By: Dhanush Reddy Chinthaparthy Reddy, Department of Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence, Madanapalle Institute of Technology and Science, Angallu(517325), Andhra Pradesh
Abstract
The incorporation of AI in a daily approach to defending computers and networks is innovative and has changed the existing cyber security environment by providing better and more enhanced technique in detecting, preventing, and counteracting cyber threats. But with the growing world of internet and cyberspace and the new different types of threats, conventional security solutions are insufficient. This void has been plugged by AI derived implement, which use machine learning, natural language processing and predictive analytics to actively approach cybersecurity. This paper explores AI as a means for everyday cyber defence and how AI does supplement the more traditional threat identification that human analysts otherwise must do. It also reviews its capacity in terms of automating the response to an incident and in minimizing the time between an incident being observed and its being resolved as well as the magnitude of an attack. Moreover, the paper also describes how predictive methodology can be used to prevent the occurrence of threats to an organization in the long run. Nevertheless, the integration of AI to serve in the cyberspace is not without some limitations. There are still many problems that need to be solved such as data privacy, the question of how often an AI can be wrong, and furthermore the issue how an Artificial Intelligence can be used to attack. Last but not the least, the paper gives an idea of future trends in cybersecurity with the help of AI and underlines the necessity of combining human intelligence and artificial intelligence to design a secured and safe environment. The results therefore show how helpful AI is in today’s cyberspace and confirms it as an instrument that must be adopted for the protection of valuable assets in the world that is becoming more and more associated digitally.
Keywords: Artificial Intelligence, Cybersecurity, Defence.
Introduction
Increasingly with change in the face of social media and new technologies the pace, complexity and number of identified cyber threats are on the rise. From simple scams like phishing to ransomware attacks and data breaches, advanced persistent threats (APTs) and more, the threats are much more complicated now. End-point security products present more of a problem because traditional approaches to security are increasingly inadequate given their reliance upon rule-based systems and manual processes, which do not react quickly enough to newer forms of threat. Lately, we have seen the evolution of complex, innovative, and sophisticated threats that have made the call for more intelligent security systems. Thus, Artificial Intelligence (AI) has become one of the main tools to fight against cyber threats as well as a new vector in the sphere of cybersecurity.
Indeed, AI’s characteristics of quickly analysing great volumes of data provide it with several unique competitive strengths regarding threat identification and containment. In contrast to the traditional systems that provision a broad signature database and disclosed attacks, it is possible for AI technologies to detect novel threats because they recognize that which does not resemble the known paradigm. This capability is more important now as the advancement of cyber criminals is alarming issuing polymorphic malware and making use of zero-day expiry. AI systems can program themselves to learn from past incidents and thus become more efficient in analysing the new incidents to reduce the impact of threats that might be unique or more frequent than others.
Among all the ways in which AI contributes to cybersecurity, possibly, the most important one is the automation of the response process. AI can remarkably decrease the time it takes to respond to a cyber threat by immediately responding to threats on in-built response procedures. This immediate response helps to prevent the damage an attack can cause; the longer a threat exists, the more harm it can do. For instance, in the ransomware attack, the AI applications help the company to contain the spread of the virus isolating some parts of the network where the malware affects, thus reducing the damage level in the company. Also, AI could be beneficial in the post-incident investigation process: it is helpful for the security teams to understand the type of the attack and adapt the protection measures.
Another significant domain that belongs to the successful implications of AI is the sphere of predictive analytics. Using past systemic information, using overview activity, and analysing the flow of network traffic it is possible to use AI to predict potential threats and estimate where in the future they might happen. This means that the organizations can move to a more proactive security by preparing for the attacks before they occur than merely defending against the attacks when they occur. This is a proactive change from the typical passive security systems allowing organizations to be proactive and greatly diminish the chances of cyber criminals penetrating a system.
