BY: Rishika Yatishwar Gaur
Things are evolving fastly towards a password-free world. This leads to excessively increasing use of biometric for identifying an individual’s unique biological to verify his or her identity also known as biometric authentication [1]. This could be done by iris, retina, voice, face, or fingerprint recognition. But still, a biometric authentication system is vulnerable to many cyberattacks like presentation attacks (attempt to interfere with the intended purpose of a biometric system) such as biometric spoofing [2].
Example of presentation attack: If an individual’s fingerprint is captured, this could be used to make a matching artifact. For face recognition, a photo of the target can be taken and used to create an artifact. Another example of biometric spoofing is Tom Cruise’s character from the Hollywood movie Minority report (2002), who successfully spoofed an iris recognition check by a fake eye, he just bought from the black market.[5]
Is voice secure enough? What if someone steals it and misuses it? Can my fingerprints be copied? These questions will keep coming to mind.[3] Therefore, an appreciable amount of resistance to spoofing attacks can be provided by using a series of field-proven and cost-effective techniques. Figure 1 shown below represents the different forms of authentication rated by their security level.

Spoofing detection systems for iris, voice, face, and fingerprint are broadly based on two deep learning approaches:-
- The first strategy consists of learning appropriate convolutional network topologies for each domain.
- The second method employs backpropagation to figure out the network’s weights.[4]
The majority of anti-spoofing techniques make use of a three-dimensional camera. It does pixel depth analysis, which ensures excellent accuracy against presentation assaults. The distinction between a face and a flat form is readily apparent. While 3D assaults continue to pose challenges, their stability makes these sorts of technologies the most promising.
Numerous spoofing detection techniques have been presented to assess whether a living person or a synthetic duplicate is in front of the biometric sensor. However, the topic remains unsolved due to the high degree of complexity associated with establishing effective characteristics with minimal computing cost for detecting spoofing attempts. Additionally, there are substantially fewer solutions that focus just on mobile devices. These are some operational difficulties that may arise.[6]
So, is spoof detection an ultimate security measure? The answer is no, there are many factors other than spoofing to breach security. So, should we trust biometric authentication systems? You may trust it as it gives better security than Passwords and PINs as proven by the survey in Figure 2 below.
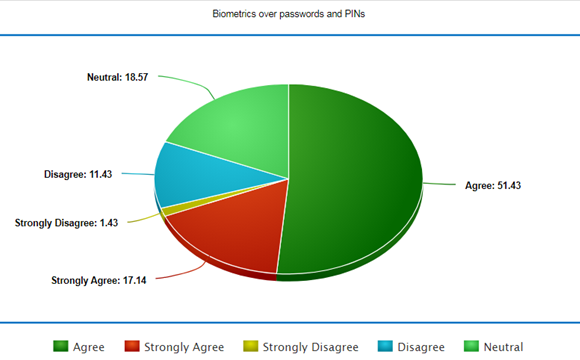
There isn’t any technology available that provides 100% security. Even then, if you are unsure, multi-factor authentication is also an option.[3]
References:
- Khairwa, A., Abhishek, K., Prakash, S., & Pratap, T. (2012, July). A comprehensive study of various biometric identification techniques. In 2012 Third International Conference on Computing, Communication and Networking Technologies (ICCCNT’12) (pp. 1-6). IEEE.
- Ali, S. S., Ganapathi, I. I., Prakash, S., Consul, P., & Mahyo, S. (2020). Securing biometric user template using modified minutiae attributes. Pattern Recognition Letters, 129, 263-270.
- https://www.bayometric.com/spoofing-fingerprint-scanner-and-spoof-detection/
- D. Menotti et al., “Deep Representations for Iris, Face, and Fingerprint Spoofing Detection,” in IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, vol. 10, no. 4, pp. 864-879, April 2015, doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2015.2398817.
- https://www.thalesgroup.com/
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/286108098_Liveness_detection_for_biometric_authentication_in_mobile_applications
Cite this article:
Rishika Yatishwar Gaur (2021) Biometric Spoof Detection, Insights2techinfo, pp.1
FAQ on this topic
If an individual’s biometric data is captured and used to make a matching artifact. It is called biometric spoofing.
In face spoofing, a photo of the target can be taken and used to create an artifact.
Iris, face, voice, and fingerprint are four types of biometrics.
Wonderful article very insightful and informative. Well summarised commendable work.
Thank you