By: Phattanaviroj Thanaporn, Business Administration Department, Asia University, Taiwan, E-mail: tp.fern@gmail.com
Abstract
This article discovers the use of chatbots in the travel and tourism manufacturers, focusing on their potential as virtual tour directors. It highlights how countries like India are experimenting with chatbots to enhance tourist experiences and generate revenue for hotels and airlines. The article aims to increase tourism by using chatbots to enhancement the industry and produce profits for hotels and airlines business. The key is to provide customization to each tourist, using the latest technological trends in Natural Language Processing (NLP).
Introduction
In the country side era, India’s Tourism Sector is speedily growing, approximately 9.2% of the country’s GDP in 2018, supporting million workers and employment, highlighting the significant impact of tourism on the economy. India fascinates both domestic and foreign tourists, and some for medical treatments. Technological trends have directed to travel agencies planning expensive tours, booking hotels, taxis, and flights, and hiring local guides for visits attracting place such as museums. The world is moving towards customization, with chatbots like Alexa, Google Assistant, and Cortona performing tasks and learning behavioral patterns. NLP and AI systems offer customization, and mostly information from tourist sites could be used for the travel industry, mainly in India, somewhere over 1000 traveler locations, with World Heritage Sites [1].
Chatbots behavior as a human
The article is considering the use of chatbots in customer facility, considering feedback to identify factors, difficulties, and improvements needed. It highlights the increasing demand for chatbots in several fields, with companies like Facebook developing them for automated support responses. The article focuses on two main objectives: Anthropomorphic Design Cues (ADCs), which involve interacting with users like humans and Foot in the Door (FITD), which responds to user requests. The findings showed that chatbots generated social responses, users correctly interacted with them, and they applied the same social replies despite knowing they were interacting with them [2].
Chatbots growth
About chatbots growth is observes the increasing movement of consuming chatbots for guesthouse reservation, location recommendation, and air company option. And the article aims to address current trends, technological advancements, third-party apps, and advanced natural language processing (NLP). A number of research communities in Bulgaria, Italy, US, and some European countries emphasis on the development of chatbots in the travel industry. Moreover, focusing on hotel and airline booking, with developers mining data from sources like Google, TripAdvisor, and Wikipedia [3].
Tourist Site Recommendation Methods
For methos recommendation is presents the perception of chatbots in the travel business and addresses two main problems: the reference of the chatbot being too large and the inconsistencies in user explorations. Progress a reference algorithm founded on ConDiag and Shannon’s Entropy algorithm, which uses typical based perceptive and Shannon’s entropy algorithm to give favorites to the features present in the problematic and eliminate conflicts in the inquiry. The sample of the chatbot successfully provides information about cultural heritage sites in Campania, suggesting context and services based on the user’s individuality [4].
Hotel Option Helper
Snap Travel is one of the popular profitable apps that assists in hotel reservation and recommendation. To discusses the workings of the chatbot, which recommends guesthouses to client and forwards cases to humanoid representatives in problematic conditions [5]. The advanced typical contains of the determined estimate element which guesses the intent of the user’s communication, supposing the customer references exploration keyword in their communication that earnings specify the chatbot to search the guesthouse for them. The ELMo model and LSTM produce decided replies to the customer [6]. The pre-processing and operation are called Allen NLP. The NER typical expressions for the town and guesthouse descriptions. The exits data used for training is CoNLL 2003 which provided city names. SPACY2 for labelled guesthouse and town titles. In the conclusion the typical forecasts the significance score, which assesses the top 1 and top 3 proposals application.
Planned Arrangement
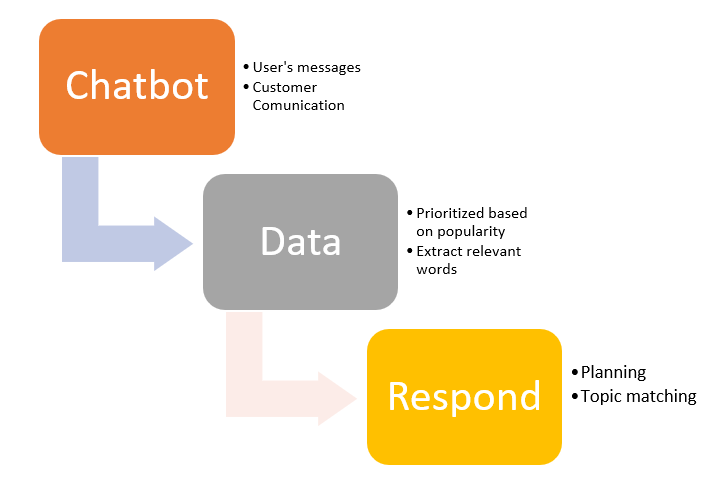
The planned arrangement goals Pune as an investigational situation study, using popular tourism firm websites like Trip Advisor, Trivago, and website reviews to mine Point of Interests, Tourist Sites, and Hotels. Tourists interact with the chatbot, asking for specific sites customer or travelers want to visit. The system includes modules such as Information Research, Subject Removal, Answer Creation, and Input Inquiry Processing [7].
