By: Ameya Sree Kasa, Department of Computer Science & Engineering (Artificial Intelligence), Madanapalle Institute of Technology & Science, Angallu (517325), Andhra Pradesh. ameyasreekasa@gmail.com
Abstract:
With the skyrocketing cases of EHR attacks, additional layers of security became a need. Artificial intelligence provides a number of benefits in the area of EHR security. It can detect threats quickly, support automatic protective mechanisms, and ensure accuracy in data. The paper aims to enlighten the readers on how machine learning, deep learning, and natural language processing protect EHRs against cyber-attacks. This study will review the state of AI technologies in EHR security today, assess the effectiveness of existing AI applications, outline challenges and limitations faced today, and discuss trends that are emerging in the development of AI for the protection of EHRs.
Keywords: Electronic Health Records, Cyber-attacks, Data Encryption, Access Control, AI.
1. Introduction:
With the development of cyber-crime activities that are being carried out all over the world, traditional security measures fail in addressing those threats effectively. One such solution has been the incorporation of AI in containing better algorithms for EHR system protection. In this context several Intelligent technologies such as Machine learning for predictive analysis Deep learning for improved anomaly detection and Natural language processing for the identification of phishing health care organizations can improve their security postures. The aim of this article is to discuss the function of AI in the enhancement of EHR security and present its functions and the problems connected with its application. If these constituents are recognized, these can help the populace realize the prospects that are embedded in the leveraging of AI in EHR security and protection against other cybercrimes in the future.
2. Importance of Protecting Electronic Health Records (EHR):
Preservation of EHR is significant especially given the fact that the data handled today is sensitive and critical and given growing instances of hackers’ attacks[1]. The opportunities of EHRs include the totality of patient information such as medical history, planned and actual treatment, test results, and other identifiable information all of which are critical in diagnosis, treatment and care. [2] It has been established that unauthorized access to, or the breach of, such record may lead to dire consequences including identity theft, financial frauds, and changes in one’s medical records, which may have adverse effects on the safety of the patient and care delivery. Furthermore, such breaches can negatively affect the patients’ confidence in the health institutions and lead to significant legal and financial implications on the organizations. In order to protect EHRs one must preserve measures of security to protect data from leaks and hackers attacks as well as unauthorized access. Preserving such data goes beyond patient’s rights to maintain the confidentiality of his/her records; it is also the imperative of safeguarding the entire healthcare system. Modern technologies are integrating into the healthcare sector hence escalating the necessity of strict security measures to protect EHRs from new and advanced threats. [3]
3. AI Technologies for EHR Security:
3.1. Machine Learning for Threat Detection:
Using big data sets, machine learning algorithms improve EHR protect by determining and recognizing risk indicators to future dangers. These algorithms are able to identify increased frequency of access, attempts to login from unknown locations, and any variation to normal user activity. ML models can develop over the time and offer real-time solutions to the new emerging threats, which means the system can quickly respond to any threats that penetrate the security system. [4]
3.2. DL for Anomaly Detection:
Neural networks, the basis of deep learning algorithms, allow identifying various patterns and outliers in the EHR data. Compared to other approaches, deep learning can identify complex structures and patterns in the data, for example, a pathological condition in patient records or coded messages. Higher analysis enables the program to detect complex and well-hidden cyber threats that a normal security system cannot detect, improving on the security of EHR systems. [1]
3.3. Natural Language Processing for phishing Detection:
Machine learning is used in order to identify phishing attacks on EHR systems through analyzing the textual data of emails, messages and other forms of communication using Natural Language Processing (NLP). [5] NLP algorithms help to detect the likelihood of phishing in particular information based on keywords inherent in phishing schemes like fake language or links. Using NLP, one is able to differentiate between genuine communication and phishing attempts which in turn prevents individuals unauthorized access to EHR information. [6]
3.4. Predictive Analysis for threat prevention:
Predictive analytics is an analysis of past activities and future possibility of security threats based on tested algorithms. Data mining takes into consideration past occurrences of cybercrimes and leverages such findings to predict future occurrences of the crime. It also enables the healthcare organizations to prevent rather than wait to treat successful breaches, which would be the end result of this approach. [7]
3.4. Real-Time Monitoring and Response Systems:
Real-time monitoring systems use artificial intelligence to constantly watch EHR systems for signs of anomalies or potential breaches. These systems use AI algorithms to analyze data flows, user activities and systems behaviors in real time. This means when there is an intrusion or violation, the system is able to set off alarms and start the remedial measures to contain these risks and protect EHR information. [8]
4. AI-Driven Access Controls:
The integration of AI to grant access rights to the electronic health records enhances security because these systems control the access based on the behaviors and circumstances of the users. With the help of complicated algorithms AI constantly observes the users’ actions and access requests to apply exact role-based access policies. [9] This dynamic approach confirms the GA/NA access attempts continuously and changes the level of GA/NA access according to the behavior and prior records. Thus, AI engine’s access control mechanisms reduce the risk of unauthorized access or data alteration of sensitive health information, which in turn helps to safeguard the confidentiality and integrity of EHR systems. [10]
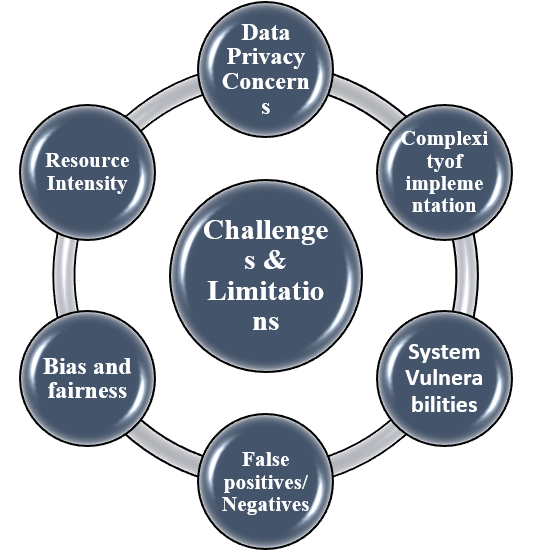
5. Challenges and Limitations:
The challenges for protecting Health information are as mentioned below in Figure 2.
