By: Rishitha Chokkappagari, Department of Computer Science &Engineering, Madanapalle Institute of Technology & Science, Angallu (517325), Andhra Pradesh. chokkappagaririshitha@gmail.com
Abstract
Cloud computing is the process of transferring computing services that includes servers, storage, databases, networking, software over the internet to offer faster innovation and provide flexible resources. Cloud servers just work like other physical servers and perform functions that are just like the storing of data and running the applications. As cloud services refer to the transfer of data through the internet it involves third party most often. When the data is being transferred through the third party it becomes necessary to provide security for the data from bring theft. Cloud security also known as cloud computing security is a discipline of cybersecurity provides protection of cloud computing systems. It involves all the required data that protects organization’s sensitive data like technologies, policies, services. It mainly aims to provide security to the cloud-based infrastructure, applications and data. The security measures that are used in the cloud-based environment mainly focuses on authentication, data and resource control, privacy protection. Cloud security includes four main solutions cloud data visibility, control over cloud data, access to cloud data and applications, and compliance. This article primarily focuses on how security is provided through the cloud computing environment.
Keywords: Cloud computing, cloud security, protection of data
Introduction
With more and more users opting for cloud storage of their data, the need, and demand for protecting such data from various forms of threats also follow the same trend. Cloud storage has the highest level of convenience, growth, and affordability as compared to any other storage option for companies and people. Businesses and companies are then able to store tremendous amounts of information and documents without requiring for physical storage devices and media while individuals are then given the flexibility that they can access their files even if they aren’t physically in front of their personal computers. Nevertheless, these stimulants make a cloud environment rather vulnerable to security threats that are quite crucial to be mitigated to avoid information loss and compromise in a cloud environment.
The integration of storage systems in clouds can indeed be viewed as one of the biggest transitions when it comes to working with information; however, it cannot be overlooked that it brings its set of challenges when it comes to security. The risks to the data enclosed in the clouds range from hacking, organized cyberattacks, and even careless errors and mishaps such as file deletion. It is imperative to point out that physical security of data when stored in the cloud cannot be achieved by mere reliance in the existing physical features that come with the cloud service offers. It requires pre-emption, which means the executed security measures are strong, suit for an individual type, and constantly evolving according to the current threats in the world of cyber-war.
In any case, when it comes to storing documents, be these personal ones, or business documents, as well as crucial data, it is necessary to adhere to the best practices regarding storage security in the cloud. This entails familiarity with the shared responsibility model by the cloud provider and the customer in the protection of data. Users still must be responsible for who gets to log in and out as well as the secure ways of encrypting data and frequently auditing the data, on the other hand cloud providers are responsible for the security of the cloud infrastructure and make sure it conforms to industry best practice.
Following this, this article will go over some strategies for ensuring the safety of files in the cloud. We will discuss basics of the best practices like selection of the right provider of the cloud services, the possibility of the reliable encryption of the information, the constant use of the strict control of the access and the continuous audits of the access records. Also, extreme importance will be paid to data backup and recovery, updating and patching systems, as well as employing security awareness for personnel. In addition, the chapter shall discuss compliance and legal requirements, the need for security audits.
Cloud Computing Security
This section presents the existing security and privacy concerns in Cloud computing. In fact, cloud computing is a very large and broad speciality, given that it transmits and hosts its facilities on the Internet. The company offers services to fulfil the needs of the clients and the cost follows, according to Hafeez[1]. This makes the Cloud crucial as people start to depend on it and organizations can now hire a Cloud service easily.
Some of the major threats or risks that Cloud computing is exposed to are as follows: flaws in virtualization/multi tenancy, Internet protocol, unauthorised access to the management interface, injections flaws, and browser and APIs. Those vulnerabilities have consequent effects which include enabling attacks on the network, enabling intruders’ control of the access, enabling unauthorized services and finally unveiling the customers’ private information or data. All these vulnerabilities place Cloud at risk, either directly at risk or indirectly as in the case of business. Some of the threats include (i) Business model change which restrain the use of Cloud computing services, (ii) abusive Cloud computing services, (iii) insecure interfaces and API, (iv) malicious insiders, (v) loss of data and leakage, (vi) service hijacking, (vii) unknown risk profile[1].
