By: Vanna karthik; Vel Tech University, Chennai, India
Abstract
Organizations now depend on cybersecurity automation to build advanced defensive measures alongside minimizing human mistakes that emerge during cyberattacks evolution. Security operations become more vulnerable because humans working within them experience both exhaustion-related mistakes and informational gaps alongside unskilled staff. The technological improvement of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) enables essential risk management solutions which combat these security risks. The paper undertakes an analysis of cybersecurity automation systems alongside their advantages along with barriers and forthcoming developments specifically for human error prevention and superior security defense. Companies that adopt automation technologies will build better abilities to detect threats as well as respond faster while reducing potential impacts.
Introduction
The sophistication of cyber threats today focuses on specific organizations by continuing their persistent attacks. Human mistakes are responsible for most security incidents that occur because of both technical errors and poor password management and inadequate security response times[1]. The surge of cybersecurity automation depends on artificial intelligence to build modern tools which stop and handle security attacks immediately. The transition to automated systems guarantees both better security quality and more efficient threat response through elimination of human-based errors. Organizations have improved their threat minimization abilities through automated security solutions which gained strength thanks to rapid AI and ML innovation.
The Role of Cybersecurity Automation
1. Threat Detection and Response
Security applications with artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) check extensive data quantities to detect recurring patterns that show threat indicators[2]. Even though traditional security operations center (SOC) teams typically face challenges from manual processing of large data volumes which causes delayed alert detection. Through automated threat detection systems organizations can detect attacks at once which decreases the chance of breaches occurring.
2. Incident Response and Remediation
With incident response automation tools, threats get contained and mitigated at rapidly increasing speed. The automated response mechanism enables the isolation of compromised devices by blocking malicious IP addresses through programmed security patch implementations[3]. Continuous protection results from the damage-reduction possibilities of this approach.
3. Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Strict authentication rules combined with abnormal access detection come from automation solutions that improve IAM functions. Risks of unauthorized access get prevented through biometric authentication together with risk-based adaptive authentication and behavioral analysis[4].
4. Compliance and Risk Management
Organizations require industry obedience to GDPR and HIPAA regulations in combination with ISO 27001 standards[5]. The monitoring of network activities with automatic log generation capabilities through cybersecurity automation produces audit reports which minimize human mistakes during regulatory compliance.
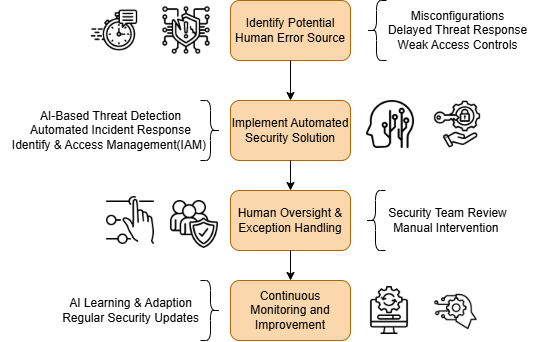
Fig : Reducing Human Errors in Cybersecurity Automation
Benefits of Cybersecurity Automation[3]
1. Reduced Human Error
Automation detects older errors because cybersecurity experts tend to perform incorrectly or show a lag in threat reactions. Through automation security professionals can handle basic tasks so they dedicate their attention to advanced security issues.
2. Improved Efficiency and Speed
Continuous automated security systems detect all threats instantly through real-time operation. The quick reaction time achieved by automation stops dangerous attacks before they can become more serious and produce losses.
3. Cost-Effectiveness
The elevated expenses for cybersecurity automation at first lead to financial savings because it decreases security incidents and regulatory fines and eliminates time-consuming manual labor.
4. Enhanced Threat Intelligence
The artificial intelligence systems of automation acquired new threat information to develop better protection strategies which improve security effectiveness. By taking this forward-thinking approach organizations maintain their lead position over cybercriminals.
Challenges in Cybersecurity Automation
1. High Initial Costs and Complexity
To begin automation organizations must make substantial technological investments and buy infrastructure components with an additional requirement to hire qualified personnel. All organizations need to achieve frictionless connectivity between their security infrastructure.