Updating information can be arranged from tourism plan sites and itinerary data can be rated or prioritized based on popularity. Input Query Processing uses LSTM to process the user’s input, while Topic Extraction uses LDA to extract relevant arguments from the web[8]. The chatbot should response the traveler’s inquiry in a specified form, with an implication engine inferring the inquiry after a convinced subject is extracted. LSTM helps process input sentences word by word, pre-processing them, and formerly giving them to Topic Extraction. This system reduces the workload of support employees and improves user experience [9].
Conclusion
The use of chatbots in the travel industry can promote tourism and reduce human workload. Companies like Facebook and Google have shifted their support to chatbots, reducing human involvement. These chatbots or another AI respond application can recognize customer mindsets and response common requests. Average earning individuals who cannot afford large tour packages may prefer a solution that plans a family tour for a base price. Advancements in Natural Language Processing (NLP) have shown remarkable outcomes, with Deep Learning being a key methodology for recognizing patterns and recommending suitable answers. Professional administrations can adjust to this trend to growth profits in addition decrease worker assignment.
Reference
- R. Mishra, Artificial Intelligence Use Technology & Future of Facial Recognition technology Its Bright Future & Ethics Of GPT AI Chat Bots Exposed effects By virtue. 2024.
- ‘(PDF) The Use of Chatbots in Digital Business Transformation: A Systematic Literature Review’. Accessed: Mar. 04, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/353537250_The_Use_of_Chatbots_in_Digital_Business_Transformation_A_Systematic_Literature_Review
- ‘Sustainability | Free Full-Text | How does an Intelligence Chatbot Affect Customers Compared with Self-Service Technology for Sustainable Services?’ Accessed: Mar. 04, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://www.mdpi.com/2071-1050/12/12/5119
- H. Nguyen, T. Tran, P. Nham, N. Nguyen, and L. Duy Anh, ‘AI Chatbot for Tourist Recommendations: A Case Study in Vietnam’, Applied Computer Systems, vol. 28, pp. 232–244, Jan. 2024, doi: 10.2478/acss-2023-0023.
- ‘(PDF) Emerging Trends in Tourism & Hospitality Business: Transition and Transformation of Tourism in Crisis’. Accessed: Mar. 04, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/354353645_Emerging_Trends_in_Tourism_Hospitality_Business_Transition_and_Transformation_of_Tourism_in_Crisis
- E. Lefever, ‘Analysing the Impact of Supervised Machine Learning on Automatic Term Extraction: HAMLET vs TermoStat’, Proceedings – Natural Language Processing in a Deep Learning World, Jan. 2019, Accessed: Mar. 04, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://www.academia.edu/94503443/Analysing_the_Impact_of_Supervised_Machine_Learning_on_Automatic_Term_Extraction_HAMLET_vs_TermoStat
- P. O’Connor, ‘User-Generated Content and Travel: A Case Study on Tripadvisor.Com’, presented at the Information and Communication Technologies in Tourism, Jan. 2008, pp. 47–58. doi: 10.1007/978-3-211-77280-5_5.
- I. Brilhante, J. Macedo, F. M. Nardini, R. Perego, and C. Renso, ‘On planning sightseeing tours with TripBuilder’, Information Processing & Management, vol. 51, Nov. 2014, doi: 10.1016/j.ipm.2014.10.003.
- B. Shawar, ‘A Chatbot as a Natural Web Interface to Arabic Web QA’, International Journal of Emerging Technologies in Learning, vol. 6, Mar. 2011, doi: 10.3991/ijet.v6i1.1502.
- Deborah, L. J., Vijayakumar, P., Gupta, B. B., & Pelusi, D. (Eds.). (2023). Secure Data Management for Online Learning Applications. CRC Press.
- Gupta, B. B. (Ed.). (2021). Advances in Malware and Data-driven Network Security. IGI Global.
Cite As
Thanaporn P (2024) Smart Travel: Directing Journeys with Tour Planning Chatbots, Insights2Techinfo, pp.1