By: Praneetha Neelapareddigari, Department of Computer Science & Engineering, Madanapalle Institute of Technology and Science, Angallu (517325), Andhra Pradesh. praneetha867reddy@gmail.com
Abstract
Artificial intelligence plays a huge role in many sectors to have a good growth in that area of sector. The integration of AI into cyber threat intelligence is the transforming task in cybersecurity. As many people and organizations come across the threats that might me dangerous no matter which type of cyberattack occurred, this is the problem that today world is facing to the cyberattacks that are dangerous. Here comes the main role of Cyber Threat Intelligence (CTI) in cyber security. This paper addresses the multifaceted role of AI in CTI that does various works on data collection, analysis and automated response. AI algorithms and machine learning models are used for processing and implementing. Many advanced technologies are used such as pattern recognition, anomaly detection, predictive analytics and may more. The implementation of AI in CTI also presents challenges. This paper involves the discussion about the challenges and highlights, future trends in AI- enhanced CTI and this article provides how AI is useful in the concept of cybersecurity.
Keywords: Artificial Intelligence, Cyber Threat Intelligence, Machine Learning, CTI lifestyle
Introduction
As for the challenges in the contemporary environment, which people, companies or governments are faced with, it is a striking threat in the recent age, and it is unknown in the cyberspace. Conventional ways of discovering and responding to cyber security threats are not often as effective as the proactive approaches implemented by the cyber criminals. Because of this, different domains such as Cyber Threat Intelligence (CTI) has just turned into important business processes for current day cyber protection strategies[1]. Therefore, to allow legal and pre-emptive responses, CTI include the acquisition, analysis, and sharing of information on potential and looming cyber threats.
AI has contributed to changing the characteristics of CTI through offering strategies to threats and how they can be fought[2]. In AI protection there is incorporation, machine learning, natural language processing and predictive analytics to evaluate the big data for machinability, to find the patterns and to look for the possible risks.
When combined with AI, and CTI real-time tracking and handling of incidents, and continuous improvement of cybersecurity is carried out[3]. AI serves the purpose of improving CTI as the risk elevates since it is proactive and proven to be effective in protecting valuable assets.
1. Introduction to Cyber Threat Intelligence (CTI)
There are many methods in Cyber Threat Intelligence (CTI) that involves the terms like collection, analyse, and disseminating information. All these components are used for the existing cyber threats to help people and organizations to protect their assets. The main aim of CTI is to enable proactive defence against any attacks.
- Types of Threat Intelligence
There are four types of threat intelligence namely,
- Strategic Threat Intelligence
- Operational Threat Intelligence
- Tactical Threat Intelligence
- Technical Threat Intelligence
Firstly, the strategic threat intelligence is about containing high level information of cyber threats that usually impact either people or organizational policies and methods. Strategic threat intelligence contains threat trends , motivations of threat actor and geopolitical considerations.
Secondly, Operational threat intelligence is about the area of information about particular specific attacks that helps in providing context to help the teams of security that makes to understand about the threat landscape and informed decisions.
Thirdly, Tactical threat intelligence is about the sector of detailed technical information about threat actors, techniques, and procedures. This can be used to enhance detection and response capabilities.
And finally, Technical threat intelligence refers to the data on specific indicators like IP addresses, domain names, malware hashes, and phishing email patterns.
2. AI in Cyber Threat Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence does the productive things to have the good implementation in every sector. Similarly, There are major role of AI in cyber threat intelligence. Certain stages are involved to have the good implementation of AI. Few of them are like pattern recognition, NLP, anomaly detection and many other concepts are involved here .
First off, AI greatly enhances data collecting and aggregation by automatically compiling threat intelligence from a range of sources, including social networking sites, blogs about security, dark web forums, and extensive threat databases. After gathering a large quantity of data, AI uses pattern recognition algorithms to sort through it all and find new patterns and hazards that human analysts might not see right away[4]. Additionally, AI can transform unstructured data sources such as news articles and danger reports into actionable intelligence by analysing and extracting insightful information using Natural Language Processing (NLP). Additionally, AI can spot possible threats that differ from known patterns by identifying anomalies in network traffic and user behaviour thanks to its anomaly detection capabilities. Lastly, AI-powered predictive analysis forecasts future cyberattacks using previous data[5].
All these components of concepts like predictive analysis, data collecting , processing, normalization all this methods are useful to make the proper implementations, so the integration of AI and CTI makes a very huge tasks.
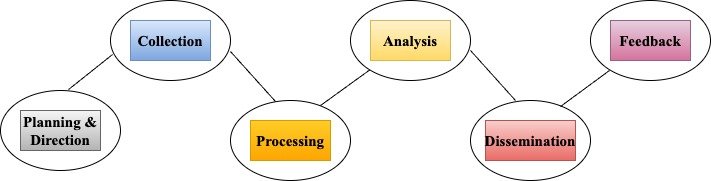
3. CTI Lifecycle
The Cyber Threat Intelligence (CTI) life cycle have many stages designed that involves to ensure the effective threat management response. The first phase is the requirement phase where it refers the organization to defines the need of intelligence and objectives with specific goals [6]. The next phase is the collection phase , in this phase the data that is raw, gathered from various internal, external sources which includes the network logs, threat feeds, and open- source intelligence (OSINT). The next phase here is the processing phase, where this data is normalized and structured for analysis is done with irrelevant information filtered out to prepare it in detail. Analysis phase is the next phase which involves the processed data to generate actionable intelligence, which also includes identifying threat actors, understanding their motivation and marking potential attacks. Once the completion of analysis, the intelligence is shared with relevant stakeholders in the phase of dissemination ensuring it is presented in a timely and actionable format. And the final phase is the feedback phase which refers, the input from stakeholders is collected to continuous refine, ensuring if it remains effective and responsive to the threats.
