By: Ameya Sree Kasa, Department of Computer Science & Engineering (Artificial Intelligence), Madanapalle Institute of Technology & Science, Angallu (517325), Andhra Pradesh. ameyasreekasa@gmail.com
Abstract:
Virtual Reality is leading a fine revolution in both education and professional training with its immersive and highly interactive experiences that strive to make learning processes and skill acquisitions smoother. Precisely, this paper views the transformative role of VR within educational settings by expounding on how it provides hands-on learning opportunities, digitally engages students in new ways of learning, and simulates complex situations for practical training. We analyze current VR applications and emerging trends through case studies, outlining how VR is shaping the future of education and training both the benefits it brings and the challenges it poses.
Keywords: Virtual Reality, skill development,
1.Introduction:
We can underline the impact that virtual reality has on education and training by going through an in-depth analysis of the current applications of VR, case studies, and emerging trends. Unlike traditional learning tools, VR immerses users inside dynamic, three-dimensional simulations where they could further interact with the material in a more intuitive and memorable manner. This is not just about a digital layer on top of existing practices; this technology fundamentally changes everything about how concepts are taught and how skills are practiced. From virtual classrooms and recreations of historical events, sophisticated industrial simulations, and training of medical professionals to experiential learning, it was all unimaginable without VR. This paper discusses how VR is modernizing education, its uses in various fields of operation, and the potential it has for future educational innovation.
2. Role of virtual reality in education and training:
Virtually, it is changing the face of education and training by creating an extremely immersive and interactive experience to make learning more engaging and effective. Today’s students don’t have to merely read about some historical event or watch a video on some part of it; instead, they can be teleported to a recreated ancient city or be present in a live surgery with the help of a 3D simulation. Such practicality not only engages learners but also allows them to remember the information more easily because they are participating in the learning process. In training situations, VR makes it possible for practice to be done in a completely safe environment, be it complex machinery, medical procedures, or even drills for emergency responses. As VR technology continues to evolve, it is set to disrupt traditional ways of education and training. [1]
3. Applications of VR in Education and Training:
Applications of VR in education and training are mentioned below and figure 1.
Virtual Classrooms: One of the most interesting uses of VR in education is virtual classrooms. Students all around the globe can log into such digital spaces and get down to business interacting with other students and instructors just like they were in a real classroom. VR classrooms enable engaging learning experiences among learners to explore highly complex subjects in 3D environments, such as ancient civilizations or other planets. The approach not only provides an interactive learning mode but also fills up the geographical gaps, bringing a global dimension to education that the traditional classroom often can’t.
Medical Training Simulations: In medical trainees, VR provides a risk-free environment for students and professionals to conduct surgeries and diagnostic procedures. Trainees practice hands-on in the more realistic simulations to develop skills without the tension or risks associated with real-life scenarios. For instance, VR can simulate complex surgical operations to give students practice in the use of a technique time and again until they perfect their skills. It is actually in the practical experience gained that valuable building up of confidence and competence would be built up before being let loose on actual patients. [2]
Industrial and Corporate Training: For industrial and corporate settings, VR is one of the most powerful tools in on-the-job training and professional skill development. Think of a new employee who has to learn how to use complex equipment or a sales team getting ready to engage with customers. Using VR, employees can practice interactive scenario-based training that includes all the elements for very realistic scenarios without real-life mistake costs. This kind of practical exercise enhances the problem-solving ability of employees to a great degree and helps them do their job much better. [3]
Historical and Scientific Investigation: VR activates history and science by providing students with the opportunity to virtually examine historical events, archaeological sites, or scientific phenomena. Walking through ancient Rome, observing what atoms do, or conducting experiments virtually builds a more in-depth understanding of the subject areas because it is based on experiential learning. Experiential learning made these highly complex ideas much easier to remember since the abstract theories were changed into experience.
