By: Dadapeer Agraharam Shaik, Department of Computer Science and Technology, Student of Computer Science and technology, Madanapalle Institute of Technology and Science, Angallu,517325, Andhra Pradesh.
Abstract: In the current digital world, cybersecurity has become one of the crucial issues affecting everyone and organizations included. They however are not as effective against the new generation of threats that are faced in the cyber space. .This article discusses on how AI is being implemented on cyber security, which includes threat detection for enhanced security, automation of security procedures, and analytical capabilities. AI implementation in cybersecurity not only improves security solutions and processes but also learn about the new forms of threats and evolves to counter them. Despite the barriers like data privacy, adversarial attacks, and the difficulties in finding individuals with advanced AI skills, AI can indeed transform the world of cybersecurity. This paper focuses on the use of AI in various areas of cybersecurity, reviews the advantages and explores the potential of AI-based security services.
Keywords: Artificial Intelligence , Cyber Security , Cyberthreats.
1.Introduction
As the number and accessibility of connected devices continue to grow with the IoT, rising threats of cyber-attacks, the importance of artificial intelligence in cybersecurity and protection has never been more important. Here, the author looks at the different forms of cyber-attacks and their changing characteristics and explains how AI can be used for countering these threats. Gender roles have also been used to map and forecast these risks. In addition, the applied predictive modelling of the cyber-attacks, prediction, and machine learning algorithms for preventing outbreaks of infectious diseases and cyber-attacks are discussed. However, amidst AI-driven concerns of cybersecurity, it is possible to acknowledge the presence of the need for its focus. There are some differences and problems with AI including limitations to the privacy of data and the increase in scalability and human-machine collaboration. In summary, the article magnifies those that are new and focuses on the new wave of cyber-attacks and new methods to defend them, with a preventive approach of employing artificial intelligence models to forecast and counter cyber incidences [1].
2. CYBERSECURITY DATA FROM INDUSTRY
As stated earlier in the year 2018, the firm of Symantec informed of a 600 percent rise in assaults on IoT/Edge devices, together with a 29% increase. The simple reason being that the threat actors are ramping up their attacks on industrial control systems (ICS). These attacks place the Edge in the middle of a cybersecurity challenge that is complex, with threats against a set of highly desirable assets. Wise managerial personalities across business corporations and organizations should develop strategies that enable their defense before any such instances are mentioned in the media, to protect their critical assets .
And, finally, the facts:
- It identified that 35 percent of attacks are fileless, meaning that antivirus software cannot detect them.
- Using this data, it is found that 40% of industrial sites have at least one connection with the internet.
- It showed that 49% of significantly attacked firms were able to successfully defend within 1 year; however, the same or other attackers can strike again.
- Thus, now 84% of industrial sites have at least one remotely accessible device [2].
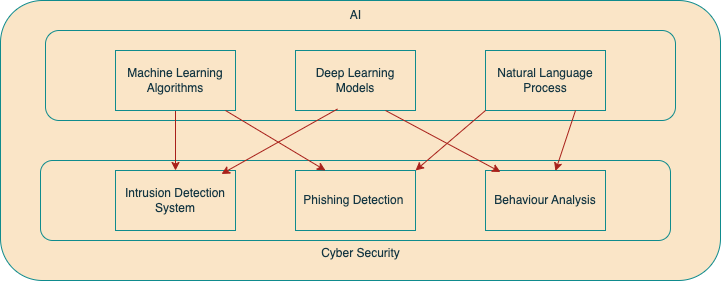
3.Artificial Intelligence Approaches for Enhancing Cybersecurity
Information technology is one of the areas of great interest today and thus, crimes against the same can be easily perpetrated. Through computers and other gadgets that are becoming more accessible to the general public, combined with high-quality merchandise it is becoming increasingly easy to launch an attack from any part of the globe and often the act cannot be traced back to the perpetrator. Cybercrime is the criminal use of computers, digital technology and the internet to commit felonies with an aim of embezzling funds, intruding into user’s privacy, creating and distributing fake identity, and targeted crime in which organized crime extorts money, steal intellectual property, launder money and spy for economic gain. Tackling these kind of attacks using traditional security measures is almost impossible or, even if they are detected, the attacks are launched way before the measures do their stuff.
AI is general in the cybersecurity industry, and it has made the difference. Currently, stakeholders in organizations, as well as researchers, work on the development of ideas that can combine AI with security effectively. AI is an approach whose ultimate goal is to increase the level of intelligence in machines so that they are capable of reproducing human behavior as seen in learning, planning, reasoning and solving of problems among others[3].
AI characteristics include:
- For the cognitive dimension, deduction, reasoning and problem solving will be used as the major strategies of teaching of Inferential comprehension.
- About neural networks and statistical models
- Knowledge representation
Both the explanation of the planning process and the formulation of the four guidelines of agent cooperation stress the word ‘multi,’ meaning multiple.
- Machine learning
- Natural language processing
- Motion and manipulation
- Perception
- Social intelligence
- Creativity
- General intelligence
AI works in three ways: AI works in three ways:
1. Assisted Intelligence: Makes current tasks better.
2. Augmented Intelligence: Can be useful with tasks that could posing a problem to human beings.
3. Autonomous Intelligence: Performs the relevant actions based on machine learning.
In this research, it unveiled how AI can complement current structures, and manage challenges such as the increasing attack of cybercrimes [4].