Thus, for the Cloud to be safeguarded from these threats and potential harm to be halted, the kinds of attack that can be carried out must be identified and comprehended. The attacks most often discussed in Cloud computing are the following:
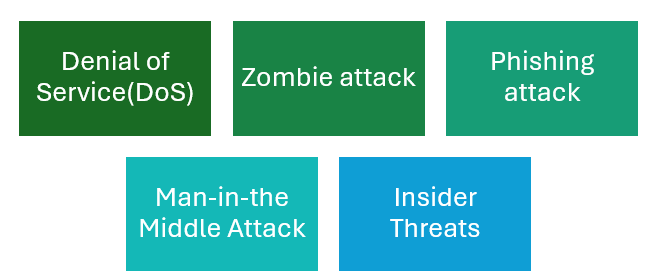
- Denial of Service (DoS): This attack is one way of trying to influence the status of services for users. DDoS is used for the use of DoS involving several computers.
- Zombie attack: when the attacker sends many requests from different genuine hosts of the network to the victim. Such an assault interferes with Cloud’s expected patterns of operation and affects how easily cloud services can be accessed.
- Phishing attack: is a bid to practice tricks and scams on people and get their details by taking them to the wrong link. The Cloud service provider can be a Cloud attacker that hosts another Cloud user’s accounts and services for the purpose of a phish site[2].
- Man-in-the Middle attack: where an attacker can get in between two users during the communication. Intruder can get information interactions of data centres in the Cloud
Some other attacks are Cloud malware injection attacks, violation of privacy, identity attacks, attacks on Virtualization and many more[3]. The fig1 below shows the types of security attacks in cloud.
Threats to Cloud Computing and the Suggested Remedial measures
The security threats that befall each of the cloud computing platforms and services described in this article can be said to be the same that most systems that are accessible via the Internet are vulnerable to. That said, several threats are compounded because of the collaboration aspect of cloud computing. This article discusses Data Breaches, Account Hijacking, and Multitenancy threats. However, such article concedes that there is a lot more that is relevant to cloud computing. For more information on additional threats, the Cloud Security Alliance proposed the list of the twelve threats for cloud computing [3]. The fig2 gives the complete details of security threats and remedial measures. The fig2 below shows the threats and remedial measures for cloud security.
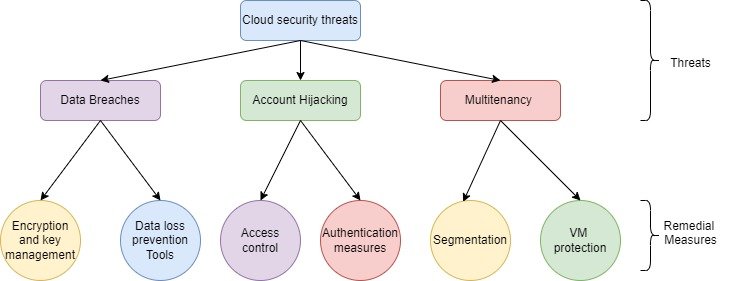
A. Data Breaches
Data breach then defines a situation where protected, sensitive or confidential information gets accessed by a third party. Cloud computing exposes the organizations to numerous risks because numerous different types of data owned by different vendors are stored in the cloud by the providers. Data breaches impact all three service models: Are of three types: Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS).
Preventive Measures:
Encryption and Key Management: Encrypt the data during transmission and storage and safeguard the encryption keys. Nonetheless, given the dynamic accessibility of the networks, attacks such as the man in the middle are still possible[4].
Data Loss Prevention (DLP) Tools: Granular control involves selective redaction, the integration of OS agents at the kernel level, data content and context, identifiable patterns in structured data, emails and cloud storage, linguistics, decryption/encryption of the web traffic. Nevertheless, there are still issues such as the scarcity of resources and the variability of classification.
B. Account Hijacking as well as Maintenance
This is evident through account issues which are primary root causes of data leaks. Some of the typical challenges that organizations face is poor access control, password issues, coded credentials and many more. Most organizations do not revoke the access rights of employees who have left organization, making the system open.
Preventive Measures:
Access Controls: It recommended to use complicated and distinctive passwords and also urged to turn on the use of multiple factor authentication (MFA). Control the rights to allow the user to access only the information needed.
Authentication Methods: Studies are being made for improving the security of the authentications such as mutual, password and smart cards, and biometric authentications. MFA can be described as efficient but not widely implemented; its usage is reported at a level of 18%. It is reported that only 1% of end users are using it as of 2015[5].