Still, the commencement of the AI utilization in ordinary cyberspace security is not without its difficulties. Modern artificial intelligence systems need immense quantities of data to operate efficiently; people worry about the protection of their information and about misusing collected data. Further on, there is always the issue of false positives, which means that normal processes and actions are considered dangerous and may thus be halted. Also, as AI applies to cybersecurity even more in the future, there is a risk of ‘AI-aided’ attacks, in which cyber attackers themselves use AI to penetrate cybersecurity systems. These pose challenges thereby the importance of proper and justified applications of AI in Cybersecurity to avoid misuse of AI in the online platform.[1]
AI-Driven Threat Detection
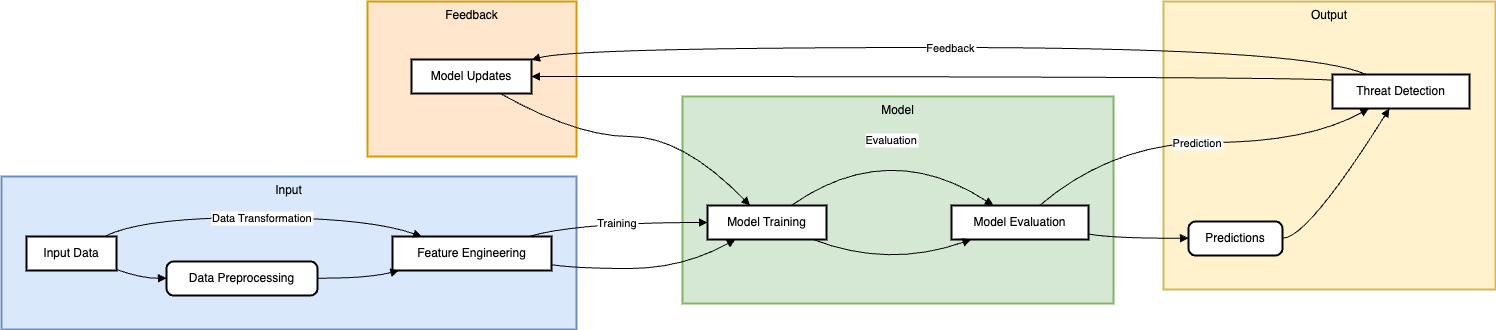
Threat detection has proven to be a vital aspect of cybersecurity and with the use of AI it has been reform established as a fluid process[2]. These more conventional approaches to threat detection have issues with basic or signature-based rules because the threats evolve much faster. On the other hand, AI-based systems employ machine learning algorithms, as well as, large sets of data such as network traffic, users’ activity and the history of cyber-attacks to learn patterns that signify a possible intrusion. Such systems are capable of learning from new data and improving their capacity to identify the sorts of activities that are suspicious[3]. This capability is useful especially in detection of new threats that security specialists are not aware of, but attackers are fully aware of since they are new to the market. When it is applied for analysing patterns, it can detect deviations from the norm and identify threats in real time, which helps to respond to new cyber threats faster. The set detection approach is a step higher than the typical detection methods used today and significantly minimizes the chances of an attacker getting through hence making AI a key tool that cannot be overlooked in the current world.
