By: Praneetha Neelapareddigari, Department of Computer Science & Engineering, Student of Computer Science & Engineering, Madanapalle Institute of Technology and Science, Angallu (517325), Andhra Pradesh. praneetha867reddy@gmail.com
Abstract
AI is being used effectively in cybersecurity since it improves the capability of identifying, blocking and handling of threats in the system. Now-a-days the cyberattacks are in the stage of more advanced and it’s a frequent concept that is growing though and there is a requirement of more robust and adaptive security solutions. The main aim of this research is to address the heterogeneous roles of AI involved in cybersecurity, expounding its applications like threat detection, vulnerabilities, phishing. The traditional methods that is used for defence strategies will not be able to solve the present increasing cyberattacks as the growth of the cyber threats is so frequent. This paper addresses that how Artificial Intelligence is useful in many concepts of cybersecurity.
Keywords: Artificial Intelligence, Cybersecurity, Machine Learning, Threat Detection, Predictive Analytics
Introduction
This has amplified the variation in the ratio of people in proportion to computer and internet use in people’s everyday life thus widening and diversifying threats in the cyber domain. This implies that artificial intelligence (AI) is a good ally and cybersecurity’s equipment. AI is changing the approach taken towards the security of our computerized structures by contributing highly effective devices for identification, analysis, and counteraction of threats[1]. Due to its capabilities to work with big data and build patterns, AI improves the capacity to identify and prevent malign actions. All in all, with the changes in threats in the cyberspace, the use of AI in the field of cybersecurity is not only advantageous, but rather crucial, as it provides an anticipatory as well as promising approach to the possible attacks.
AI has the power to make cybersecurity to be less complicated by implementing its concepts and also enables the businesses to be safe and remain ahead of thieves. AI is assisting in a new era of digital security where there is a need of safeguarding the sensitive data and systems is not just a reactive but also proactive strategy, additionally it improves the speed and accuracy of attack response. This article explores how an AI will shape the cybersecurity in future and discover how it will make navigating the digital world later on. This introduction focuses on the context highlighting the importance of AI implementation in cybersecurity that constructs the safer digital world.
1. Basic Definitions and concepts
Artificial Intelligence: Sometimes it’s about the statement “AI is similar to the human” but AI represents the human intelligence, that has the power to think out of the box. When we compare human thinking and the clear solutions of the AI , the position level of thinking in AI will have the enough standards for solving certain queries with minimum amount of time[2]. AI is a chapter of many important implementations like one of them is Machine Learning, which is a branch that contains various number of algorithms which are used in every sector as there are more number of algorithms that help systems to make decisions or predictions which is depends on the data. ML covers several techniques such as supervised learning where models are trained using labelled data and unsupervised learning where models look for patterns in the data without labels, and reinforcement learning where systems learns through feedback from its surround environment[3].
Cyber Security: Cyber security therefore entails shielding against threats on the internet for instance, ransomware, phishing scams, malware and any other disturbing activities that exploit flaws in computers together with their networks[4]. This protection encompasses many subjects such as information protection, which is the protection of data confidentiality and privacy, network security which tackles the prevention of unauthorized access to internal as well as external networks and application security which attempts to avoid weaknesses in software and applications. There are many encompassed specialized areas in cyber security such as network security, information security, application security, cloud security, data security and the main objective of all these areas is to protect data from attacks.
2. Complexities of Cybersecurity Environment
The modern cybersecurity threat scape presents various challenges due to the ever-growing threat volume, development in technology, and expansion in the integration of the systems linkages. Indeed, cyber threats are on the rise and the threats include zero-day exploits, ransomware, and phishing, among others, which can be executed through social engineering efforts to penetrate the organizational systems and data. Furthermore, it is implied that due to the IoT and growth of cloud usage, it became even more difficult to protect all the access points and data transfer.
2.1 Types of Cyberattacks
Cyberattacks can led in various ways, each of the attack do have different methods and techniques of operation.
- Malware
- Phishing
- Ransomware
3. The Historical Background of AI in Cybersecurity
If we see the historical background of AI in cybersecurity, there has been a considerable changes and evolution in integrating the concept of AI with cybersecurity.
3.1 Early stages of AI in Cybersecurity
Over time, the applications of AI in the concept of cybersecurity has grown considerably.
1950’s – 1960’s: In early 1950’s, the idea of artificial intelligence started to take shape. Early research mostly concentrated on rule-based systems and symbolic AI. The cybersecurity started when the need to protect computers from illegal access surfaced while usage of computers became increasingly common.