4. Cybersecurity Threats and Traditional Security Measures
Indeed, within the past ten years or so, several forms of cyber threats have presented themselves. Here are the top 10 cyberthreats we face today: Here are the top 10 cyberthreats we face today:
- Denial of Service (DoS) Attacks: These attacks flood a system’s resources with a large number of requests thus most often difficult to identify since the attacker tools are readily available and with the emergence of Cybercrime as a Service (CCaaS). This is true solely because DDoS attacks involve the participation of several attacker machines.
- Man-in-The-Middle(MITM) Attacks: These attacks got in the middle of the conversation between two parties and pretend to be the sender of wanted messages. Some of the variants are the IP address spoofing and message replay attacks.
- Phishing and Spear-Phishing Attacks: Phishing is a practice of sending emails that seem to originate from reputable sources with an intention of the user to release individual details. Spear-phishing is a well-planned form of the attack that is executed with the help of well-researched information to seem genuine[5].
- Drive-by Attacks: Criminals inject a malware script into the said site; therefore, any visitor is at risk of getting infected by the said program.
- Password Attacks: these attacks include shoulder surfing, brute force, and other advanced intelligent methods to guess the passwords.
- Structured Query Language (SQL) Injection Attacks: Attackers than take advantage of the flaws in the SQL and inserts code into input fields to allow them to load up the stored content from backend servers.
- Cross-site Scripting Attacks: Penetrating other servers, specially webservers, which loads a virus on the visitor’s computer when he visits the specified website, which results in data theft and complete control over the victim’s machine.
- Eavesdropping Attacks: Intercepting the network data transmission channels to get or modify some information as well. It can be also used to gather information without any interference or to obtain the status of a client in order to send fake messages.
All these threats call for increased protection of important information and systems to deter and prevent intrusions from the evil-doers.[6-9]
Conclusion:
In summary, it can be said that application of artificial intelligence in cybersecurity can be named as breakthrough in struggle with cyber criminals. And as time passes by, the dimension of a virtual world advances equally; in fact, most of the time conventional security measures are insufficient to put a halt or eliminate current threats. First of all, it is essential to mention that AI enhances the chances of detecting, fighting, and preventing the usage of cyber threats due to characteristics, such as learning, reasoning, and making decisions. It also suggests coverage of all the risks from assisted, augmented, and autonomous intelligence including cyber robbery and hacking, blackmailing, and economic spying. This means that the introduction and an on-going process of implementing and integrating of Artificial Intelligence based security products remains vital in the surge for secure protection of sensitive data and the overall sanctity of computerized networks. Since many organizations and researchers go ahead in creating the AI system, the incorporation of the AI system in the cybersecurity system will be very vital in ensuring that the digital world is safe and secure.
References:
- K. Meduri, G. Nadella, and H. Gonaygunta, “Enhancing Cybersecurity with Artificial Intelligence: Predictive Techniques and Challenges in the Age of IoT,” Int. J. Sci. Eng. Appl., vol. 13, pp. 30–33, Mar. 2024, doi: 10.7753/IJSEA1304.1007.
- L. Lazic, BENEFIT FROM AI IN CYBERSECURITY. 2019.
- M. Rahaman, C.-Y. Lin, P. Pappachan, B. B. Gupta, and C.-H. Hsu, “Privacy-Centric AI and IoT Solutions for Smart Rural Farm Monitoring and Control,” Sensors, vol. 24, no. 13, Art. no. 13, Jan. 2024, doi: 10.3390/s24134157.
- A. Anandita Iyer and K. S. Umadevi, “Role of AI and Its Impact on the Development of Cyber Security Applications,” in Artificial Intelligence and Cyber Security in Industry 4.0, V. Sarveshwaran, J. I.-Z. Chen, and D. Pelusi, Eds., Singapore: Springer Nature, 2023, pp. 23–46. doi: 10.1007/978-981-99-2115-7_2.
- B. D. Alfia, A. Asroni, S. Riyadi, and M. Rahaman, “Development of Desktop-Based Employee Payroll: A Case Study on PT. Bio Pilar Utama,” Emerg. Inf. Sci. Technol., vol. 4, no. 2, Art. no. 2, Dec. 2023, doi: 10.18196/eist.v4i2.20732.
- S. Zeadally, E. Adi, Z. Baig, and I. A. Khan, “Harnessing Artificial Intelligence Capabilities to Improve Cybersecurity,” IEEE Access, vol. 8, pp. 23817–23837, 2020, doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2968045.
- Chui, K. T. (2023, November). A Lightweight Generative Adversarial Network for Imbalanced Malware Image Classification. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Information Management & Machine Intelligence (pp. 1-4).
- Chui, K. T., et al. (2023). A survey of internet of things and cyber-physical systems: standards, algorithms, applications, security, challenges, and future directions. Information, 14(7), 388.
- Sharma, A., et al. (2021, September). Multi-dimensional hybrid Bayesian belief network based approach for apt malware detection in various systems. In International Conference on Cyber Security, Privacy and Networking (pp. 177-190). Cham: Springer International Publishing.
Cite As
Shaik D.A. (2024) The Role of AI in Enhancing Cybersecurity Measures, Insights2Techinfo, pp.1