By: Poojitha Nagishetti, Department of Computer Science and Engineering (Data Science), Madanapalle Institute of Technology and Science, Angallu,517325, Andhra Pradesh, poojimurali2330@gmail.com
Abstract –
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) is an auto-immune disease of unknown cause that damages the joints leading to inflammation, pain and, possibility of distortion of the involved joint. In conventional treatment the strategies do not apply to the patients separately and so based upon the stages and types of the disease different results variations can be experienced. Again, it is also said that AI is also on the brink for a more suitable interventionism for enhancing the specific management of RA. This paper will focus on the potential use of AI systems in understanding RA patient’s management using, predictive modelling, treatment recommendation, diagnostic tools among others. Analysing the contribution of the algorithm of machine learning on disease prognosis, care management, as well as personal estimations of drug reaction. Furthermore, it remains fundamental to identify the modern tendencies of the analysis of images and biomarkers with the help of AI that contributes to increasing the correctness of the diagnosis and the outcomes of therapy. Nevertheless, it is still not perfect regarding; privacy in handling data, issues of bias in the selected algorithm, and transitioning to practice. The concluding part of the paper concerns the prospects; where, the authors opine that there is a need to conduct further research on AI in the management of RA with emphasis on patient data. In this respect, this study is to uncover the ways of how AI could improve patients’ quality of life and contribute to the developmental advancements in the rheumatoid arthritis treatment.
Keywords – Rheumatoid Arthritis, Artificial Intelligence, Personalized treatment, Early detection, Predictive modelling.
Introduction –
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) remains as one of the significant autoimmune diseases with its main concentration on the joint areas that lead to persistent swelling, pain, and even twisting of the joints due to its continuous inflammation[1]. RA as a global health concern affects millions of individuals, and to a considerable degree limits QoL and functional status. The conventional management of RA has depended on the conventional treatment style for addressing the signs of inflammation as well as halting the progression of the disease. Of course, since patients under this disease experience diverse symptoms and symptoms’ severity, the general management of the problem is often less effective and sometimes even harmful. AI has rapidly emerged as a significant component in the improvement of healthcare services and is expected to grow dramatically soon.
The field of artificial intelligence or commonly referred to as AI is revolutionizing the health care industry through the development of unique approaches to issues in the health care sector[2]. It is a broad term that covers technology like machine learning, deep learning, and analytical computing utility which can take a large amount of data and processing the data to reveal patterns that were indiscernible before. When applied to the management of RA, the capacity of AI to combine and interpret various types of data, including patients’ EHR, imaging, and genetic data, can transform the disease process.
AI in Rheumatoid Arthritis Management –
Due to the capabilities of AI, it is possible to extend current possibilities of the RA management and make use of modern tools for forecasting, diagnostics, and individualized treatment planning. Risk assessments use AI in a way that helps to anticipate the evolution of the sickness, and the patients’ reaction to medications, so that proper defensive and treatment plans can be implemented. Machine learning platforms are used to scrutinize heterogeneous patient data to ensure therapies are congruous with the patient’s plan and possibly eliminating the bull and cow concept. Also, AI improves the reliability of the diagnostics due to more precise image analysis and biomarker identification, which may go unnoticed by conventional means. The direction of AI in managing RA will thus require meeting some challenges and Mantel et al. has pointed out that despite of the existing advancement, the following challenges needs to be overcome and they include data quality, concerns to privacy, algorithm bias and integration of AI into practice. Fig 1 shows the AI integration in Rheumatoid Arthritis.
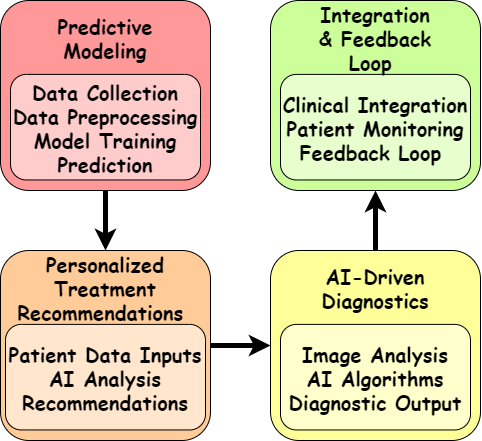
Predictive Modelling in RA Management:
A case of artificial intelligence (AI) in predictive modelling involves the use of models to estimate the course of Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) as well as the effectiveness of applications of treatment procedures. In fact, through processing big data in terms of patients’ demographics, clinical history, genetic profiles, and treatment effectiveness AI models can reveal patterns and forecast further developments. This strategy allows the clinician to predict the way RA is likely to progress in an individualized patient, so that the treatment plan is much more preventive in nature. For example, machine learning methods can generate data concerning which patients are candidates for a fast disease worsening or adverse drug reactions and can suggest changes in the therapy. Decision making also facilitates the identification of the best treatment regimen by relating patient characteristics to the previous response to the treatment. This results in refined and personalized treatment plans to handle RA cases hence help enhance patient experiences and eliminate the trial method of handling the illness.