1970’s: In 1970’s researchers began looking for the ways to identify unapproved access to computer systems. As a result, the first intrusion Detection System (IDS) were created. James Anderson created one of the first intrusion detection system (IDS) in 1980. It used a set of criteria to examine user behaviour and system records in order to find any security breaches.
1980s: In this era, artificial intelligence algorithms were created to simulate human experts for decision-making processes which became more popular in 1980’s. All the cybersecurity systems identified the possible security threats and took required response based on specific rules[5].
1990’s: In 1990s, the neural network research for cybersecurity anomaly detection began. This concept was first used by researchers to know the typical system behaviour and to identify the anomalies that might point to malevolent activity. In this stage, the concept of intrusion detection systems (IDS) was introduced and also pattern recognition methods were implemented to identify the threats.
3.2 Evolution of AI in Cybersecurity
The reason for today’s more sophisticated AI- driven cybersecurity solutions was established by early stages of efforts in the concept of cybersecurity and artificial intelligence. AI’s efforts and efficacy in identifying and reducing cyberthreats have increased along with processing power and data availability[6]. AI has become an essential aspect of contemporary cybersecurity strategies because of the enhancement of the ability to detect intricate attacks, data processing, and response automation. Specific approaches that come under this category are the machine learning approaches, deep learning approaches, and natural language processing.
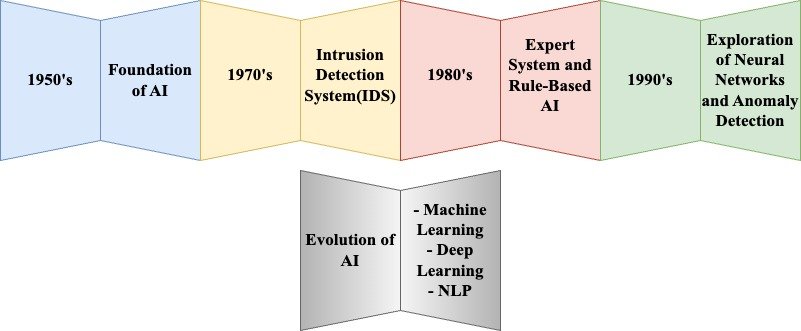
Figure : Key Points of AI in Cyber Security (Early Days) & Modern Concepts Implementation
4. Role of AI in Cybersecurity
The role of AI in cybersecurity plays an important task and is most actively used by companies. The capacity to analyse both structured and unstructured data such as statistics and natural language reduces the time and costs as well as securing data[7]. Artificial intelligence (AI) systems, especially those that use machine learning, are capable of quickly analysing enormous volumes of data and spotting trends and anomalies that can point to hostile activity[8]. With the help of this capacity, risks that conventional security procedures could overlook, such advanced persistent threats (APTs) and zero-day vulnerabilities, can be quickly identified. Routine security chores like network traffic monitoring, log analysis, and protocol updates can be automated by AI-driven systems, which lessens the burden on human security teams and lowers the possibility of human error[9]. One of the most important tasks of AI is to predict the future attacks based on the already existing data, allowing enterprises to actively bolster their defences. AI implements contribution to a cybersecurity system which makes it more responsive and resilient by constantly adapting to new threats.
4.1 Methods used by AI In Cyber Security
AI uses many diverse techniques and tools in cybersecurity to improve the detections, response, and recovery. Here are few methods used in order to overcome the cyber issues.
1. Machine Learning: A key component of AI applications for cybersecurity is machine learning. In order to find patterns and generate predictions, it entails training algorithms on huge datasets. Machine learning is applied to cybersecurity in a number of crucial ways. Its main application is in anomaly detection, where it assists in locating anomalous patterns in system performance, network traffic, or user activity that can indicate a possible security risk[3]. Furthermore, machine learning is applied to categorization activities, which facilitate the management and response to threats by differentiating between benign and dangerous files or emails.
2. Deep Learning: Complex data is processed and interpreted by deep learning, a specific subfield of machine learning, which uses multilayer neural networks. Deep learning is also helpful in the critical application of natural language processing (NLP)[10], which is concerned with deciphering and comprehending written materials, using human language. When looking for unusual activity in chat logs or spotting phishing attempts in emails, this is crucial. Through the ability to analyse complicated data more accurately and efficiently, these examples demonstrate how deep learning improves security measures.
