By: Dadapeer Agraharam Shaik, Department of Computer Science and Technology, Student of Computer Science and technology, Madanapalle Institute of Technology and Science, Angallu,517325, Andhra Pradesh.
Abstract:
Major pieces of infrastructure include electricity and gas supplies, transportation networks, and telecommunication networks, which are the backbone of today’s societies. These systems are becoming more integrated and as a result prone to cyber risks hence the need to enhance security measures. Toplined Since the cyber threat is real and constantly increasing Artificial Intelligence (AI) provides powerful solutions to improve the security of the critical infrastructure increases in real-time the detection, prevention, and response to cyber threats. This article discusses the opportunities, risks, and potential future developments of using AI for protecting the infrastructure facilities.
Keywords: AI, Cyber Security, Infrastructure Protection, Threats, ML, Real-Time Alerts, Anomaly Identification, Prognosis.
1.Introduction:
The dependency on critical infrastructure is quintessential to the functionality of societies meaning that it interfaces with sectors like energy, water provision, transportation, and communication. Through the use of these technologies, such structures have been integrated hence improving on their performance and versatility. But on the same note, the interactions that exist between entities in these networks expose them to a higher risk of being attacked by cyber criminals. As<|reserved_special_token_279|> the case with other forms of attacks, cyber-attacks on critical infrastructure can lead to massive economic losses, disruptions of vital services, and threats to national security.
Machine learning has proved to be very relevant in addressing cyber threats and modern security solutions are based in part on this element of AI. The primary value that AI brings to the protection of critical infrastructure is the capacity for large-scale data analysis, performance of pattern recognition and the capacity to predict future security threats. This paper focuses on the application of AI in defending key infrastructures against cyber-attacks; the article investigates the pros, cons and the future of AI in countering cyber threats.
2.Background and significance of AI in Cybersecurity
Given the nature of the threat that IT driven communities face constantly from the red team and other cyber criminals, there is no room for complacency in the field of cybersecurity. Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a powerful tool that has appeared to be very effective in improving the security level and minimizing cyber threats. AI in cybersecurity is the usage of artificial intelligence technologies in order to ensure security within computers and networks and fighting cyber criminals. This is crucial because it can assist in improving the means for detection, prevention, and handling of threats that are in the cyberspace domain coupled with the limitations that come with human activity in traditional forms of security[1].
AI in cybersecurity also has vast advantages. It can study large and complicated structures of data concerning activities and practices to point out patterns, irregularities, and weaknesses that would point towards unpleasant practices or possible threats. AI can work through prior data and experience for new and potential threats, and can also come up with preventive and prescient solutions. Cubing monotonous and time-consuming work of system monitoring, malware filtering, incident documentation, and other similar jobs, AI can release human efforts for more critical and imaginative roles. Thus, AI improves the effectiveness, productivity, and velocity of security measures and minimizes the losses and the time taken to handle the security incidences.
While the AI in cybersecurity not a really novel idea, it has became more relevant and researched in the recently because of a variety of reasons including enhancement in the forms and degree of cyber threats, the continuously excrescence of data and devices that require security. The other related technologies are also seen to impact AI in cybersecurity with the prospects of new emerging technologies like cloud computing, blockchain, IoT, and 5G impacting AI security. Thus, the application of the AI in the sphere of cybersecurity is a groundbreaking and promising area that needs to be regularly developed and studied based on the cooperation of several subjects, including the government, companies, scientific institutions, and non-governmental organizations.
The first key milestones of AI in cybersecurity include anomaly detection, intrusion prevention system, which belong to the 1990s and 2000s categories. New in the 2010s, machine learning algorithm added more features to the AI cybersecurity solutions as far as identification, analysis and prognosis of threats are concerned. When progress in deep learning started from the 2020s, the capabilities of AI have been advanced to understand even more specific structures in the techniques of cyber threats and patterning of attacks, including capability in detecting zero-day attack with latent patterns[2].