Automated Response Mechanisms
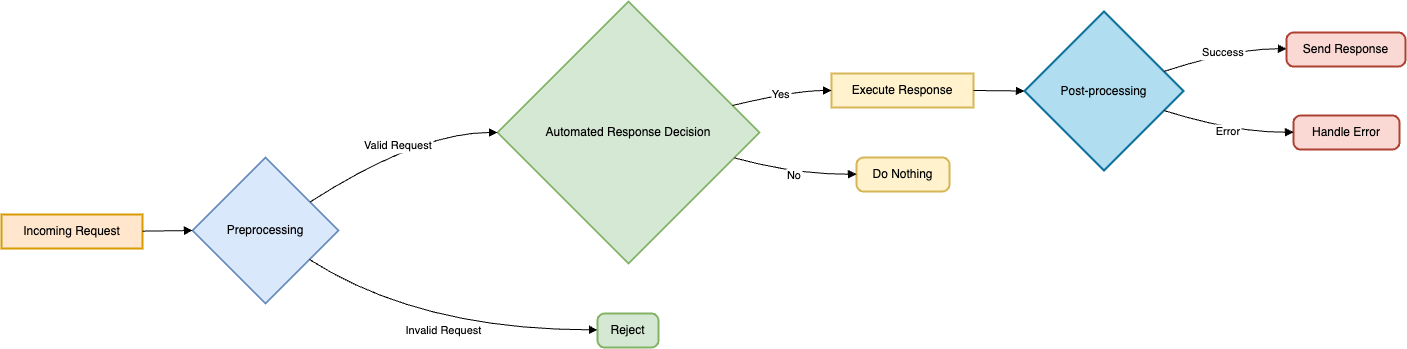
Even when a threat is identified, it only takes a few hours or even minutes to escalate the attack into a much larger issue. Cyber defence is an area where employment of AI is most effective to provide substantial time efficiencies in tackling the threats on operations. AI can also immediately deliver specified patterns when a threat is detected because of computerize reflexive tactics that have been set in advance. Such rapid response is critical for containing malware outbreaks or stopping data leakage or quarantining affected hosts[4].
For instance, where ransomware has been injected into the network, AI can recognize the dishonourable encryption activity, and trigger a reaction that would involve the severance of affected assets, interception of the attacker’s command and control servers, and notify the security team members. This not only prevents the spread of the effect but also frees human responders to other tasks such as the cause-and-effect analysis and mitigation[5]. The application of AI in managing incidents ensures the best strategic defence such that minor attacks are prevented from escalating, hence no interruption and least cost is incurred.
Predictive Analytics and Proactive Security
Based on the use of superior technologies such as artificial intelligence, predictive analytics is fast becoming the future of cybersecurity owing to its capability of preparing organizations for an attack even before it happens. Promisingly, AI can learn from the past data and patterns and detect signs of early-stage cyberattacks – suspicious logins, increased traffic or users’ behaviours. This helps security teams to act pre-emptively and ensure that they fix a vulnerability; improve monitoring or change an already existing policy that can help in minimizing an attack before it occurs[6].
We now have the capacity to anticipate where and how the future danger will evolve – a dramatic leap from the conventional methods of having to respond to threats. [7]It is different from waiting for an emergence of an attack and then formulating how to go about it due to it gives power to organization to be one step ahead of an attacker. The foresight of anticipating a threat also fortifies an organisation’s general security stance as it means that those potential security breaches can be fixed before they are utilised as a tool by an attacker.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
Of course, there are advantages of applying AI in cybersecurity, but there are problems with its application. A major fear are false positives, that is the cases when legitimate activity is recognized as negative. This could occasionally cause unwanted disturbances affecting security and a waste of security resources as it takes time to attend to such alarms even as they turn out to be false. To counter this, AI systems should be updated and trained again and again using different kinds of data to maximise efficiency and to eliminate false positive alerts.
Another important problem is the relation between AI and such ethical issues as data protection for cybersecurity. AI depends on data and therefore there is a question mark over how this data is acquired, processed, and managed. AI implementing cybersecurity must follow the GDPR and other data protection laws to retain user trust and avoid legal repercussions.
Furthermore, the use of AI is not exactly safe from the threats as with its increased integration into cybersecurity there can occur AI cyberattacks meaning that criminals could also upgrade the AI algorithms to outdo the securities. This highlights the roll of having a middle ground between fully AI implementation and the incorporation of human analytical input into the AI systems as well as ongoing supervision of the systems.