3. Natural Language Processing (NLP): Neural network parsing (NLP) is important in several domains of cybersecurity. A critical use case for natural language processing (NLP) is threat intelligence, where it is applied to examine and mine rich data from massive unstructured datasets such as social media, dark web forums, and security reports[10]. In recognizing possible dangers and new trends, this is helpful. Utilizing natural language processing (NLP) to detect phishing attempts is another significant application of NLP. This process involves identifying questionable language patterns in emails or other messages.
Conclusion
Artificial intelligence (AI), plays a very important role that makes the concept of cybersecurity to be more easier and keep safe from cyberattacks from this digital world. The traditional ways that are used for identifying and handling threats in cybersecurity strategies are completely changed by using artificial intelligence (AI). AI technologies that are used mostly such as machine learning, natural language processing, deep learning that provide tools for quick and accurate for identifying possible security threats from huge amount of data. Organizations can remain safe from the threats and many more cyberattacks by using advanced technologies in the concept of AI. Artificial intelligence reduces the workload for human security teams by improving predictive capabilities and security tasks, which really increases the accuracy, efficacy, and efficiency of security measures. So, this concludes that application of AI in cybersecurity is very essential to safe the digital world.
References:
- S. Sharma, “Role of Artificial Intelligence in Cyber Security and Security Framework,” in Artificial Intelligence and Data Mining Approaches in Security Frameworks, John Wiley & Sons, Ltd, 2021, pp. 33–63. doi: 10.1002/9781119760429.ch3.
- P. Pappachan, Sreerakuvandana, and M. Rahaman, “Conceptualising the Role of Intellectual Property and Ethical Behaviour in Artificial Intelligence,” in Handbook of Research on AI and ML for Intelligent Machines and Systems, IGI Global, 2024, pp. 1–26. doi: 10.4018/978-1-6684-9999-3.ch001.
- D. P. F. Möller, “Machine Learning and Deep Learning,” in Guide to Cybersecurity in Digital Transformation: Trends, Methods, Technologies, Applications and Best Practices, D. P. F. Möller, Ed., Cham: Springer Nature Switzerland, 2023, pp. 347–384. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-26845-8_8.
- Q. Atta Ul Haq, “Cyber Crime and Their Restriction Through Laws and Techniques for Protecting Security Issues and Privacy Threats,” in Security Issues and Privacy Threats in Smart Ubiquitous Computing, P. N. Mahalle, G. R. Shinde, N. Dey, and A. E. Hassanien, Eds., Singapore: Springer, 2021, pp. 31–63. doi: 10.1007/978-981-33-4996-4_3.
- J. Srinivas, A. K. Das, and N. Kumar, “Government regulations in cyber security: Framework, standards and recommendations,” Future Gener. Comput. Syst., vol. 92, pp. 178–188, Mar. 2019, doi: 10.1016/j.future.2018.09.063.
- S. Kumar, U. Gupta, A. K. Singh, and A. K. Singh, “Artificial Intelligence: Revolutionizing Cyber Security in the Digital Era,” J. Comput. Mech. Manag., vol. 2, no. 3, Art. no. 3, Aug. 2023, doi: 10.57159/gadl.jcmm.2.3.23064.
- M. Rahaman, C.-Y. Lin, P. Pappachan, B. B. Gupta, and C.-H. Hsu, “Privacy-Centric AI and IoT Solutions for Smart Rural Farm Monitoring and Control,” Sensors, vol. 24, no. 13, Art. no. 13, Jan. 2024, doi: 10.3390/s24134157.
- K. R. Bhatele, H. Shrivastava, and N. Kumari, “The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Cyber Security,” in Countering Cyber Attacks and Preserving the Integrity and Availability of Critical Systems, IGI Global, 2019, pp. 170–192. doi: 10.4018/978-1-5225-8241-0.ch009.
- A. Yaseen, “ACCELERATING THE SOC: ACHIEVE GREATER EFFICIENCY WITH AI-DRIVEN AUTOMATION,” Int. J. Responsible Artif. Intell., vol. 12, no. 1, Art. no. 1, Jan. 2022.
- S. Sharma and T. Arjunan, “Natural Language Processing for Detecting Anomalies and Intrusions in Unstructured Cybersecurity Data,” Int. J. Inf. Cybersecurity, vol. 7, no. 12, Art. no. 12, Dec. 2023.
Cite As
Neelapareddi P (2024) AI in Cybersecurity: Simplifying the Future of Digital Defence, Insights2Techinfo, pp.1