4. Benefits of VR in education and training:
- Improved Engagement: VR transforms learning into a thrilling experience by immersing students in dynamic environments that stimulate their imagination. Instead of being a mere intake of information, learners are actively involved—simulating events, visiting historical sites, conducting virtual experiments, or moving through complex situations. This activity makes lessons all the more engaging and enjoyable, therefore motivating students to learn more about the subject matter and retain information more effectively. [4]
- Safe Learning Environments: Probably the most important advantage of VR in education and training is skills practice in a safe environment. For example, medical students can conduct virtual surgeries without putting patients at risk; similarly, industrial trainees can practice running heavy machinery without fearing an accident. Since this is a risk-free environment, learners can make mistakes and learn from them with no real-world consequences, building confidence and competence before they are pitched against an actual challenge.
- Accessibility and Flexibility: The application of VR breaks the barriers to education, enhancing the flexibility of learning. In this way, students are able to attend virtual field trips to faraway locations, listen to guest lectures across the world, or practice skills at their own convenience and pace, all from the comfort of home. Much more specifically, this is particularly the case with people who live in remote areas or are physically challenged, providing them with opportunities that might have hitherto been impossible.
- Better Retention and Understanding: Due to its tremendous potential for providing learners with simulated, realistic, hands-on experiences, VR reinforces learning and improves retention. The interaction with the content concretizes in a 3D space; abstract concepts are made more concrete and remembered. For example, visualizing some event of history or certain scientific phenomenon in a virtual environment makes it easier to understand and remember, thus opening up access to complicated subjects that had been less perceived earlier on. [5]
5. Challenges and Concerns:
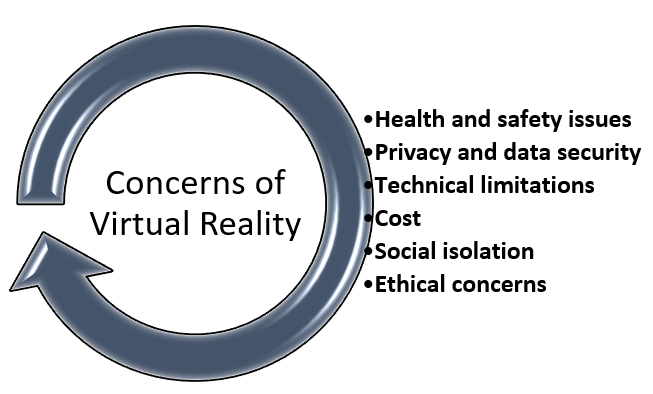
There are many challenges to VR in education and training. Inadequate funds to purchase and run the VR equipment and software undoubtedly present a big entry barrier to its use, hence rendering it less accessible to some institutions or organizations. Some also fear that the technology may cause motion sickness or discomfort if used for too long, hence hurting the learning experience. Another challenge is the quality and accuracy of the content, in that badly designed simulations can result in misunderstanding or ineffective training. Finally, how to integrate it into extant curricula and workflows: The inclusion of VR in already existing educational material needs careful planning and training for teachers and trainers in order to bring out its full potential. Only when these challenges are addressed will VR really start to become an effective tool that is also more widely adopted within education and training. [6]
The major concerns of VR are mentioned below in figure 2.