2. False Positives and Over-Reliance
The automated systems occasionally produce incorrect positive results which results in unwarranted interruptions of systems. A systems failure can occur when organizations place too much trust in automation since human oversight is absent because complex cyberattacks may circumvent automated defenses.
3. Evolving Cyber Threats
The security advantages achieved through automation do not fool cybercrime specialists who develop sophisticated new attack methods with help from AI. Businesses need to maintain regular enhancements of their automated security systems when combatting developing security threats.
Prospects of Automation of Cybersecurity in the Future
As AI, ML, and behavior analytics evolve, detection and response capabilities for threats will become stronger. Cybersecurity automation has a rosy future. AI-driven threat intelligence, network healing automatically, and automated security platforms will all be combined to improve cyber resilience and minimize human errors even more. To make sure there are effective security defense systems, organizations must embrace automation but also maintain harmony between human intelligence and machine capability.
Conclusion
Cybersecurity automation is revolutionizing threat management through efficiency and reduction in human error. There are some issues, but automation is an important part of current cybersecurity measures since it has advantages in the identification of threats, incident response, IAM, and compliance. Automation must be leveraged by organizations to stay ahead of cyber threats and proper ly safeguard their digital assets as technology evolves. Businesses are able to notably minimize exposures as well as reinforce overall resilience through ongoing improvements on automated security tools. Cybersecurity automation, the pillar of online defense, will ensure the businesses remain watchful amid constantly changing threat spaces.
References
- R. P. Griffin, U. Tatar, and B. Yankson, ICCWS 2022 17th International Conference on Cyber Warfare and Security. Academic Conferences and Publishing Limited, 2022.
- A. Yaseen, “AI-DRIVEN THREAT DETECTION AND RESPONSE: A PARADIGM SHIFT IN CYBERSECURITY,” Int. J. Inf. Cybersecurity, vol. 7, no. 12, Art. no. 12, Dec. 2023, Accessed: Feb. 20, 2025. [Online]. Available: https://publications.dlpress.org/index.php/ijic/article/view/73
- J. K. Manda, “Cybersecurity Automation in Telecom: Implementing Automation Tools and Technologies to Enhance Cybersecurity Incident Response and Threat Detection in Telecom Operations,” Adv. Comput. Sci., vol. 4, no. 1, Art. no. 1, Jul. 2021, Accessed: Feb. 20, 2025. [Online]. Available: https://acadexpinnara.com/index.php/acs/article/view/370
- Researcher, “SECURING DIGITAL IDENTITY: THE CONVERGENCE OF CYBERSECURITY AND IAM IN CONTEMPORARY ORGANIZATIONS,” Dec. 2024, doi: 10.5281/ZENODO.14504231.
- “ISO/IEC 27001:2022,” ISO. Accessed: Feb. 20, 2025. [Online]. Available: https://www.iso.org/standard/27001
- Widodo, A. M., Wisnujati, A., Prasetyo, E., & Rahaman, M. (2024). Active-Reconfigurable intelligent surfaces for unmanned aerial vehicles. In Advances in computational intelligence and robotics book series (pp. 187–230). https://doi.org/10.4018/979-8-3693-2707-4.ch009
- Rahaman, M., Lin, C., Pappachan, P., Gupta, B. B., & Hsu, C. (2024). Privacy-Centric AI and IoT solutions for smart rural farm monitoring and control. Sensors, 24(13), 4157.
- Deveci, M., Pamucar, D., Gokasar, I., Köppen, M., Gupta, B. B., & Daim, T. (2023). Evaluation of Metaverse traffic safety implementations using fuzzy Einstein based logarithmic methodology of additive weights and TOPSIS method. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 194, 122681.
- Li, S., Gao, L., Han, C., Gupta, B., Alhalabi, W., & Almakdi, S. (2023). Exploring the effect of digital transformation on Firms’ innovation performance. Journal of Innovation & Knowledge, 8(1), 100317.
- Neelapareddigari P (2024) Reinforcement Learning for Cybersecurity, Insights2Techinfo, pp.1
Cite As
Karthik V. (2025) The Rise of Cybersecurity Automation : Reducing Human Errors, Insights2techinfo pp.1