By: Praneetha Neelapareddigari, Department of Computer Science & Engineering, Student of Computer Science & Engineering, Madanapalle Institute of Technology and Science, Angallu (517325), Andhra Pradesh. praneetha867reddy@gmail.com
Abstract
The Internet of Things (IOT) is a simple concept that occurs every day in everyone’s daily routine which is rapidly growing network of interconnected devices in every sector around the world. Though there are many benefits using IOT but while some connectivity implementations, IOT introduces significant cybersecurity challenges. These challenges include the weak authentication mechanisms, insecure communication protocols, lack of regular software updates, and insufficient encryption. AI is the main component in enhancing the cybersecurity of IOT world. AI have the enough tools and techniques to offer the capabilities in threat detection, behavioral analysis, predictive analytics and automated response. AI uses the concept of machine learning to identify anomalies. This paper addresses the intersection of AI and cybersecurity with the context of IOT, describing the common vulnerabilities of IOT devices, the role of AI in solving the issues. Additionally, this paper addresses the challenges and considerations that occurs while implementing AI into IOT cybersecurity and the issues that arises and presents future directions in the field.
Keywords: Artificial Intelligence, Cybersecurity, Internet of Things, Machine Learning, Security
Introduction
Internet of Things is mostly used concept in every sector, IoT is the subject that connects everyday devices such as smart home gadgets and industrial machines, to the internet for sharing of data and communication, which helps in improving efficiency[1]. IoT generally refers to the network of interconnected physical devices where the commutation and sharing of data over the internet is taking place. The usage of IoT devices ranges from everyday household items such as smart thermostats to complex industrial machinery and infrastructure components like smart grids. The ecosystem of IoT can be described by its vast scale, devices and generation of huge volumes of data.
IoT provides many advantages to the world, but it also introduces a wide array of cybersecurity challenges. This is because as many devices are connected to the internet so this chance can be taken as the advantage by cybercriminals, making IoT devices attractive for various malicious activity which includes like data breaches, device hijacking, and privacy invasion[1].
Here comes the picture of AI in enhancing IoT security which is the powerful weapon in addressing the cybersecurity challenges in IoT. By using AI, the security systems can be more adaptive, intelligent and capable of handling the problems that are raised in IoT environment.
This introduction describes that the integration of AI into IoT cybersecurity is very much crucial for managing the complexities in IoT ecosystem. As the number of connected devices are more the need for robust security measures is required to protect against evolving attacks[2]. AI helps in various ways to solve the issues.
1. Basic Concepts of IoT
Internet of Things
IoT refers to the concept of interconnection of physical devices that involves communication and sharing of the data through the internet. As discussed, these devices range from everyday items to industrial machinery sectors.
The basic concepts of IoT covers the topics such as connected devices, data collection and communication, data analysis, sensors and actuators and many more. The concept of connectivity is that IoT devices connect to other networks and allowing them to send and receive data. The real-time communication is allowed in connectivity. The other components in IoT are the sensors and actuators which refers the collection of data from environment and the role of actuators is to perform actions.
Data collection and analysis is about the data gathered by IoT devices which is transmitted to central systems where the data is stored and analyzed. This analysis can provide insights, drive decision-making, and trigger automated responses. So, there are many basic topics of IoT topics that covers various content related to IoT.
2. Common Vulnerabilities in IoT Devices
IoT subject is about the connectivity of devices and here is the problem that creates many vulnerabilities. The criminals grab these situations as advantage to attack and even to destroy the data[3].
Weak Authentication Mechanisms
Many IoT devices are transported with default passwords, weak passwords, or even in few situations there would be no password protection at all. There are some devices that uses the outdated authentication methods which are easy to bypass. As the result there would be many impacts where the attacks can easily gain access to the device using default passwords. This situation causes to steal the sensitive information that is stored on the device, and this is also known as data theft.
Insecure Communication Protocols
IoT devices generally uses many protocols to communicate that are not secure, such as HTTP instead of HTTPS. These insecure communications are sometimes dangerous. The impacts that occur due to this kind of situations are data interception, data manipulation, replay attacks. All this impacts that occur due to insecure communication describes that attackers have several ways to steal the data.
Lack of Regular Software Updates
Many IoT devices do not have the regular software updates. This leads to many issues where the manufacturers may fail to provide updates. The impacts of this concept are persistent vulnerabilities, increased risk over time, exploitation
Insufficient Encryption
Several IoT devices do not adequately encrypt sensitive data. This situation includes data that is stored on the devices and data that is being transmitted to and from the device. The impacts of this context can be data breaches, privacy violations, data integrity.