6. Implementation strategies:
Implementation of VR for education and training requires a thoughtful approach if it is going to be effective and sustainable. Begin by identifying clear objectives aligning VR applications with those goals, whether it will be an immersive, historic exploration, hands-on medical training, or an interactive corporate simulation. Buy good VR equipment and make sure educators and learners are accordingly trained in how to use it effectively. [7]It’s equally important to develop or source engaging and accurate VR content that will improve learning outcomes. Gradually integrate the use of VR into your curriculum or training programs with pilot projects that test for effect and adjust where appropriate. Further, get feedback from users in order to continuously make improvements in the VR experience and for solving any problems. This will ensure that through such steps, VR will be well integrated in educational and organizational training practices, providing enrichment to the learning experience by being both entertaining and efficient. [8]
7. Future advances:
Looking ahead, some very exciting futures of new developments in applying VR to education and training could continue changing how we learn and develop. Improvements such as haptic feedback will let people feel through the VR experience by mimicking the sense of feeling, and thus be able to better interact with virtual environments in much more real and engaging ways. Improvements to hardware mean lighter, more comfortable headsets with higher resolution displays bring less struggle and more fun to extended use. Next, innovations in AI and machine learning could make Virtual Reality more adaptive and individualized, tailoring its content to a variety of individual modes of learning. While VR technology itself becomes increasingly accessible and affordable, we can also foresee its broader adoption across a range of educational and training contexts, from K-12 classrooms to professional development programs. [9]
8. conclusion:
Ultimately, virtual reality reshapes the contours of education and training with its immersive and interactive experiences that a learner enjoys for better engagement and improved learning outcomes. From expensive solutions to user discomfort, although issues do populate the scene, the benefits that VR brings in the form of safe learning environments, better retention, and greater accessibility make it one of the most powerful tools for modern education and skill development. The potential for VR to create much more dynamic and personalized learning experiences is huge as technology continues to evolve. By carefully implementing the strategies of VR and further keeping a tab on improvements, it is that educators and trainers can tap into the potential of VR, paving a path for a more effective and innovative way to learning in the future.
9. References:
- S. Alshammari, “The Role of Virtual Reality in Enhancing Students’ Learning,” Int. J. Educ. Technol. Learn., vol. 7, pp. 1–6, Jan. 2019, doi: 10.20448/2003.71.1.6.
- B. Murdoch, “Privacy and artificial intelligence: challenges for protecting health information in a new era,” BMC Med. Ethics, vol. 22, no. 1, p. 122, Sep. 2021, doi: 10.1186/s12910-021-00687-3.
- P. Pappachan, Sreerakuvandana, and M. Rahaman, “Conceptualising the Role of Intellectual Property and Ethical Behaviour in Artificial Intelligence,” in Handbook of Research on AI and ML for Intelligent Machines and Systems, IGI Global, 2024, pp. 1–26. doi: 10.4018/978-1-6684-9999-3.ch001.
- F. Biocca, “Virtual Reality Technology: A Tutorial,” J. Commun., vol. 42, no. 4, pp. 23–72, 1992, doi: 10.1111/j.1460-2466.1992.tb00811.x.
- C. Anthes, R. J. García-Hernández, M. Wiedemann, and D. Kranzlmüller, “State of the art of virtual reality technology,” in 2016 IEEE Aerospace Conference, Mar. 2016, pp. 1–19. doi: 10.1109/AERO.2016.7500674.
- P. Anand, Y. Singh, A. Selwal, M. Alazab, S. Tanwar, and N. Kumar, “IoT Vulnerability Assessment for Sustainable Computing: Threats, Current Solutions, and Open Challenges,” IEEE Access, vol. 8, pp. 168825–168853, 2020, doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3022842.
- M. Rahaman, B. Chappu, N. Anwar, and P. K. Hadi, “Analysis of Attacks on Private Cloud Computing Services that Implicate Denial of Services (DoS),” vol. 4, 2022.
- P. Kuna, A. Hašková, and Ľ. Borza, “Creation of Virtual Reality for Education Purposes,” Sustainability, vol. 15, no. 9, Art. no. 9, Jan. 2023, doi: 10.3390/su15097153.
- J. Frank, “Arti cial Intelligence and Intrusion Detection: Current and Future Directions”.
- Gupta, B. B., & Panigrahi, P. K. (2022). Analysis of the Role of Global Information Management in Advanced Decision Support Systems (DSS) for Sustainable Development. Journal of Global Information Management (JGIM), 31(2), 1-13.
- Gupta, B. B., & Narayan, S. (2021). A key-based mutual authentication framework for mobile contactless payment system using authentication server. Journal of Organizational and End User Computing (JOEUC), 33(2), 1-16.
Cite As
Kasa A.S. (2024) The Role of Virtual Reality in Education and Training, Insights2Techinfo, pp.1