By: Nicko Cajes; Northern Bukidnon State College, Philippines
Abstract
Internet have become one of the most important parts for the modern life. However, it also brings critical cybersecurity threats. With that being said, malware and spyware are among of these treats that have a high risk, having the ability to compromise personal data, financial security, and privacy of the users. This article will explore on the extensive nature of these threats, how do these attack operates, the impact it can provide, and the strategies that is effective in countering against them.
Introduction
Due to the peoples growing reliance to digital technology, threats in cybersecurity have also becomes more advanced and rampant. Two of those threats that gives a huge potential damage are the malware and spyware which provides a significant threat to individuals and organizations. Malware is the common term used to describe a malicious software which are software that has the ability to shut down the operation of the system, perform data theft, and cause harm financially [1]. Spyware on the other hand, is a specific type of malware which has the risk of gather information secretly from the victims without asking for their consent [2]. Knowing how these threats can operate in the digital world have become more essential as we are going on in our way to digitalization, with the help of knowing it, our online security can become more ensured.
Understanding Malware
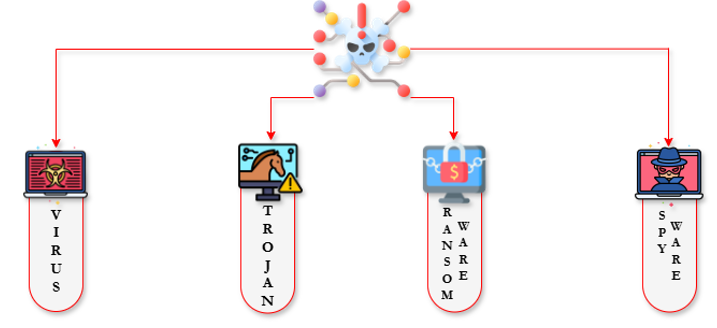
Malicious software or what is well-known as malware, represents to any kind of software which is designed to harm, exploit, or cause damage into a computer system [3]. Malware come in different forms, this includes, viruses, worms, ransomware, and Trojans, which cybercriminals utilizes for financial gain, spying individuals, or cause operational shut-down [4]. The following are few of the common types of malwares.
Viruses and Worms: Viruses is a type of malware which make themselves attached to a program that is legitimate and will then spread when the program runs [5]. On the other hand, is worms, which typically do not need a human interaction for it to spread [6]. These malwares have become the common type and one of the most harmful as it can operate with less attention made, making them highly dangerous for connected networks.
Trojans: A type of malware that disguise themselves a s a legitimate software and then executes malicious activities once installed is called trojans, this type of malware has become the most common gateway of cybercriminals to gain access or take over for the control over a network or device [7].
Ransomware: Another type of malware that encrypts the file of the victim and demands a money or ransom for decrypting the file is called ransomware. This attack type is done by targeting individuals, businesses, and even government institution to gain money, which can result in a great financial loss [8].
The Threat of Spyware
Another type of malware that has the ability to gather the victim’s data secretly is well-known as spyware. This attack is usually used for malicious activities, including theft of identity and espionage. Spywares have variety of ways in its operation including the following.
Keyloggers: A keylogger is a type of spyware operation that will record every keystroke of a user which effectively captures important information such as the username, password, bank details, and even confidential messages [9].
Adware: This type of spyware operation displays advertisement with embedded malware, even when some types of adware are very irritating, this type of attack operation can gather personal data without the consent of the victim [10].
Remote Access Trojans (RATs): RATs, another type of spyware attack that gives the cybercriminal an ability to control the device that was infected remotely. When this happens, they can access the files, activate the victims webcam, and manipulate the functions of the system without the victim noticing it [11].
The Impact of Malware and Spyware
Being a victim of these type of attacks can give major compensations as the infections of malware and software can be critical, which can affect individuals and organization in a lot of different ways.
Financial Losses: Cybercriminals can utilize malware to steal banking credentials from the victims and conduct money transactions, this can be done by effectively deceiving the victim to disclose their personal information [12].
Data Breaches: The confidential information including the business secrets and personal details can be exposed with the used of malware and software, this can become more dangerous as cybercriminals can exposed this or use in illegal ways [13].
Violations on Privacy: This impact can be provided mostly by the spyware. With the use of spyware, privacy of the victim can be compromised, this can be done through tracking their activity online such as browsing, their location, and their personal conversation with other users [14].

Protection Strategies
To effectively protect ourselves form the threat provided by malware and software, we need to implement a proactive cybersecurity measure. The following strategies are the most commonly used to prevent being the victim of this attack.
Use Reliable Security Software: Installation and utilization of well-known working anti-virus and anti-malware software is one of the best strategies to prevent being attacked by cyber-threats, as this software can directly detect, and neutralize cyber threats before they can provide any harm to your system [15].
Keep Software and Systems Updated: Doing a regular update on the new patch for your systems can provide an additional security vulnerability protection, this can lessen the chance of cybercriminals in penetrating and will give a hard time for malware to exploit its vulnerabilities [15].
Be Cautious with Downloads and Links: As internet users have a high tendency to download files on the internet, being cautious while downloading is also one of the proactive approaches that can be implemented to prevent being attacked. Files that come from unknown sources and links that comes from suspicious emails or messages are one of the things that needed to avoid [16].