To stop these common vulnerabilities, IoT manufacturers and users should use the robust security practices. This includes implementation of strong authentication mechanisms, practice of secure communication protocols, applying regular software updates and using comprehensive encryption methods. The security of IoT devices can be improved, if there are any changes in vulnerabilities.
3. AI’s Role in IoT Security
Various mechanisms are used to transform IoT security by using different strategies and implementations, few are listed below.
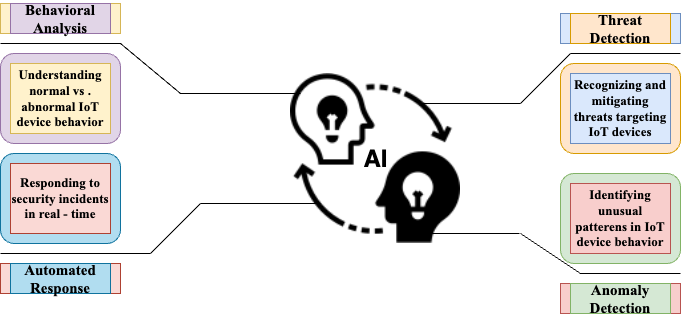
Anomaly Detection
It involves machine learning algorithms to analyze the generated data by IoT devices and to identify the patterns. This mechanism is very useful in recognizing the security threats that do not expected behavior[4]. This detection follows few phases. Firstly, the data collection phase, where the continuous data streams from IoT devices are collected for analysis purposes. Secondly, the model is trained using machine learning models on the historical data to understand what constitutes normal behavior for each device.
The trained model in the previous phase analyzes the incoming data in real time and compares it to the established baseline of normal behavior. This phase is known as real – time analysis. The last phase is the anomaly identification that describes any deviations from the norm are flagged as potential anomalies that could indicate a cyberattacks.
Behavioral Analysis
Behavioral analysis refers in creating a detailed profile of any device that have a normal behavior and uses this profile to detect deviations that could indicate the activities that are malicious. This analysis also follows few phases describing how this analysis works. Firstly, the historical analysis of data is done by AI to establish a baseline of normal behavior for each device. This phase is called as behavior profiling[5]. The behavior of the device is monitored continuously and then it is compared against the established baseline and this phase is called as continuous monitoring. Deviations from normal behavior are detected and analyzed to determine if they represent any security threat and this phase is known as deviation detection. When the deviations are detected then the appropriate responses can be initiated by taking automated actions.
Threat Prediction
Threat prediction is about allowing for proactive measures to be taken before any attack that occurs. All the historical data of device behaviors, network traffic patterns are analyzed to identify the future threats[6]. This mechanism uses machine learning models that are trained to recognize the patterns and anomalies that have the historical preceded security incidents. This model predicts the threats by identifying similar patterns in real-time data. Based on the predictions, certain security measures are taken such as hardening, access restrictions.
Automated Response
It involves AI to take immediate actions to the detected threats, minimizing the time between detection and mitigation and reducing the potential impact of cybersecurity[7]. There is a continuous monitoring of IoT devices and network traffic for signs of security threats. When a threat is detected, AI algorithm is used to analyze the threat to determine the nature and impact, this phase is called as automated analysis phase.
By using all this mechanisms IoT security can be significantly enhanced. These mechanisms provide robust, real – time defenses against evolving cyber threats and ensure the confidentiality, integrity and availability of IoT systems.
4. Cybersecurity Strategies for IoT
IoT settings require a multi-layered security strategy that combines cutting-edge AI-driven solutions with established cybersecurity best practices. The device authentication and authorization are very necessary and this makes sure that only approved devices are able to connect to network. The main purpose of data encryption is necessary for securing information while it’s in transit and if it is case at rest it prevents unwanted access and guarantees the privacy and accuracy of the data. In order to control and restrict the spread of possible breaches, network segmentation entails splitting the network into discrete segments. This improves the overall security posture by isolating vulnerable regions from the rest of the network. Last but not least, AI-Powered Security Analytics is essential since it constantly scans network traffic for indications of potential cyberthreats[8]. Security systems can identify abnormalities, anticipate possible risks, and automate actions by utilizing AI. This gives them a strong and proactive protection against changing cyber threats in Internet of Things settings[9].
5. Challenges
IoT security powered by AI confronts a number of difficulties. The massive collecting and analysis of sensitive data raises privacy concerns that need for strong protection and legal compliance. In threat detection, false positives and negatives can result in missing threats or needless warnings, necessitating ongoing model improvement. It is challenging to implement sophisticated AI algorithms locally on IoT devices due to resource limitations including limited processing power and battery life, which frequently calls for a hybrid strategy combining edge and cloud computing. The wide variety of IoT devices and the absence of common protocols lead to interoperability problems, which make it more difficult to deploy all-encompassing security solutions.
