By: Dhanush Reddy Chinthaparthy Reddy, Department of Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence, Madanapalle Institute of Technology and Science, Angallu(517325), Andhra Pradesh
ABSTRACT
But, as the undeniable trends pronounced in the field of digital technologies indicate, cybersecurity is an especially acute problem. The type of threats emanating from the digital frontier is on the rise and so is the level of complexity of the threats, conventional security measures prove to be irrelevant or inadequate. AI comes out as a powerful player in the fight against cyber threats and possesses more potential in threat identification and prevention. This paper focuses on how the AI acts and responds to identify and halt cyber threats. We explore several aspects like machine learning, deep learning, and neural networks through which systems can analyse untoward events, estimate possible attacks, and act independently. Additionally, we describe the use of AI in extending security features for filtering of malicious traffic, improving of the intrusion detection systems, and giving the adaptive security solutions. In this paper, we discuss how AI enhanced cybersecurity and future trends for AI implementation in this field based on case study and practical examples.
Keywords: Threat Detection, Artificial Neural Network, Q- Model.
INTRODUCTION
Artificial Intelligence (AI) involves simulating human intelligence in machines, enabling them to reason and act to achieve specific objectives. AI is used widely across industries such as healthcare and finance, with popular applications including recommendation algorithms and chatbots like Alexa or Siri. In cybersecurity, AI and machine learning are crucial for processing large quantities of data to detect threats like phishing and malware. AI can identify new malware variants by learning from previously detected threats, even when malicious code is hidden within benign code. AI-powered network monitoring tools can observe user activity, detect anomalies, and respond appropriately. As hackers continually evolve their tactics, AI provides essential defence against unknown threats, despite its resource-intensive nature and the risk of cybercriminals using AI to enhance their attacks.
Cybersecurity involves protecting systems and data from damage, loss, and unauthorized access. With increasing digital reliance, cybersecurity has become more critical. The ever-changing threat landscape includes actors like hackers, cybercriminals, nation-states, and hacktivists exploiting vulnerabilities for espionage, disruption, or financial gain. Key elements of cybersecurity include network privacy, node authenticity, software and information privacy, and identity and access management (IAM). Common threats such as malware, phishing, distributed denial of service (DDoS) attacks, and Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) attacks challenge cybersecurity efforts. AI advancements are pivotal in combating these sophisticated threats through anomaly detection, behavioural analysis, AI-powered antivirus, automation, user verification, and biometric authentication. While AI significantly enhances cybersecurity, a comprehensive strategy combining AI, human expertise, and other protective measures is essential for effective defence. [1]
AI Techniques in Cyber Threat Detection
Artificial Neural Networks
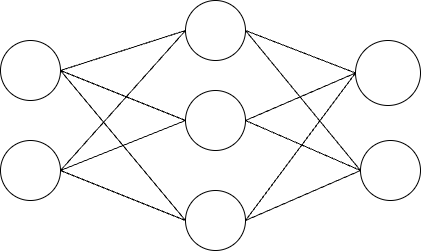
Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs) which in fact work same as the human brain where all the logical related work and the instant simulation is regulated by what is known as neurons. In this case, the words and phrases which are used are as follows which consist of neuronal networks which and learn and solve problems when combined in the right way and with the right connection figures. Neural Networks have As a result, the features like to learn, to process the distributed information, to self-organize and to be adaptable can be useful to solve the problems that need It is equally precise, conditional, and ambiguous to a certain degree. Since, neural networks are composed of a large number of synthesized neurons that can possess the capability of parallel learning and decision making with fast speed, the later assist them in the identification of patterns and choice of reactions to such incidents. [2]
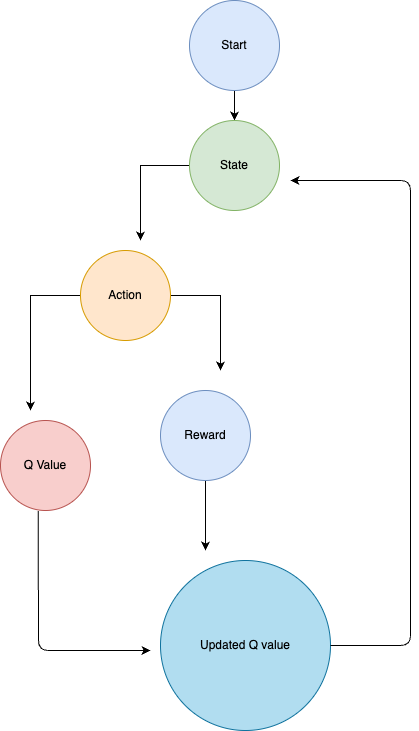
Q – Learning Model
Q-learning is a model-free reinforcement learning algorithm that is particularly useful for learning policies to make decisions in environments with uncertainty. In cybersecurity threat detection, Q-learning techniques are used to develop adaptive security systems that can learn optimal responses to detected threats over time. Here are some specific ways Q-learning is applied in cybersecurity
Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDPS)
Q-learning can be used to dynamically adjust the settings of an intrusion detection and prevention system based on the evolving nature of network traffic and detected threats.