C. Multitenancy Threats
It imparts the capability to maintain and support different organizations through infrastructure being multiple tenanted; the applications in SaaS service model and software stacks in PaaS being multiple tenanted[6]. Sharing the physical facilities and resources means that different groups work with the same virtual space; this includes risks as the unauthorized monitoring of the sessions, failed login attempts, spread of malware, man-in-the-middle attacks, etc.
Preventive Measures:
Segmentation: Tenant resources can be isolated with the help of segmentation which is provided by cloud providers. APIs do assist with correct division and seclusion; however, this is often up to the end users to put into place.
VM Introspection: This technique offers specific section assistance to hypervisor and covers the shortcoming of other segmentation approaches. While being rather effective, it is rather complicated to employ, and its primary application reverts to the end user, which means that it is not used to its full potential[7].
Conclusion
Data protection in cloud storage is now almost mandatory due to the rising prevalence of data loss, missing login credentials, and multitenant dangers. One of the biggest advantages of using cloud storage on the modern market is the possibility of enhancing the conveniences and flexibility with the further development and decrease in costs, but this model demands the constant check and specific methods of protection of information. Knowing the shared responsibility model is important as it outlines that both the provider and the user of cloud services have duties when it comes to protection of data. If you are going to trust your applications and data in the cloud you must partner with reliable cloud providers with robust security records and standards compliance. Some of the methods which must be employed include strong and effective encryption, strict user and access controls, and modern DLPs among others.
In conclusion, cloud security can be considered as a continuous process that requires constant focus and evolution according to the constantly appearing threats. In today’s world being knowledgeable and practicing good security measures one is able to accept the advantages of cloud storage while keeping personal information private from third parties and viruses. Security is paramount, should update the practices at regular intervals and be on your guard that your data is safe in the cloud.
References
- D. Dave, N. Meruliya, T. D. Gajjar, G. T. Ghoda, D. H. Parekh, and R. Sridaran, “Cloud Security Issues and Challenges,” in Big Data Analytics, V. B. Aggarwal, V. Bhatnagar, and D. K. Mishra, Eds., Singapore: Springer, 2018, pp. 499–514. doi: 10.1007/978-981-10-6620-7_48.
- M. Bešić, “Benefits and Risks of Artificial Intelligence in Cybersecurity and Phishing Attacks,” E-Bus. Technol. Conf. Proc., vol. 3, no. 1, Art. no. 1, Jun. 2023.
- A. B. Nassif, M. A. Talib, Q. Nasir, H. Albadani, and F. M. Dakalbab, “Machine Learning for Cloud Security: A Systematic Review,” IEEE Access, vol. 9, pp. 20717–20735, 2021, doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3054129.
- B. Jana, J. Poray, T. Mandal, and M. Kule, “A multilevel encryption technique in cloud security,” in 2017 7th International Conference on Communication Systems and Network Technologies (CSNT), Nov. 2017, pp. 220–224. doi: 10.1109/CSNT.2017.8418541.
- M. Rahaman, F. Tabassum, V. Arya, and R. Bansal, “Secure and sustainable food processing supply chain framework based on Hyperledger Fabric technology,” Cyber Secur. Appl., vol. 2, p. 100045, Jan. 2024, doi: 10.1016/j.csa.2024.100045.
- Tabassum F, Rahaman M (2024) An Enhanced Multi-Factor Authentication and Key Agreement Protocol in Industrial Internet of Things, Available: https://insights2techinfo.com/an-enhanced-multi-factor-authentication-and-key-agreement-protocol-in-industrial-internet-of-things/
- N. C. Paxton, “Cloud Security: A Review of Current Issues and Proposed Solutions,” in 2016 IEEE 2nd International Conference on Collaboration and Internet Computing (CIC), Nov. 2016, pp. 452–455. doi: 10.1109/CIC.2016.066.
- Gupta, B. B. (Ed.). (2021). Cloud Security: Concepts, Applications and Perspectives. CRC Press.
- Chaturvedi, C., & Gupta, B. B. (2020). Cloud computing security: Taxonomy of issues, challenges, case studies, and solutions. In Handbook of Research on Intrusion Detection Systems (pp. 306-325). IGI Global.
Cite As
Chokkappagari R. (2024) Securing Your Data: Best Practices for Cloud Storage Security, Insights2Techinfo, pp.1