By: Soo Nee Kee1,2
1Universiti Malaya, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia.
2International Center for AI and Cyber Security Research and Innovations, Asia University, Taiwan, Email: nee.kee2001.nks@gmail.com
Abstract
Internet of Things (IoT) is widely used in many industries, from public sectors to private sectors, hospitality to agriculture. The use of IoT enhances efficiency, scalability and connectivity by enabling real-time data collection, processing and automation. It also plays an important role in the supply chain to help in monitoring and automating processes. Supply chain means the process of transferring products, services or information from the producers to consumers. As IoT becomes the central to supply chain, it also introduces security vulnerabilities, especially phishing attacks. This is because diverse network environments and interconnected IoT devices are always susceptible to cybersecurity attacks. This paper proposes the integration of blockchain to secure IoT-based supply chains.
Keywords: IoT, Supply Chain, Blockchain, Four-layer Architecture, Phishing
Introduction
Supply chain is the companies or individuals that are involved in the production and delivery of goods or services to customers. It involves processes like logistics management, asset tracking, sales and operations and inventory management. IoT devices such as sensors and actuators help in data collection and exchange in real-time, allowing producers, consumers and stakeholders to obtain accurate information about the products or services, such as their status and conditions. [1] To secure the data transmission across the network, blockchain is implemented to store the data. Blockchain is a decentralized ledger that stores data in a distributed manner. It provides traceability, transparency and immutability for the supply chain, making it difficult to modify or delete the data and enhance the security and accountability of the supply chain.
Techniques
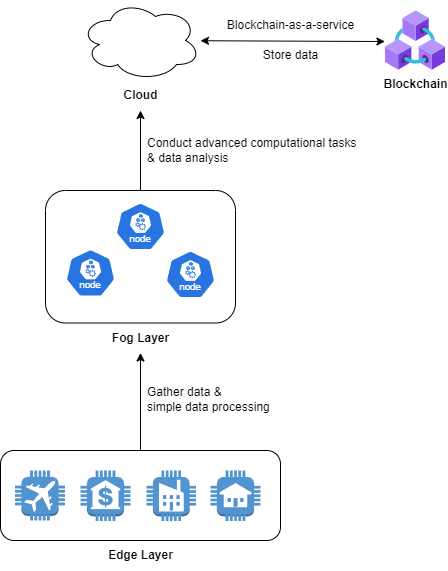
A three-layer architecture is proposed in this paper: edge layer, fog layer and cloud. Edge layer consists of a lot of IoT devices such as sensors, cameras, and actuators to detect conditions and anomalies while fog layer is the middle layer that gathers data from the IoT devices and performs simple data processing and analysis. Fog nodes are normally placed near the edge devices as they have to collect and analyze data, as well as respond to the abnormal immediately. The data collected at fog layer will then be sent to cloud for further processing. Cloud consists of advanced computational capabilities that can analyze data for a complex and larger dataset. Besides, cloud also supports advanced computational tasks like machine learning. To secure data storage, blockchain is integrated in the cloud layer. There are many blockchain-as-a-service (BaaS) offered on Cloud like Oracle Blockchain Cloud Service and Azure Blockchain. [1] By utilizing blockchain on cloud can ensure the security of the supply chain as well as foster users trust, due to its immutable nature. Thus, after storing data on blockchain, it is impossible for anyone to change, modify or delete the data. In addition, Smart Contracts is used to automate storing process and govern transactions, eliminating the need of third parties. [2]
Conclusion
In conclusion, a blockchain-based three-layer architecture can address the security issues in supply chain effectively. The use of smart contracts can further strengthen security, automate processes, improve efficiency and eliminate the need of third parties, reducing the risk of phishing attacks. Fog layer plays important roles in the three-layer architecture, as it helps reduce network latency by conducting simple data analysis without transferring data to a main server. It also bridges the gap between the edge layer and cloud layer. By implementing blockchain on cloud, the system can monitor and analyze data, detect anomalies, as well as store data in a secure manner. It provides scalable, secure and efficient solutions to supply chain operations. This solution not only strengthens security of the system, but also enhances transparency and performance.
Reference
- “Secure pharmaceutical supply chain using blockchain in IoT cloud systems – ScienceDirect.” Accessed: Oct. 09, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2542660524001562
- “Exploring the integration of edge computing and blockchain IoT: Principles, architectures, security, and applications – ScienceDirect.” Accessed: Oct. 04, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1084804524000614
- Gupta, B. B., & Nedjah, N. (Eds.). (2020). Safety, Security, and Reliability of Robotic Systems: Algorithms, Applications, and Technologies. CRC Press.
- Gupta, B. B., & Srinivasagopalan, S. (Eds.). (2020). Handbook of research on intrusion detection systems. IGI Global.
- Gupta, B. B., Chui, K. T., Gaurav, A., Arya, V., & Chaurasia, P. (2023). A novel hybrid convolutional neural network-and gated recurrent unit-based paradigm for IoT network traffic attack detection in smart cities. Sensors, 23(21), 8686.
Cite As
Kee S.N. (2024) Securing IoT-Based Supply Chains: Blockchain and Phishing Attack Prevention, Insights2Techinfo, pp.1