4. Sources of Threat Intelligence
There are broadly three types of sources namely internal sources, external sources, collaborative sources. Internal sources deals with the data generated within organization which includes the network logs that helps to capture traffic patterns, security incidents that provides the past context and internal threat reports. External sources are that which includes threat intelligence feeds, that provides real – time data on emerging threats from external providers[7]. It also includes the gathering of information from publicly available resources such as news articles and social media. Collaborative sources involves the interchange of threat intelligence with industry peers, and specialized entities like Information Sharing and Analysis Centre’s (ISACs).
5. Benefits of Cyber Threat Intelligence
There are many number of benefits in the concept of cyber threat intelligence. Organizations may foresee and get ready for such dangers before they materialize with the help of proactive defence. By offering comprehensive threat intelligence, Enhanced Incident Response expedites and enhances incident response times[8]. Security teams may more efficiently allocate and prioritize resources with the aid of informed decision-making, which is based on actionable information. Last but not least, better risk management helps businesses recognize hazards, deal with them, and put effective mitigation plans in place. These advantages support overall cybersecurity.
6. Cyber Threat Intelligence – Future
The importance of the machine learning and AI in cybersecurity have a huge transformation in cybersecurity as organizations depend more on these advanced technologies to automate data gathering, analysis, and threat prediction[9]. By exchanging critical intelligence, improved cooperation and information sharing across sectors and organizations increase collective defence even more. Furthermore, improvements in real-time threat intelligence allow for quick and useful insights, which boost the efficiency and seed of threat response.
Conclusion
AI significantly is transforming the cyber threat intelligence in the sector of cybersecurity by automating data collection, improving threat detection and analysis, and taking proactive measures. The concept of CTI is much improved by using the concepts of AI such as machine learning. If this would continue then in the days of future there would be more advanced AI techniques that makes the concept of implementation still more easier. However, the implementation of AI in CTI is impossible without challenges. But looking ahead, AI will continue to evolve a lot bringing up many concepts and introduces many implementation to the digital world.
References
- N. G. Camacho, “The Role of AI in Cybersecurity: Addressing Threats in the Digital Age,” J. Artif. Intell. Gen. Sci. JAIGS ISSN3006-4023, vol. 3, no. 1, Art. no. 1, Mar. 2024, doi: 10.60087/jaigs.v3i1.75.
- A. Dutta and S. Kant, “An Overview of Cyber Threat Intelligence Platform and Role of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning,” in Information Systems Security, S. Kanhere, V. T. Patil, S. Sural, and M. S. Gaur, Eds., Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2020, pp. 81–86. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-65610-2_5.
- S. Mittal, A. Joshi, and T. Finin, “Cyber-All-Intel: An AI for Security related Threat Intelligence,” May 07, 2019, arXiv: arXiv:1905.02895. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.1905.02895.
- R. Montasari, F. Carroll, S. Macdonald, H. Jahankhani, A. Hosseinian-Far, and A. Daneshkhah, “Application of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Producing Actionable Cyber Threat Intelligence,” in Digital Forensic Investigation of Internet of Things (IoT) Devices, R. Montasari, H. Jahankhani, R. Hill, and S. Parkinson, Eds., Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2021, pp. 47–64. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-60425-7_3.
- M. Rahaman, F. Tabassum, V. Arya, and R. Bansal, “Secure and sustainable food processing supply chain framework based on Hyperledger Fabric technology,” Cyber Secur. Appl., vol. 2, p. 100045, Jan. 2024, doi: 10.1016/j.csa.2024.100045.
- J. Cha, J. H. Jo, J. Kang, and J. H. Park, “CTI Lifecycle for network attack prevention,” Proc. Korea Inf. Process. Soc. Conf., pp. 470–472, 2019, doi: 10.3745/PKIPS.y2019m10a.470.
- B. D. Alfia, A. Asroni, S. Riyadi, and M. Rahaman, “Development of Desktop-Based Employee Payroll: A Case Study on PT. Bio Pilar Utama,” Emerg. Inf. Sci. Technol., vol. 4, no. 2, Art. no. 2, Dec. 2023, doi: 10.18196/eist.v4i2.20732.
- A. Berndt and J. Ophoff, “Exploring the Value of a Cyber Threat Intelligence Function in an Organization,” in Information Security Education. Information Security in Action, L. Drevin, S. Von Solms, and M. Theocharidou, Eds., Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2020, pp. 96–109. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-59291-2_7.
- S. Samtani, M. Abate, V. Benjamin, and W. Li, “Cybersecurity as an Industry: A Cyber Threat Intelligence Perspective,” in The Palgrave Handbook of International Cybercrime and Cyberdeviance, T. J. Holt and A. M. Bossler, Eds., Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2020, pp. 135–154. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-78440-3_8.
- Chui, K. T., Gupta, B. B., Chi, H. R., Arya, V., Alhalabi, W., Ruiz, M. T., & Shen, C. W. (2022). Transfer learning-based multi-scale denoising convolutional neural network for prostate cancer detection. Cancers, 14(15), 3687.
- Masud, M., Hossain, M. S., Alhumyani, H., Alshamrani, S. S., Cheikhrouhou, O., Ibrahim, S., … & Gupta, B. B. (2021). Pre-trained convolutional neural networks for breast cancer detection using ultrasound images. ACM Transactions on Internet Technology (TOIT), 21(4), 1-17.
Cite As
Neelapareddigari P. (2024) AI in Cyber Threat Intelligence, Insights2Techinfo, pp.1