By: Aiyaan Hasan, International Center for AI and Cyber Security Research and Innovations (CCRI), Asia University, Taiwan, rayhasan114@gmail.com
Abstract:
The merging of Machine Learning (ML) and Artificial Intelligence (AI) technologies is bringing about an important change in the constantly changing field of cybersecurity. The article explores the application of ML and AI in threat detection, response, and ethical considerations, delving into their dynamic interaction in cybersecurity. ML and AI have become increasingly important tools to support security measures as cyber threats become more automated and sophisticated. The transformational potential, difficulties, and ethical implications of ML and AI in protecting digital assets from an ongoing series of attacks are uncovered in this paper.
Introduction:
The ongoing series of cyberattacks, which can take the form of opportunistic ransomware cases or sophisticated state-sponsored campaigns, has forced enterprises to look for creative ways to safeguard their digital assets.[1] In this race of technology, cybersecurity and artificial intelligence (AI/ML) is becoming more and more important as a key tactic to strengthen defenses and adjust to the changing threat scenario.
The importance that AI and ML play in cybersecurity is explored in this article. We will explore the potential of these technologies as we navigate this intersection, as well as the creative uses of them in threat detection, response, and event analysis. We will also closely examine the moral issues surrounding their use.
Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence in the domain of Cybersecurity
In the domain of cybersecurity, Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence in Cybersecurity have become essential allies. Threat detection has been transformed by its capacity to examine large datasets, identify trends, and make choices instantly.[2] Systems with AI and ML capabilities can sort through enormous volumes of network traffic data, looking for anomalies that could point to a cyber-attack or even predict possible dangers before they happen. The ability to forecast the future is revolutionary in the fight against cyberattacks.[3]
Furthermore, quick incident response is one area where AI and ML are integrated. AI-driven systems have the ability to automatically initiate predefined reactions in the event of a possible threat or notify human operators for more inquiry. This lessens the impact of an attack while also speeding up the response time.
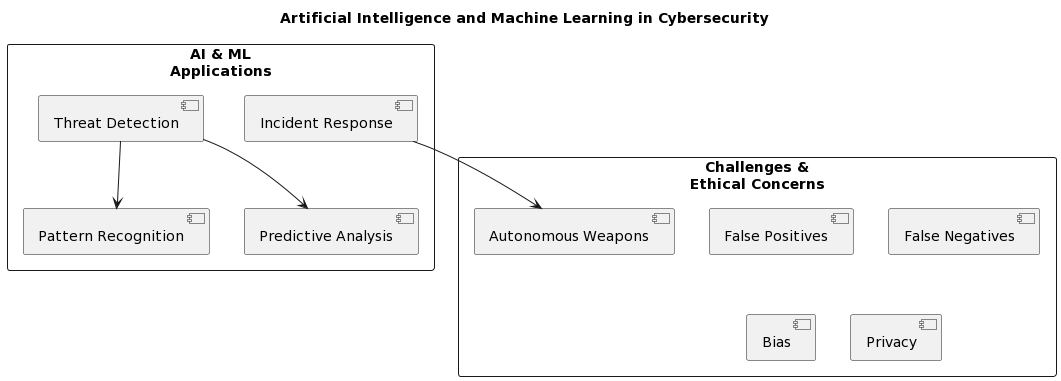
Difficulties and Ethical Issues:
Although AI and ML have many benefits for cybersecurity, there are drawbacks as well. There are persistent worries about false positives, in which harmless actions are reported as threats, and false negatives, in which real dangers are missed. It can be difficult to find the ideal balance between a strong defense and a reasonable amount of notifications.
ML and AI ‘s Future in Cybersecurity
ML and AI in cybersecurity have a bright future ahead of them. We should expect even more advanced threat detection, real-time incident response, and automated cyber protection measures as these technologies develop further.[4]
Furthermore, the use of AI and ML to cloud security, autonomous threat hunting, and IoT security is imminent. Still, it’s critical to maintain alert given the always changing danger scenario. Threat actors are using AI and ML in their attack plans, therefore the cybersecurity community needs to react with at least as sophisticated of a response.[5] The future of ML and AI in cybersecurity will be largely shaped by cooperation between AI specialists, cybersecurity experts, and ethical considerations. Furthermore, it is impossible to minimize the ethical implications of ML and AI in cybersecurity. Serious worries include the possibility of biased decision-making, invasions of privacy, and the creation of autonomous cyberweapons. In the context of cybersecurity, it demands a thorough assessment of ethical implications and the creation of ethical frameworks to regulate AI and ML.
Conclusion:
The combination of cybersecurity with AI/ML heralds a revolutionary new age in digital protection. With the help of these technologies, threat detection, response, and resilience are being redefined, giving users the advantage in the never-ending war against cyber enemies. Digital ecosystems’ ability to resist new dangers will depend on how relentlessly innovation and vigilance persist, even in the face of ongoing obstacles like false positives and ethical dilemmas. The combination of AI and ML is a powerful ally in the constantly changing field of cybersecurity, providing new levels of protection and opening the door to a more secure digital future.
References
- Kim, S. H., Wang, Q. H., & Ullrich, J. B. (2012). A comparative study of cyberattacks. Communications of the ACM, 55(3), 66-73.
- Geluvaraj, B., Satwik, P. M., & Ashok Kumar, T. A. (2019). The future of cybersecurity: Major role of artificial intelligence, machine learning, and deep learning in cyberspace. In International Conference on Computer Networks and Communication Technologies: ICCNCT 2018 (pp. 739-747). Springer Singapore.
- Juneja, A., Juneja, S., Bali, V., Jain, V., & Upadhyay, H. (2021). Artificial intelligence and cybersecurity: current trends and future prospects. The Smart Cyber Ecosystem for Sustainable Development, 431-441.
- Juneja, A., Juneja, S., Bali, V., Jain, V., & Upadhyay, H. (2021). Artificial intelligence and cybersecurity: current trends and future prospects. The Smart Cyber Ecosystem for Sustainable Development, 431-441.
- Sarker, I. H., Furhad, M. H., & Nowrozy, R. (2021). Ai-driven cybersecurity: an overview, security intelligence modeling and research directions. SN Computer Science, 2, 1-18.
- Mishra, A., Gupta, N., & Gupta, B. B. (2021). Defense mechanisms against DDoS attack based on entropy in SDN-cloud using POX controller. Telecommunication systems, 77, 47-62.
- Nguyen, G. N., Le Viet, N. H., Elhoseny, M., Shankar, K., Gupta, B. B., & Abd El-Latif, A. A. (2021). Secure blockchain enabled Cyber–physical systems in healthcare using deep belief network with ResNet model. Journal of parallel and distributed computing, 153, 150-160.
- Elgendy, I. A., Zhang, W. Z., He, H., Gupta, B. B., & Abd El-Latif, A. A. (2021). Joint computation offloading and task caching for multi-user and multi-task MEC systems: reinforcement learning-based algorithms. Wireless Networks, 27(3), 2023-2038.
- Masud, M., Gaba, G. S., Alqahtani, S., Muhammad, G., Gupta, B. B., Kumar, P., & Ghoneim, A. (2020). A lightweight and robust secure key establishment protocol for internet of medical things in COVID-19 patients care. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 8(21), 15694-15703.
- Kumar, N., Poonia, V., Gupta, B. B., & Goyal, M. K. (2021). A novel framework for risk assessment and resilience of critical infrastructure towards climate change. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 165, 120532.
Cite As
Hasan A. (2023) Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence in Cybersecurity, Insights2Techinfo, pp.1