6. Future of IoT
IoT cybersecurity and AI developments in the future are probably going to concentrate on improving privacy-preserving methods like federated learning, which enables models to be trained on-device without exchanging raw data. Threat detection will be more accurate thanks to enhanced behavioural analysis and anomaly detection models that decrease false positives and negatives. Despite resource limitations, edge AI integration will proliferate, allowing real-time processing and reaction directly on IoT devices. Standardizing protocols and fostering interoperability among various IoT ecosystems will also be essential for enabling smooth integration and all-encompassing security[10]. These advances will be fuelled by increased cooperation between academic institutions, industrial players, and regulatory agencies. This will guarantee strong and flexible security protocols for IoT environments that are always changing.
Conclusion
IoT is used in every sector which is something that is used every single day and is a part of everyone’s daily routine . It is a content of the connectivity of devices. The integration of AI in IoT cyber security provides the protection for the interconnected devices, enhancing threat detection and enabling automated responses. There are many challenges that occur because of the concept cyber security and AI. However all the issues can be solved by using few techniques. Future directions will focus on the concepts of the privacy-preserving methods, improved anomaly detection, edge AI deployment and standardized protocol’s to ensure the robust security. So, this concludes that IoT have the great transformation in present and future days of digital world.
References
- S. N. Swamy and S. R. Kota, “An Empirical Study on System Level Aspects of Internet of Things (IoT),” IEEE Access, vol. 8, pp. 188082–188134, 2020, doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3029847.
- I. Lee, “Internet of Things (IoT) Cybersecurity: Literature Review and IoT Cyber Risk Management,” Future Internet, vol. 12, no. 9, Art. no. 9, Sep. 2020, doi: 10.3390/fi12090157.
- X. Jiang, M. Lora, and S. Chattopadhyay, “An Experimental Analysis of Security Vulnerabilities in Industrial IoT Devices,” ACM Trans Internet Technol, vol. 20, no. 2, p. 16:1-16:24, May 2020, doi: 10.1145/3379542.
- G. Pang, C. Shen, L. Cao, and A. V. D. Hengel, “Deep Learning for Anomaly Detection: A Review,” ACM Comput Surv, vol. 54, no. 2, p. 38:1-38:38, Mar. 2021, doi: 10.1145/3439950.
- Z. Elamrani Abou Elassad, H. Mousannif, H. Al Moatassime, and A. Karkouch, “The application of machine learning techniques for driving behavior analysis: A conceptual framework and a systematic literature review,” Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell., vol. 87, p. 103312, Jan. 2020, doi: 10.1016/j.engappai.2019.103312.
- N. Kaloudi and J. Li, “The AI-Based Cyber Threat Landscape: A Survey,” ACM Comput Surv, vol. 53, no. 1, p. 20:1-20:34, Feb. 2020, doi: 10.1145/3372823.
- S. D. P. Rao, “Harnessing Ai for Evolving Threats: From Detection to Automated Response,” J. Sci. Technol. Res. JSTAR, vol. 5, no. 1, pp. 91–97, 2024.
- M. Rahaman, C.-Y. Lin, and M. Moslehpour, “SAPD: Secure Authentication Protocol Development for Smart Healthcare Management Using IoT,” in 2023 IEEE 12th Global Conference on Consumer Electronics (GCCE), Oct. 2023, pp. 1014–1018. doi: 10.1109/GCCE59613.2023.10315475.
- L. Triyono, R. Gernowo, P. Prayitno, M. Rahaman, and T. R. Yudantoro, “Fake News Detection in Indonesian Popular News Portal Using Machine Learning For Visual Impairment,” JOIV Int. J. Inform. Vis., vol. 7, no. 3, pp. 726–732, Sep. 2023, doi: 10.30630/joiv.7.3.1243.
- R. Yugha and S. Chithra, “A survey on technologies and security protocols: Reference for future generation IoT,” J. Netw. Comput. Appl., vol. 169, p. 102763, Nov. 2020, doi: 10.1016/j.jnca.2020.102763.
- Sharma, A., Singh, S. K., Kumar, S., Thakur, R., Gupta, B. B., & Arya, V. (2024). IoT-enabled smart farming with Industry 5.0. Journal of High Speed Networks, (Preprint), 1-20.
- Gupta, B. B., Gaurav, A., Attar, R. W., Arya, V., Alhomoud, A., & Chui, K. T. (2024). Sustainable IoT Security in Entrepreneurship: Leveraging Univariate Feature Selection and Deep CNN Model for Innovation and Knowledge. Sustainability, 16(14), 6219.
Cite As
Neelapareddigari P. (2024) AI and Cybersecurity in Internet of Things (IOT), Indights2Techinfo, pp.1