Case Studies: Artificial Intelligence in Cyberspace Security
With a view of showing how implementations of AI are evident in daily cyberspace protection, various examples showcasing how organizations from various fields have employed AI in implementing their cybersecurity measures are presented below. In the financial sector, for instance, AI is applied in the identification and elimination of fraudulent trade in a real-time mode for the benefit of the financial organization and its clients. AI is being adopted in this context by healthcare organizations so as to protect data from hackers and thus maintain security of patients’ data. Moreover, AI is being used in a significant way to safeguard important assets like energy and transport systems from cyber threats that, in the worst-case scenarios, can affect large populations.
Conclusion
The incorporation of AI in normal cyberspace protection is a milestone in combating cyber incidences. One of the biggest benefits of using AI in cybersecurity is that it can supplement people in the tasks in which they are most valuable; identifying threats, developing methods to respond to them, and to prevent them in the first place. But like any other technology, use of AI in cybersecurity has its own drawbacks, which if well managed, can enhance the safety of an organization.
As threats to the cyberspace persist, the use of AI in cybersecurity is set to enhanced as threats advances. The organizations that develop the ways of integrating the AI-based security solutions in practice, and at the same time, pay attention to the threats and the ethical issues, will be able to prevent the threats and cyberattacks and to have a stronger position in cybersecurity. The future of cybersecurity engages artificial intelligence in a combination with human practice so that we make more effective protections against new and unknown risks.
References
- M. Rahaman, C.-Y. Lin, and M. Moslehpour, “SAPD: Secure Authentication Protocol Development for Smart Healthcare Management Using IoT,” Oct. 2023, pp. 1014–1018. doi: 10.1109/GCCE59613.2023.10315475.
- D. V. V. Vegesna, “Enhancing Cyber Resilience by Integrating AI-Driven Threat Detection and Mitigation Strategies,” Trans. Latest Trends Artif. Intell., vol. 4, no. 4, Dec. 2023, Accessed: Aug. 13, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://ijsdcs.com/index.php/TLAI/article/view/396
- A. Yaseen, “AI-DRIVEN THREAT DETECTION AND RESPONSE: A PARADIGM SHIFT IN CYBERSECURITY Asad Yaseen,” Dec. 2023.
- T. Toth and C. Kruegel, “Evaluating the impact of automated intrusion response mechanisms,” in 18th Annual Computer Security Applications Conference, 2002. Proceedings., Dec. 2002, pp. 301–310. doi: 10.1109/CSAC.2002.1176302.
- V. Mateos, V. A. Villagrá, F. Romero, and J. Berrocal, “Definition of response metrics for an ontology-based Automated Intrusion Response Systems,” Comput. Electr. Eng., vol. 38, no. 5, pp. 1102–1114, Sep. 2012, doi: 10.1016/j.compeleceng.2012.06.001.
- M. Danish, “Enhancing Cyber Security through Predictive Analytics: Real-Time Threat Detection and Response,” Jul. 15, 2024, arXiv: arXiv:2407.10864. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2407.10864.
- C.-Y. Lin, M. Rahaman, M. Moslehpour, S. Chattopadhyay, and V. Arya, “Web Semantic-Based MOOP Algorithm for Facilitating Allocation Problems in the Supply Chain Domain,” Int J Semant Web Inf Syst, vol. 19, no. 1, pp. 1–23, Sep. 2023, doi: 10.4018/IJSWIS.330250.
- Gupta, B. B., Gaurav, A., & Panigrahi, P. K. (2023). Analysis of retail sector research evolution and trends during COVID-19. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 194, 122671.
- Aldweesh, A., Alauthman, M., Al Khaldy, M., Ishtaiwi, A., Al-Qerem, A., Almoman, A., & Gupta, B. B. (2023). The meta-fusion: A cloud-integrated study on blockchain technology enabling secure and efficient virtual worlds. International Journal of Cloud Applications and Computing (IJCAC), 13(1), 1-24.
Cite As
Reddy D.R.C. (2024) AI in Everyday Cyber Defence, Insights2Techinfo, pp.1