By: Soo Nee Kee1,2
1Universiti Malaya, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia.
2International Center for AI and Cyber Security Research and Innovations, Asia University, Taiwan Email: nee.kee2001.nks@gmail.com
Abstract
With the rapid growth of Internet of Things (IoT) networks, many edge devices, such as sensors, cars, computers, and wearable devices are able to connect and communicate without the restriction of locations and time, enabling data exchange efficiently. However, security is the primary issue as the data is transmitted across the network from all around the world. Security threats like phishing, botnets, and ransomware often occur. Therefore, blockchain with a four-layer architecture is proposed to address the issues above.
Keywords: IoT, Blockchain, AES-256, Four-layer Architecture
Introduction
Blockchain technology is a database that maintains a continuously growing number of data using hash pointer scheme. Each block containing data connects previous blocks in the cryptographic chain, which maintains a consistent view of the entire blockchain and makes it difficult to tamper. [1] This guarantees the truthfulness and correctness of the data and fosters trust from the users. There are many types of blockchain, such as off-chain and blockchain-as-a-service. Off-chain is used in handling a large distribution of data. InterPlanetary File System (IPFS) is one of the examples of off-chain. Blockchain-as-a-service can be used in managing tokens, reputations, and incentives. [2]
Technologies
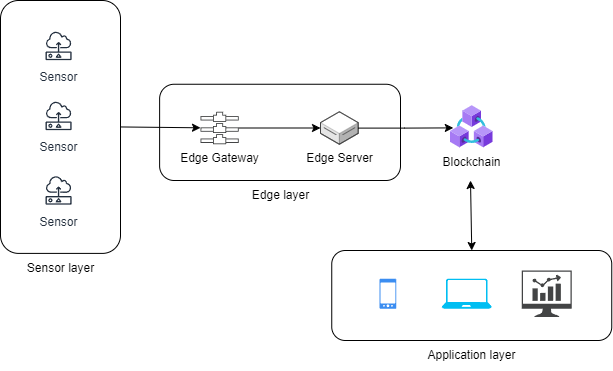
This paper proposes an integration of IoT and blockchain to secure data transmission. The system architecture consists of 4 layers: sensor layer, edge layer, blockchain layer, and application layer. The sensor layer, also known as the data generator layer, is the layer that consists of various types of devices for data collection. In this layer, the sensors or smart compliances collect data from the environment. For example, the IoT used in healthcare may collect data such as human temperature, glucose level and oxygen saturation. The data will be encrypted by using symmetric-key algorithms like AES and DES to ensure the authenticity of the data owner. [2] The data will be sent to edge layer to further process. Edge layer includes two main components, edge gateway and edge servers. [2] Edge gateway receives data from various sensors. The data will then be transferred to edge server. Edge servers can run more complex algorithms like deep learning. Thus, edge servers can be used to perform the vulnerability detection. After that, the safe data will then be encrypted before being transferred to the next layer using AES-256.
Blockchain layer with its cryptographic chain of blocks maintains the decentralized ledger for secure data transmission. It ensures immutability and a trustless environment, giving users unrivalled control and certainty over their transactions. Blockchain can allow authorized users to access private data only, which can improve security and prevent unauthorized access. The last layer is the application layer, which means the user interface that provides real-time monitoring dashboards and analytics tools to detect anomalies. Users can interact with the system via web or mobile devices to monitor the data flows and set access policies.
Conclusion
In conclusion, blockchain plays a critical role in safeguarding IoT networks. By leveraging the blockchain, the proposed system enhances the privacy and immutability of data transmission. The four-layer architecture—sensor, edge, blockchain, and application— ensures the data is securely transmitted and analysed across the network. This approach can effectively prevent unauthorised access and vulnerable attacks, as well as foster trust among IoT users.
Reference
- “Blockchain-based IoT security solutions for IDS research centers – ScienceDirect.” Accessed: Oct. 05, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2542660524002488
- “Exploring the integration of edge computing and blockchain IoT: Principles, architectures, security, and applications – ScienceDirect.” Accessed: Oct. 04, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1084804524000614
- Raj, B., Gupta, B. B., Yamaguchi, S., & Gill, S. S. (Eds.). (2023). AI for big data-based engineering applications from security perspectives. CRC Press.
- Gupta, G. P., Tripathi, R., Gupta, B. B., & Chui, K. T. (Eds.). (2023). Big data analytics in fog-enabled IoT networks: Towards a privacy and security perspective. CRC Press.
- Chaudhary, P., Gupta, B. B., & Singh, A. K. (2022). XSS Armor: Constructing XSS defensive framework for preserving big data privacy in internet-of-things (IoT) networks. Journal of Circuits, Systems and Computers, 31(13), 2250222.
Cite As
Kee S.N. (2024) Blockchain as a Solution for Secure Data Transmission in IoT Networks, Insights2Techinfo, pp.1