AI systems process large sets of data from various sources, which helps constructively predict threats, even if they are still incipient. AI systems can help with the fast response to the incident concerning the containment or the rectification of the problem, or the restoration of the service. Artificial intelligence also uses the past data and the current trends in making likely predictions of cyber attacks, facilitate decision making and management of resources on how best to prevent future attacks. However, it is also possible to make AI systems adapt security solutions according to the particular conditions and threats, increasing its suitability and productivity. AI can contribute to solving the problem of the shortage of IT staff with cybersecurity skills by automating processes and supporting people’s work [3].
3.AI and cybersecurity of critical infrastructure
AI makes the negative impact of the attackers even stronger in terms of the modification of the informational sphere in society since AI technologies are typically for good as well as evil. For instance, face-recognition, and general generation capabilities for synthetic pictures and audios, or for tampering with these images and sounds are applicable to compromise the political processes. Recently, the literature on cybersecurity has turned its attention to the cyber vulnerabilities emerging from: Recently, the literature on cybersecurity has turned its attention to the cyber vulnerabilities emerging from:
one of the examples is the trend of integration of advanced artificial intelligence into the complex of cyber-physical systems where their hacking or hostile reorientation is potentially capable of creating new types of threats for critical objects.
Which of the following is NOT an example of the interaction of AI with critical infrastructure:
of that, implemented with new AI capabilities to stage more serious attacks threatening infrastructures.
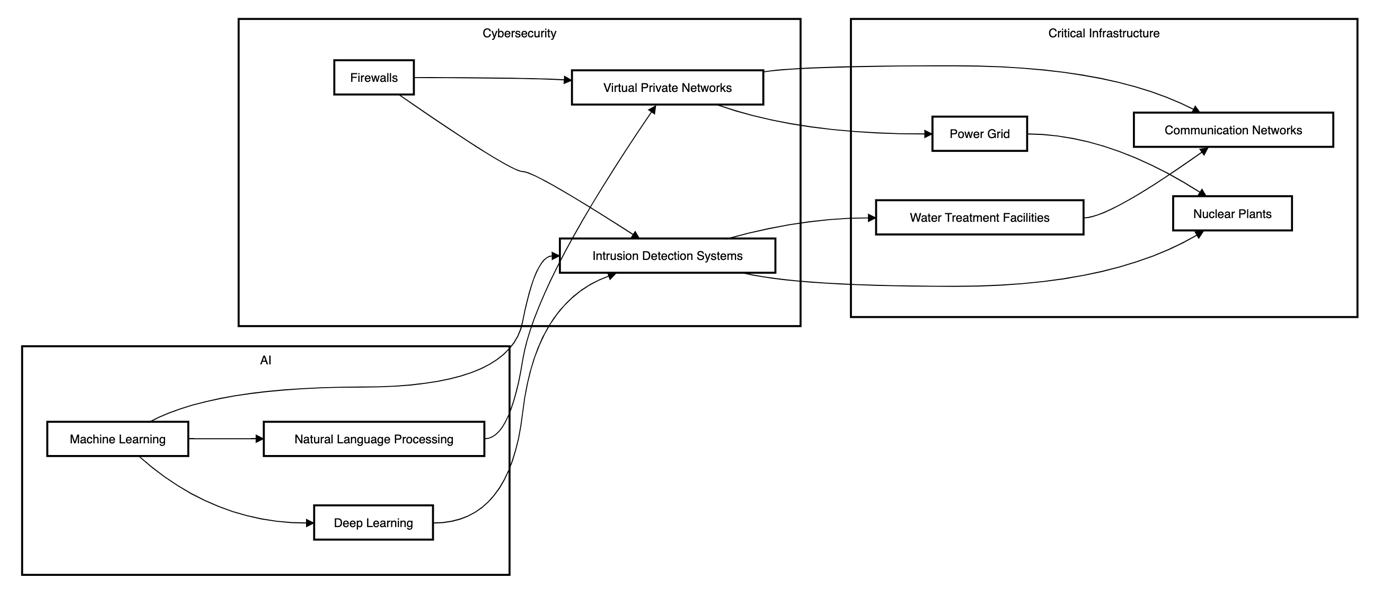
An example of (a) is the incorporation of self-driving cars. Their AIs generate their openings for adversarial examples that lead to crashes. If the attack is of sufficiently wide impact, then it should be set as an attack to country’s road, which are considered to be infrastructure. Another case is the transformation of commercial AI complexes into real weapons against buildings. For instance, unmanned aerial vehicles and autonomous vehicles that are already in existence could be employed to convey explosives to targets constituting physical structures including the power grid, water, and generators, hospitals and schools among others; these are attacks that belong to case A1 in the four categories we used in analysing the problem.
Examples of type (b) stem from the corresponding idea that AI-categorized services are questionable for such threats as adversarial examples. A type of situation related to a particular C-IS, for instance, hospitals is the vulnerability of diagnostic appliances that use AI to adversarial attacks. These can be classified as B2 in terms of our breakdown.
Last but not the least, an example of type (c) is the application of AI to increase the impact of attacks targeting critical infrastructures. The independence of the AI also introduces the ability for one person, assuming they have exclusive control of the AI, to do great harm. Both A1 and B2 cyber-attacks falling into the literature are described. Coordinated assault by multitudes of interconnected automated units (swarming) such as swarms of drones may be realized through multi-agent swarming networks that fall under AI. Navigation and face-recognition, planning are like enhancement of robotic systems, which can be used to execute physical attacks (A1) to the infrastructures. Additionally, AI can be applied for improving the search for such vulnerabilities, so it is a possibility to expand the scale or level of sophistication of attacks regarding the software residing in the infrastructure. The impact can be the disruption of the function (B2) or harm (A1) where the structure depends on information and communication technology for its operations or security. [4]
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the integration of Artificial Intelligence in cybersecurity means a huge step forward in safeguarding critical infrastructure against cyber threats that are ever changing. This proactive security approach is therefore better than traditional methods in terms of AI’s ability to process large volumes of data, recognize patterns and anticipate possible threats that may arise. From detecting anomalies in the early days to deep learning algorithms which can detect zero-day attacks, AI has come a long way to become an integral part of contemporary cyber defence strategies.
On the one hand, there are numerous advantages associated with AI including enhancement of detection abilities, faster reaction times and prevention techniques. It is however crucial to note that development and adaptation must be ongoing as it becomes more intricate. In addition, collaboration among governmental organizations, private firms, scientific institutions and non-state actors becomes crucial as cyber threats become more advanced. This will ensure continuous refinement and optimization of AI technologies for emerging challenges.
Reference:
- P. Pappachan, Sreerakuvandana, and M. Rahaman, “Conceptualising the Role of Intellectual Property and Ethical Behaviour in Artificial Intelligence,” in Handbook of Research on AI and ML for Intelligent Machines and Systems, IGI Global, 2024, pp. 1–26. doi: 10.4018/978-1-6684-9999-3.ch001.
- M. Rahaman, B. Chappu, N. Anwar, and P. K. Hadi, “Analysis of Attacks on Private Cloud Computing Services that Implicate Denial of Services (DoS),” vol. 4, 2022.
- A. Adewusi, U. Okoli, T. Olorunsogo, E. Adaga, D. Daraojimba, and O. Obi, “Corresponding author: Donald Obinna Daraojimba Artificial intelligence in cybersecurity: Protecting national infrastructure: A USA review,” World J. Adv. Res. Rev., vol. 21, Feb. 2024, doi: 10.30574/wjarr.2024.21.1.0313.
- M. Christen, B. Gordijn, and M. Loi, Eds., The Ethics of Cybersecurity, vol. 21. in The International Library of Ethics, Law and Technology, vol. 21. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2020. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-29053-5.
- Gupta, B. B., & Narayan, S. (2021). A key-based mutual authentication framework for mobile contactless payment system using authentication server. Journal of Organizational and End User Computing (JOEUC), 33(2), 1-16.
- Vajrobol, V., Gupta, B. B., & Gaurav, A. (2024). Mutual information based logistic regression for phishing URL detection. Cyber Security and Applications, 2, 100044.
- Gupta, B. B., Gaurav, A., Panigrahi, P. K., & Arya, V. (2023). Analysis of cutting-edge technologies for enterprise information system and management. Enterprise Information Systems, 17(11), 2197406.
Cite As
Shaik D. A. (2024) AI in Protecting Critical Infrastructure from Cyber Threats, Insights2Techinfo, pp.1