Adaptive Thresholding
Q-learning agents can learn to set thresholds for alerts that minimize false positives and false negatives by continuously adjusting based on feedback from past decisions.
Benefits of AI in Cybersecurity
Overcoming Ethical Hurdles: The main issue in the AI development remains and the consent problems, algorithmic bias and other similar issues. Innocent York, where prejudice is used to make the training data, biased information is created that is unhelpful wherever the consequences may impact people adversely, such as in criminal justice systems, healthcare, and other professions. This is mainly because the machine learning algorithms’ decision making is particularly vulnerable to be labeled as “black box. ” These ethical concerns are personally relevant to address in AI and therefore there is need to assemble ethicists, lawyers, and computer scientists. Hence, the following papers should be to present explainable AI, employ the neutral data acquisition methods, and establish ethical guidelines.
Advancing AI-ML Integration: When implemented, AI and ML can inoculate intelligent systems into real life practices. AI can be defined as the emulation of human intelligence while ML means the development of models which are able to learn from the given data[3]. Together, they are able to develop systems which are consider to have high reliability but there is still issue such as for instance computational complexity or scarcity of data. The future work should concentrate on obtaining new algorithms as well as other that is going to be a blend between rule predicated AI and data predicated AI to get more accurate and comprehensible AI tools{Citation}.
Preparing for Adversarial AI: The adversarial attacks in the development of AI systems with new conventional ways of getting into attacking even the data input and the model. All current research works toward the enhancement of the robustness in adversarial training and robust optimization but raise issues like the growth of model complexity [4]and additional resources needed for the mentioned problems. Creating A. I systems that are well protected against such an attack is crucial and more so when it comes to the application of the safety of users such as in Motor vehicles and cybersecurity[5]
Conclusion
Today, AI is widely used in cybersecurity operations, and it has proven to be very important in the detection and prevention of different types of cyber threats. AI technologies like machine learning, deep learning, and natural language processing allow analyzing large amounts of data in real-time and detecting synergistic signs of threats. This way, the cyber threats can be detected before they cause much harm to the organization, in most cases before they even attack. Further, human interventions seem to be more susceptible to new and emerging threats as human processes permanently remain fixed and cannot learn from such cases.
AI not only improves the time to identify threats and their sources but also controls the threats and their mitigation, thus decreasing the threats’ exploitation on human analysts. With the development of the threats being present online, along with the need to analyze large amounts of data, AI is an essential tool required to ensure the protection of virtually any online structure.
Nonetheless, since AI can be beneficial in the campaign against cyber threats, it is not devoid of problems. Despite the great success of deep learning systems, learning from large datasets, and the high potential for algorithmic prejudice there are some crucial areas needing further improvement: privacy issues with the data and its transparency. Thus, there should be certain guidelines and ethical principles in regards to the development and usage of AI in the future of cybersecurity.
REFERENCES
- S. Duary, P. Choudhury, S. Mishra, V. Sharma, D. D. Rao, and A. Paul Aderemi, “Cybersecurity Threats Detection in Intelligent Networks using Predictive Analytics Approaches,” in 2024 4th International Conference on Innovative Practices in Technology and Management (ICIPTM), Feb. 2024, pp. 1–5. doi: 10.1109/ICIPTM59628.2024.10563348.
- A. Kamtam, A. Kamar, and U. Patkar, “International Journal on Recent and Innovation Trends in Computing and Communication Artificial Intelligence approaches in Cyber Security,” vol. Volume: 4, pp. 05–09, Feb. 2019.
- S. Al-Mansoori and M. B. Salem, “The Role of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Shaping the Future of Cybersecurity: Trends, Applications, and Ethical Considerations,” Int. J. Soc. Anal., vol. 8, no. 9, Art. no. 9, Sep. 2023.
- M. Rahaman, C.-Y. Lin, P. Pappachan, B. B. Gupta, and C.-H. Hsu, “Privacy-Centric AI and IoT Solutions for Smart Rural Farm Monitoring and Control,” Sensors, vol. 24, no. 13, p. 4157, Jun. 2024, doi: 10.3390/s24134157.
- M. Rahaman, L. Triyono, – Prayitno, – Sukamto, and A. Yobioktabera, “Smartphone-based Indoor Navigation for Guidance in Finding Location Buildings Using Measured WiFi-RSSI,” JOIV Int. J. Inform. Vis., vol. 6, no. 4, pp. 829–834, Dec. 2022, doi: 10.30630/joiv.6.4.1528.
- Bai, S., Shi, S., Han, C., Yang, M., Gupta, B. B., & Arya, V. (2024). Prioritizing user requirements for digital products using explainable artificial intelligence: A data-driven analysis on video conferencing apps. Future Generation Computer Systems, 158, 167-182.
- Rahaman, M., Lin, C. Y., Pappachan, P., Gupta, B. B., & Hsu, C. H. (2024). Privacy-Centric AI and IoT Solutions for Smart Rural Farm Monitoring and Control. Sensors, 24(13), 4157.
Cite As
Reddy D.R.C. (2024) How AI Detects and Stops Cyber Threats, Insights2Techinfo, pp.1