Personalized Treatment Recommendations:
Using patient data and Machine learning AI produces patient-specific treatment plans that speak of the detail of an RA patient. Closely associated with the patient data aggregation capability, AI systems combine elements like electronic medical records, genetic makeup, and the prior treatment outcomes to estimate the optimal treatments. These recommendations consider the intensity of the disease, the presence of other conditions, and the reactions of the organism to these and other drugs. For instance, it can estimate a patient’s reaction to a specific drug when prescribing with reference to the patient’s genetic makeup and past health records, thus delivering effective solutions without undesirable reactions[3]. Besides, it strengthens the effectiveness of therapeutic procedures and addresses the issues of compliance and satisfaction as therapy reflects the patient’s needs and disorders. Individualized treatment plans are superior to generic treatment approaches, hence making the changes vital in precisely handling RA. The below table explains the key aspects of AI- driven solutions for personalized treatment in Rheumatoid arthritis.
Table 1: The key aspects of AI-driven solutions for personalized treatment in Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
Aspect | Description | Examples/Applications |
Predictive Modeling | Uses AI algorithms to forecast disease progression and patient responses to treatments. | Predicts disease progression, Anticipates adverse reactions, Tailors proactive treatment plans |
Personalized Treatment | Tailor’s medical interventions to individual patient characteristics using AI analysis of diverse data sources. | Recommends optimal therapies, predicts individual drug responses, Reduces trial-and-error in treatment strategies |
AI-Driven Diagnostics | Enhances diagnostic accuracy through advanced imaging analysis and biomarker discovery. | Analyzes X-rays, MRIs, ultrasounds, detects subtle joint damage, Identifies novel biomarkers for early diagnosis |
Integration & Feedback Loop | Integrates AI tools into clinical workflows and uses real-time data and patient outcomes to refine and improve AI models. | Implements AI in clinical settings, Monitors patients via wearables, continuously updates models based on feedback |
Challenges | Addresses issues related to data quality, algorithmic bias, and clinical integration. | Ensuring high-quality data, maintaining patient privacy, Overcoming resistance to new technologies in clinical practice |
Future Trends | Explores emerging trends such as real-time monitoring, genomic integration, and advancements in explainable AI. | Real-time patient monitoring, Personalized therapies based on genetic profiles, Greater transparency in AI algorithms |
AI-Driven Diagnostics –
Using artificial intelligence in analysing the patient’s data and condition, the diagnosis, and management of Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) have been upgraded through the improvement of efficiency and accuracy. Machine learning methods which include deep learning approach in the diagnosis of diseases from medical images like X-ray, MRI, and ultrasound scans are used to diagnose joint inflammation and damage that may not be visible to normal human eyes of a radiology doctor. Such tools give comprehensive and first-hand information on how diseases evolve, and treatment can be made on time with high accuracy. Also, it supports the refinement of new biomarkers associated with RA, which improves the diagnosis of the disease and increases the accuracy of disease activity monitoring. If incorporated properly into the frameworks of today’s clinical setting, these diagnostic tools enabled by AI will serve as powerful means of enabling physicians and other care professionals to gain enhanced insights about their patients’ conditions and, therefore, ensure that they apply more effective treatment plans and care management protocols.
Challenges and Limitations –
However, to optimally utilise AI solutions mixed for Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA), few challenges and limitations need to be considered[4]. However, there is a major issue of data quality and privacy; collecting large, accurate and relevant training data are relevant for the proper running of AI models while patient data must be protected from falling into the wrong hands. However, there are still worries about algorithmic bias because AI algorithms trained on a biased or insufficient dataset can give a wrong result, which may magnify the disparity of medical treatment between males and females. Three main issues of the AI tools integration into existing clinical processes are discussed: clinician education, changes in clinical practice, and compliance with the current state of healthcare. Additionally, explain ability of AI models often remains an issue, which means that the clinicians would not be able to fully comprehend the recommendations made to them by the systems. Acquiring these challenges is crucial for the further development of AI for RA and addressing the question about higher and more equitable patient care.