Use Secure Networks: The practice of easily connecting to public Wi-Fi is also a thing need to prevent in this situation as public Wi-Fi networks vulnerable to cyber-attacks, instead if it is done, the use of virtual private network is advised at it can help in encrypting the data which aids in enhancing the security.
Conclusion
Hidden dangers are circulating on the internet nowadays, this includes the malware and spyware which gives a huge threat in the security and privacy of its victim. By effectively understanding these threats and applying proactive preventive measures, individuals and organizations can prevent being a victim of this attack and will significantly aid in protecting their confidential information. By gaining fundamental knowledge and being informed of the way these threats operate, users can lessen the chance of being exposed by this attack and can enjoy more on navigating the cyber space without worrying of their safety.
Reference
- Dutta, N., Jadav, N., Tanwar, S., Sarma, H. K. D., Pricop, E., Dutta, N., … & Pricop, E. (2022). Introduction to malware analysis. Cyber Security: Issues and Current Trends, 129-141.
- Rosdiana, D. (2023). Spyware in intelligence espionage operations as a threat to the state. Kyiv-Mohyla Law and Politics Journal, (8-9), 161-171.
- Akhtar, M. S., & Feng, T. (2022). Malware analysis and detection using machine learning algorithms. Symmetry, 14(11), 2304.
- Pachhala, N., Jothilakshmi, S., & Battula, B. P. (2021, October). A comprehensive survey on identification of malware types and malware classification using machine learning techniques. In 2021 2nd international conference on smart electronics and communication (ICOSEC) (pp. 1207-1214). IEEE.
- Arora, P., Gupta, R., Malik, N., & Kumar, A. (2023, November). Malware Analysis Types & Techniques: A Survey. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Information Management & Machine Intelligence (pp. 1-6).
- Yadav, D., Kumar, G., Lakshmi Kameshwari, D., Gunjan, V. K., & Kumar, S. (2022, May). Malware techniques and its effect: A survey. In ICCCE 2021: Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Communications and Cyber Physical Engineering (pp. 1215-1225). Singapore: Springer Nature Singapore.
- Chandy, J. Review on Malware, Types, and its Analysis.
- Oz, H., Aris, A., Levi, A., & Uluagac, A. S. (2022). A survey on ransomware: Evolution, taxonomy, and defense solutions. ACM Computing Surveys (CSUR), 54(11s), 1-37.
- Zebua, D., Pamungkas, B. A., Prayogi, H. E., Muhammad, R., Wahyudi, S., & Samudra, W. (2023). Keylogger Threats in Computer Security Aspects. International Journal of Integrative Sciences, 2(6), 855-860.
- Jayadatta, S. (2025). Impact and Effect of Spyware, Adware, and Malware on Digital Environment in Modern Society. In Digital Transformation in the Customer Experience (pp. 73-89). Apple Academic Press.
- Mohammadi, R., Hosseini, M. M., & Bahrami, R. (2025). Uncovering security vulnerabilities through multiplatform malware analysis. Security and Privacy, 8(1), e455.
- Jayadatta, S. (2025). Impact and Effect of Spyware, Adware, and Malware on Digital Environment in Modern Society. In Digital Transformation in the Customer Experience (pp. 73-89). Apple Academic Press.
- Bhadouria, A. S. (2022). Study of: Impact of Malicious Attacks and Data Breach on the Growth and Performance of the Company and Few of the World’s Biggest Data Breaches. Int. J. Sci. Res. Publ.
- Roy, S. (2023). The Impact of the Recent Pegasus Spyware Controversy on the Right to Privacy in India. International Journal of Law Management and Humanity, 6(3), 1060.
- Yadav, C. S., Singh, J., Yadav, A., Pattanayak, H. S., Kumar, R., Khan, A. A., … & Alharby, S. (2022). Malware analysis in IoT & android systems with defensive mechanism. Electronics, 11(15), 2354.
- Kalla, D., Samaah, F., Kuraku, S., & Smith, N. (2023). Phishing detection implementation using databricks and artificial Intelligence. International Journal of Computer Applications, 185(11), 1-11.
- Jakka, G., Yathiraju, N., & Ansari, M. F. (2022). Artificial Intelligence in Terms of Spotting Malware and Delivering Cyber Risk Management. Journal of Positive School Psychology, 6(3), 6156-6165.
- Rahaman, M., Pappachan, P., Orozco, S. M., Bansal, S., & Arya, V. (2024). AI Safety and Security. In Challenges in Large Language Model Development and AI Ethics (pp. 354-383). IGI Global.
- Rahaman, M., Lin, C. Y., Pappachan, P., Gupta, B. B., & Hsu, C. H. (2024). Privacy-centric AI and IoT solutions for smart rural farm monitoring and control. Sensors, 24(13), 4157.
- Jain, A. K., & Gupta, B. B. (2022). A survey of phishing attack techniques, defence mechanisms and open research challenges. Enterprise Information Systems, 16(4), 527-565.
- Deveci, M., Pamucar, D., Gokasar, I., Köppen, M., & Gupta, B. B. (2022). Personal mobility in metaverse with autonomous vehicles using Q-rung orthopair fuzzy sets based OPA-RAFSI model. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 24(12), 15642-15651.
- Neelapareddigari P. (2024) AI in Malware Detection and Analysis, Insights2Tecginfo, pp.1
Cite As
Cajes N. (2025) From Malware to Spyware: The Hidden Dangers Lurking Online, Insights2Techinfo, pp.1