By: I. Cvitić, M. Sai, D. Peraković
Cheating is simply another method of acquiring resources that enables players to get an advantage over their opponents. Cheating can be defined as an unfair advantage obtained by one player over another in violation of the game’s regulations. In single-player games, players do not have to contend with another player attempting to deceive them into a bad gaming experience. Cheats, which are frequently used in single-player games, enable the user to alter how the game is played. Some disable statistics to ensure that other players’ game experience is not impacted [1]. Figure 1 illustrates several cheating techniques [2].
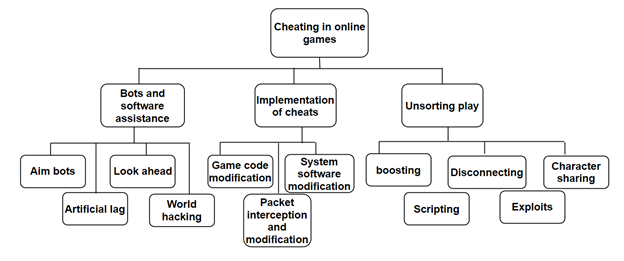
Cheating in online games may be done in various forms, ranging from the simplest to the most sophisticated. Some of the standard types of cheating techniques used by the players are as following [6-9]:
- Trust exploitation: Client-side cheating involves altering the game code, configuration data, or both on the client’s end of the transaction. A cheater may use computer software to change data in his game client and the game’s system files, then replace the older versions with new ones. Alternatively, code and data may be modified or replaced on the fly.
- Collaboration: In online games such as online bridge, a group of cheaters may band together to obtain an unfair edge over their honest opponents.
- Escaping: A cheater is just someone who takes advantage of the game’s functioning process. One frequent scenario that we have seen in many online games is escaping: when a cheater knows he is about to lose, he disconnects himself from the gaming system and runs away.
- Driver modification: The gamer may cheat by altering his operating system’s client infrastructure, such as device drivers. For instance, he might alter a graphics driver to render a wall transparent, allowing him to see through it
- Denying service: The cheater sometimes floods the victim’s networks with bogus requests, causing the victim’s network connection to lag, preventing him from responding fast to the game, which causes other participants to remove the victim from the competition.
- Look ahead cheat: Cheater sometimes delays his move in the online games to analyze his opponent’s moves.
- Lack of Authentication: Sometimes, the game server’s authentication protocols are not adequate; therefore, a cheater can get many user IDs of different players. With fake user IDs, cheaters easily create legitimate players.
- Boosting: It is a form of collaboration in which the boosting party helps from the player’s level increase in order to earn in-game incentives.
- Experience Selling: Certain players may elect to sell improved accounts to avoid working as hard to reach a specific level [3].
For individuals lacking technological expertise or the desire to modify the game, cheating can be accomplished through the use of in-game methods and game faults. Losing an online match might result in a player falling levels or receiving lower-level prizes [4]. This occurs when it is clear that the player will lose, at which point the match is halted, and the device is turned off to prevent the player from continuing. By flouting the established rules, this game subverts the system and defrauds the winning player, who typically earns the match’s prize. Cheating through bugs and loopholes is a distinct form of cheating, as long as the player does so to circumvent the game’s completion requirements [5]. A glitch enables players to bypass a significant chunk of the game in order to complete it faster or grab items that are not generally available. These vulnerabilities may be sold to other players in third-party markets rather than purchased directly from the game provider.
Open research issues and challenges [10, 11]
- Different techniques need to develop that identify the game vulnerabilities that allow malicious users to introduce modes and manipulate various game resources.
- Preventing the exploitation of defects and vulnerabilities through anti-cheat codes in games that alter gameplay when an abnormality is detected.
- Detecting anomalous patterns or behaviors of users or a group of users and modifying their gaming as a result
- Using machine learning algorithms or fuzzy techniques, developing methods for detecting bugs in games.
- Maintaining the integrity of the game’s users’ identities through the use of various authentication techniques or identity checks of legitimate users and inventing new authentication methodologies.
- Effective data encryption methods used during information exchange and the development of new encryption schemes that are difficult to crack assure data transit security between the client and server.
References
- Saudi, M. H. (2021). Gaming Mobile Applications: Proof of Concept for Security Exploitation. Turkish Journal of Computer and Mathematics Education (TURCOMAT), 12(8), 1761-1766.
- Boluk, S., & LeMieux, P. (2017). Metagaming: Playing, competing, spectating, cheating, trading, making, and breaking videogames (Vol. 53). U of Minnesota Press.
- Fox, J., Gilbert, M., & Tang, W. Y. (2018). Player experiences in a massively multiplayer online game: A diary study of performance, motivation, and social interaction. New Media & Society, 20(11), 4056-4073.
- Parizi, R. M., Dehghantanha, A., Choo, K. K. R., Hammoudeh, M., & Epiphaniou, G. (2019). Security in online games: Current implementations and challenges. In Handbook of Big Data and IoT Security (pp. 367-384). Springer, Cham.
- Yan, J., & Randell, B. (2005, October). A systematic classification of cheating in online games. In Proceedings of 4th ACM SIGCOMM workshop on Network and system support for games (pp.1-9).
- Sahoo, S. R., et al. (2020). Fake profile detection in multimedia big data on online social networks. International Journal of Information and Computer Security, 12(2-3), 303-331.
- Chaudhary, P., et al. (2019). A framework for preserving the privacy of online users against XSS worms on online social network. International Journal of Information Technology and Web Engineering (IJITWE), 14(1), 85-111.
- Gupta, S., et al. (2018). Hunting for DOM-Based XSS vulnerabilities in mobile cloud-based online social network. Future Generation Computer Systems, 79, 319-336.
- Sharma, Y., Bhargava, R., & Tadikonda, B. V. (2021). Named Entity Recognition for Code Mixed Social Media Sentences. International Journal of Software Science and Computational Intelligence (IJSSCI), 13(2), 23-36.
- Sahoo, S. R., et al. (2021). Multiple features based approach for automatic fake news detection on social networks using deep learning. Applied Soft Computing, 100, 106983.
- Lin, D., Bezemer, C. P., & Hassan, A. E. (2019). Identifying gameplay videos that exhibit bugs in computer games. Empirical Software Engineering, 24(6), 4006-4033.
Cite this article:
I. Cvitić, M. Sai, D. Peraković (2021), Cheating in Online Gaming, Insights2Techinfo, pp.1
Also Read: