By: Syed Raiyan Ali – syedraiyanali@gmail.com, Department of computer science and Engineering( Data Science ), Student of computer science and Engineering( Data Science ), Madanapalle Institute Of Technology and Science, 517325, Angallu , Andhra Pradesh.
ABSTRACT –
In recent times, artificial intelligence (AI) has significantly increased the pace of innovations in health care especially with regards to diagnosing diseases and treating patients. The research paper focuses on the impact that AI-based solutions have made to various parts of health systems considering their contribution towards better diagnosis accuracy, improved treatment protocols as well as reformed patient care practices. More specifically, it explains how machine learning and deep learning algorithms are being used through AI algorithms for instance to interpret medical images or analyze information from patients and deliver personalized health care services. Moreover, this study looks at some case studies together with empirical evidence which prove that most such innovations driven by AI help in diagnosing complex illnesses predicting treatment outcomes besides improving health delivery systems. Besides these ethical issues such as those related to patients’ privacy then the need for transparency in algorithms as well as equitable adoption across all sectors should be equally considered. Overall, this paper provides an extensive overview of the different kinds of applications AI can find in medical sector which will ultimately lead to changing diagnostic methods and make it more focused on patients themselves than before.
Keywords : Artificial Intelligence, Healthcare, Diagnostics, Patient Care, Machine Learning, Deep Learning, Personalized Medicine, Ethical Considerations
INTRODUCTION-
In the field of healthcare, the transformative power of artificial intelligence (AI) is already there to see. This promises that it will greatly improve patient care through sophisticated techniques that analyze data and make predictions.[1] In this article, we look at the various ways in which AI is changing treatment of patients with a focus on increased accuracy for diagnosis and customized therapies. Through AI tools, healthcare providers are able to offer much more efficient care which results in better health outcomes for their clients.
AI IN DIAGNOSTICS-
Enhancing Diagnostic Accuracy
The diagnostic precision of AI calculations, most notably machine learning and deep learning, has been greatly enhanced. Such algorithms compute substantial volumes of medical information, including images and genetic details, looking for shared features that might otherwise go unnoticed by human doctors.[2] For example, AI-based instruments in radiology can recognise cancerous cells on X-ray films, enabling correct identification of the disease earlier than expected.
The below diagram explains the work flow of AI in health care, showing how data is collected, processed, and used for diagnosis, treatment optimization, and personalized care.
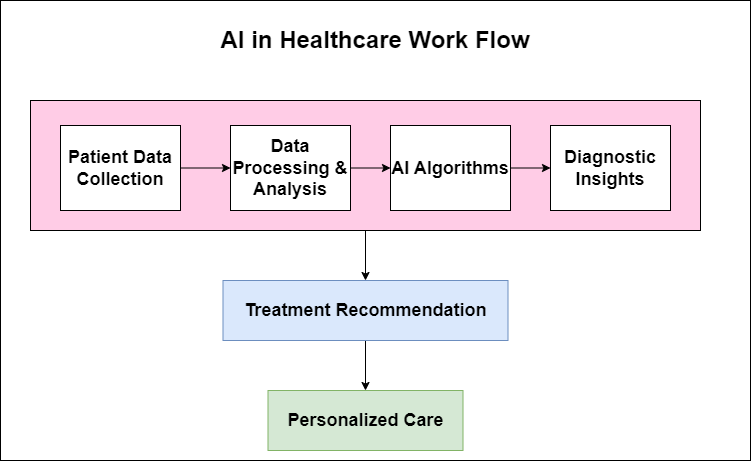
Case Studies in AI Diagnostics
The competency of AI in diagnostics is demonstrated by various case studies. One prominent application of AI is its utilization in interpreting mammograms for breast cancer detection. Research has shown that AI algorithms can match or even surpass diagnostic performance compared to radiologists, diminishing false positives and negatives.[3]
AI IN TREATMENT OPTIMIZATION
Personalized Medicine
In the medical field, personalized treatment plans based on AI analyses could lead to better outcomes for patients and more effective interventions[4]. These systems assess intricate datasets to provide actionable insights. AI decision support systems have transformed precision medicine by equipping doctors with the means to customize patient care.
Advancements in Cancer Treatment
In cancer therapeutics, artificial intelligence is bringing innovative techniques which include early detection methods and directed treatments for some specific genetic alterations. As a result of identifying optimal treatment regimens for individual patients, even in case they have malignant ailments AI aids cancer patients to live longer and healthier lives.
AI IN VACCINE DEVELOPMENT
Human beings have been made to possess the greatest skills ever that include being able to create vaccines so quickly for infectious diseases just using the AI. The knowledge from biological science could be analysed through thousands of millions of biological data resources to obtain vaccine candidates very quickly, thanks to this when compared with traditional methods of searching for drugs. This sort of things happened at the height of COVID-19 pandemics where Artificial Intelligence (AI) had its most notable contributions in vaccine development and delivery.[5]
ETHICAL CONSIDERATIONS
Patient Privacy and Data Security
The healthcare system faces some major ethical issues as a result of the increased use of artificial intelligence, especially in relation to patient privacy and data security. The protection and ethical use of patient information are critical and must be guaranteed. Therefore, health institutions have to set up strong data governance structures for the protection of patients’ data.
Algorithm Transparency and Fairness
There are fairness needs in health care decision-making and biases in health care decision-making can be avoided through being transparent about AI algorithms. Health care stakeholders have a duty to comprehend the making of decisions made by them so as to avoid perpetuating existing disparities in healthcare[6]. Furthermore, continuous efforts are required that focus on improving the transparency of algorithms as well as ensuring just distribution of artificial intelligence technologies.
CHALLENGES AND FUTURE DIRECTIONS
Data Integration and Interpretation
Integration and interpretation of different sources of data are some of the biggest challenges facing AI deployment in health care today. Comprehensive, high-quality data is needed for effective AI solutions; however, collection and standardization may pose a challenge in some cases. The suggested direction for future research involves learning how to combine different kinds of data without difficulty as well as enabling better understanding o the kind o models used by AI.
Education and Training for Healthcare Professionals
Healthcare specialists have to develop their ability to comprehend and correctly embrace AI technologies. It includes fundamental artificial intelligence literacy, data management guidelines, as well as the effects of these technologies on medical procedures. Sponsored educational initiatives are necessary for teaching healthcare workers about this automated age that revolves around artificial intelligence.
CONCLUSION
There are numerous ways in which AI-based information can promote quality patient management. This involves diagnosis correctness improvement, optimized treatment guidelines, and customized ways of medication delivery. Therefore, implementing such technologies into healthcare professionals’ working processes will allow them be more cost-efficient while resulting into better outcomes as well as influencing future practices in medicine.
REFERENCES-
- B. Y. Kasula, “AI-Driven Innovations in Healthcare: Improving Diagnostics and Patient Care,” Int. J. Mach. Learn. Artif. Intell., vol. 2, no. 2, Art. no. 2, Dec. 2021.
- J. A. Swets, D. J. Getty, R. M. Pickett, C. J. D’Orsi, S. E. Seltzer, and B. J. McNeil, “Enhancing and Evaluating Diagnostic Accuracy,” Med. Decis. Making, vol. 11, no. 1, pp. 9–17, Feb. 1991, doi: 10.1177/0272989X9101100102.
- G. Rong, A. Mendez, E. Bou Assi, B. Zhao, and M. Sawan, “Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare: Review and Prediction Case Studies,” Engineering, vol. 6, no. 3, pp. 291–301, Mar. 2020, doi: 10.1016/j.eng.2019.08.015.
- M. Rahaman, B. Chappu, N. Anwar, and P. K. Hadi, “Analysis of Attacks on Private Cloud Computing Services that Implicate Denial of Services (DoS),” vol. 4, 2022.
- G. Arora, J. Joshi, R. S. Mandal, N. Shrivastava, R. Virmani, and T. Sethi, “Artificial Intelligence in Surveillance, Diagnosis, Drug Discovery and Vaccine Development against COVID-19,” Pathogens, vol. 10, no. 8, Art. no. 8, Aug. 2021, doi: 10.3390/pathogens10081048.
- L. Triyono, R. Gernowo, P. Prayitno, M. Rahaman, and T. R. Yudantoro, “Fake News Detection in Indonesian Popular News Portal Using Machine Learning For Visual Impairment,” JOIV Int. J. Inform. Vis., vol. 7, no. 3, pp. 726–732, Sep. 2023, doi: 10.30630/joiv.7.3.1243.
- Zhou, Y., Song, L., Liu, Y., Vijayakumar, P., Gupta, B. B., Alhalabi, W., & Alsharif, H. (2023). A privacy-preserving logistic regression-based diagnosis scheme for digital healthcare. Future Generation Computer Systems, 144, 63-73.
- Xu, Z., He, D., Vijayakumar, P., Gupta, B. B., & Shen, J. (2021). Certificateless public auditing scheme with data privacy and dynamics in group user model of cloud-assisted medical WSNs. IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics, 27(5), 2334-2344.
Cite As
Ali S. R. (2024) Enhancing Patient Care with AI-Driven Insights, Insights2Techinfo