Future Trends –
This paper identifies the opportunity of the use of AI in management of Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) to experience drastic change in future due to technological evolvement coupled with a focus on data integration[5]. Current trends are the advancement of better algorithms to utilize the influx of big and varied data, patient monitoring data acquired from wearables and mHealth applications. These innovations are said to increase the prediction and personalization degrees for eventually paving way for adaptive treatments that adapt to the changes in patients’ health conditions[6]. Embracing of artificial intelligence with genomic and personal health is also believed to lead to more specific treatment solutions associated with patients’ genetic traits and disease processes. In addition, growth in explainable AI will enhance the accessibility of AI-backed advice in the field of medical profession since the primary reason for the rejection of the utilization of AI tools in the diagnosis of diseases is the issues of the efficiency and interpretability of such systems. With the development of AI technology, its uses in RA management will increase hence, provide more accurate and individualized approaches to dealing with the disease and enhance the health of patients with RA.
Conclusion –
Artificial intelligence (AI) is gradually playing a vital role in shaping the care delivery of Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA). Thus, the issue of increasing the accuracy of treatments and patients’ outcomes is promising for employing high-level predictive modelling, customized treatments, and intelligent diagnostics. AI makes it possible to predict the future course of the illness, adjust the treatment programs according to the patient characteristics, and use enhanced image analysis, as well as new biomarkers discovery. However, issues like the quality of data, algorithms that may contain bias and clinical application of AI are some of the issues that require further input on the way AI should be used. The future of AI remains optimistic in the field of RA management and treatment because more features can still be developed and incorporated in RA’s treatment plans with the help of the AI system, such as more flexible strategies and perhaps, with the help of Gene mapping as well. Thus, as these technologies are constantly improved, the opportunity to address many aspects of RA and improve the quality of its management and the outcome of treatment are introduced.
References –
- A.-F. Radu and S. G. Bungau, “Management of Rheumatoid Arthritis: An Overview,” Cells, vol. 10, no. 11, Art. no. 11, Nov. 2021, doi: 10.3390/cells10112857.
- J. Kedra, T. Davergne, B. Braithwaite, H. Servy, and L. Gossec, “Machine learning approaches to improve disease management of patients with rheumatoid arthritis: review and future directions,” Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol., vol. 17, no. 12, pp. 1311–1321, Dec. 2021, doi: 10.1080/1744666X.2022.2017773.
- M. Wei and C.-Q. Chu, “Prediction of treatment response: Personalized medicine in the management of rheumatoid arthritis,” Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol., vol. 36, no. 1, p. 101741, Mar. 2022, doi: 10.1016/j.berh.2021.101741.
- T. Haksoro, A. S. Aisjah, Sreerakuvandana, M. Rahaman, and T. R. Biyanto, “Enhancing Techno Economic Efficiency of FTC Distillation Using Cloud-Based Stochastic Algorithm,” Int. J. Cloud Appl. Comput. IJCAC, vol. 13, no. 1, pp. 1–16, Jan. 2023, doi: 10.4018/IJCAC.332408.
- K. T. Putra, A. Z. Arrayyan, R. Z. Syahputra, Y. A. Pamungkas, and M. Rahaman, “Design a Two-Axis Sensorless Solar Tracker Based on Real Time Clock Using MicroPython,” Emerg. Inf. Sci. Technol., vol. 4, no. 1, Art. no. 1, May 2023, doi: 10.18196/eist.v4i1.18697.
- S. Momtazmanesh, A. Nowroozi, and N. Rezaei, “Artificial Intelligence in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Current Status and Future Perspectives: A State-of-the-Art Review,” Rheumatol. Ther., vol. 9, no. 5, pp. 1249–1304, Oct. 2022, doi: 10.1007/s40744-022-00475-4.
- Sarin, S., Singh, S. K., Kumar, S., Goyal, S., Gupta, B. B., Arya, V., & Chui, K. T. (2024). SEIR‐driven semantic integration framework: Internet of Things‐enhanced epidemiological surveillance in COVID‐19 outbreaks using recurrent neural networks. IET Cyber‐Physical Systems: Theory & Applications.
- Chhabra, A., Singh, S. K., Sharma, A., Kumar, S., Gupta, B. B., Arya, V., & Chui, K. T. (2024). Sustainable and intelligent time-series models for epidemic disease forecasting and analysis. Sustainable Technology and Entrepreneurship, 3(2), 100064.
Cite As
Nagishetti P. (2024) AI-Driven Solutions for Personalized Treatment in Rheumatoid Arthritis, Insights2Techinfo, pp.1