6. Conclusion:
In conclusion, AI-driven access controls will dramatically shift in the EHR security field because it has next-generation protection based on adaptive and behavior-based management of user permissions. These technologies improve the accuracy of access control, reducing the risk of unauthorized breaches to data and protecting sensitive health information. The ability of these devices to perform optimally, however, remains limited by some challenges: protection of the data from intrusion, possibility of false positives and negatives, and finally, the system integration that comes with its own share of complexities. Robust AI-driven security needs updates constantly against the changing threats, high-quality data, and conformance to regulations. Even with these challenges, AI-driven access controls do offer some potential to promote higher EHR security and generally reliability in healthcare data management.
7. References:
- Rahaman M (2024) Foundations of Phishing Detection Using Deep Learning: A Review of Current Techniques Available: https://insights2techinfo.com/foundations-of-phishing-detection-using-deep-learning-a-review-of-current-techniques/
- J. Frank, “Arti cial Intelligence and Intrusion Detection: Current and Future Directions”.
- B. Murdoch, “Privacy and artificial intelligence: challenges for protecting health information in a new era,” BMC Med. Ethics, vol. 22, no. 1, p. 122, Sep. 2021, doi: 10.1186/s12910-021-00687-3.
- A. Alonso and J. J. Siracuse, “Protecting patient safety and privacy in the era of artificial intelligence,” Semin. Vasc. Surg., vol. 36, no. 3, pp. 426–429, Sep. 2023, doi: 10.1053/j.semvascsurg.2023.06.002.
- M. Rahaman, C.-Y. Lin, and M. Moslehpour, “SAPD: Secure Authentication Protocol Development for Smart Healthcare Management Using IoT,” Oct. 2023, pp. 1014–1018. doi: 10.1109/GCCE59613.2023.10315475.
- a. Almethen, “Challenges in implementing artificial intelligence applications in secondary-level education: A teacher-centric perspective,” مجلة کلية التربية أسيوط, vol. 0, no. 0, pp. 0–0, May 2024, doi: 10.21608/mfes.2024.270936.1776.
- S.-T. Liaw et al., “Ethical Use of Electronic Health Record Data and Artificial Intelligence: Recommendations of the Primary Care Informatics Working Group of the International Medical Informatics Association,” Yearb. Med. Inform., vol. 29, pp. 51–57, Apr. 2020, doi: 10.1055/s-0040-1701980.
- M. Markevych and M. Dawson, “A Review of Enhancing Intrusion Detection Systems for Cybersecurity Using Artificial Intelligence (AI),” Int. Conf. Knowl.-BASED Organ., vol. 29, no. 3, pp. 30–37, Jun. 2023, doi: 10.2478/kbo-2023-0072.
- E. Martins and K. P. Extension, “Appraisal of Artificial Intelligence and Cost Reduction Management in Educational Institutions,” vol. 3, pp. 1–7, May 2024.
- P. Pappachan, Sreerakuvandana, and M. Rahaman, “Conceptualising the Role of Intellectual Property and Ethical Behaviour in Artificial Intelligence,” in Handbook of Research on AI and ML for Intelligent Machines and Systems, IGI Global, 2024, pp. 1–26. doi: 10.4018/978-1-6684-9999-3.ch001.
- Mamta, & Gupta, B. (2021). An attribute-based keyword search for m-health networks. Journal of Computer Virology and Hacking Techniques, 17(1), 21-36.
- Khan, A., & Gupta, B. B. (2022). WSNs and IoTs for the Identification of COVID-19 Related Healthcare Issues: A Survey on Contributions, Challenges and Evolution. Security and Privacy Preserving for IoT and 5G Networks: Techniques, Challenges, and New Directions, 225-262.
Cite As
Kasa A.S. (2024) AI in Protecting Electronic Health Records (EHR) from Cyber Attacks, Insights2Techinfo, pp.1