtual and actual worlds have blurred beyond recognition [1].
The meaning and origin of the term “Metaverse”
Metaverse is a virtual world term available in virtual reality (VR) that allows people to chat, socialize, travel, shop, and collaborate with avatars and holograms in a 3D virtual world. [2][5].
Its name is a mash-up of two words:
- The prefix “meta” comes from the Greek word “meta” which means “beyond.”
- The universe.
Author Neal Stephenson created the phrase in his novel “Snow Crash,” published in 1992, and defined it as “a computer-generated universe. In Snow Crash, the metaverse is a 3D virtual reality domain that can be accessed by personal computers and virtual reality goggles.
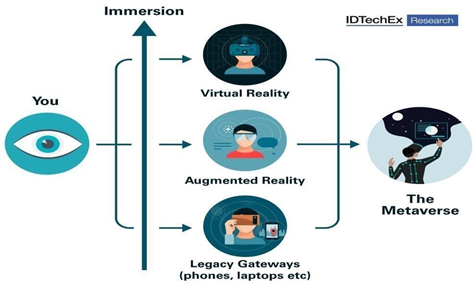
The influence of the metaverse on the world and the future of technology
Virtual reality, or augmented reality as we know it now, might be used in the metaverse to immerse people in an alternative world [3-4]. Despite the fact that the technology is still in its infancy, companies like Meta claim to be developing and improving these devices. Meta’s Oculus Quest, which is presently in its second version, is one such device.
Businesses will not operate in the same way they do now. This trend of online purchasing and using e-commerce sites will be aided by the metaverse [5]. People will no longer need to visit physical businesses to check out new items before making a purchase. They will be able to examine various items from various companies from nearly anywhere in the metaverse thanks to VR/AR technologies [3][6].
In addition, blockchain technology would prosper in the metaverse. The financial transactions in the metaverse would be governed by cryptocurrency and blockchain technology [2].
Role of High number of users country in building Metaverse
Mark Zuckerberg expressed his excitement about India’s involvement in the future of Metaverse, which would be the successor to the mobile internet because India is a big marketplace from the business point of view.
“That’s because India’s talent pool — engineers, developers, and producers, as well as the country’s thriving startup environment — is molding the future. By 2024, India is expected to have the world’s largest app developer base as it already has one of the largest groups of ‘Spark AR’ developers [5-6].
Security Risks in the Metaverse
For one reason, individuals who grow addicted to VR/AR technology may become more alienated from reality. Simply said, the 3D virtual environment has the potential to cause real-life sadness [4][5]. People will spend more time in the metaverse and less time on real-world duties as a result of this.
Cybersecurity issues, on the other hand, are the metaverse’s most pressing concerns. Experts predict that the metaverse will not be an exception and that cybercrime, online abuse, and online fraud will likely rise[7].
Conclusion
People would be able to accomplish practically whatever they could in the actual world in the metaverse virtual environment. Big IT companies are attempting to establish a more secure virtual reality platform. However, due to recent cybercrime events, rumors are still common.
The metaverse’s future reality is taking shape, but it isn’t quite ready yet. It’s only a matter of time until we see what this new frontier will bring.
References
- Kumar, S., Singh, S. K., Aggarwal, N., & Aggarwal, K. (2021). Evaluation of automatic parallelization algorithms to minimize speculative parallelism overheads: An experiment. Journal of Discrete Mathematical Sciences and Cryptography, 24(5), 1517–1528. doi:10.1080/09720529.2021.1951435
- Aggarwal, K., Singh, S. K., Chopra, M., & Kumar, S. (2022). Role of Social Media in the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Literature Review. Data Mining Approaches for Big Data and Sentiment Analysis in Social Media, 91-115.
- Singh, I., Singh, S. K., Kumar, S., & Aggarwal, K. (2021). Dropout-VGG based Convolutional Neural Network for Traffic Sign Categorization. In the proc. of 2nd Congress on Intelligent Systems (CIS 2021), Lecture Notes on Data Engineering And Communication Technologies. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg.
- G. Khade, S. Kumar and S. Bhattacharya, “Classification of web pages on attractiveness: A supervised learning approach,” 2012 4th International Conference on Intelligent Human Computer Interaction (IHCI), 2012, pp. 1-5, doi: 10.1109/IHCI.2012.6481867.
- Singh, S., Singh, R., & Bhatia, M. (2012). Performance evaluation of hybrid reconfigurable computing architecture over symmetrical FPGAs. International Journal of Embedded Systems & Applications, 2(3), 107-116.
- Madan, R., Singh, S. K., & Jain, N. (2009). Signal filtering using discrete wavelet transform. International journal of recent trends in engineering, 2(3), 96.
- Singh, S. K., Kumar, A., Gupta, S., & Madan, R. (2011). Architectural performance of WiMAX over WiFi with reliable QoS over wireless communication. International Journal of Advanced Networking and Applications, 3(1), 1017.