By: Vanna karthik; Vel Tech University, Chennai, India
Abstract
Cyber criminals have relied on spear phishing as a crucial security threat since ancient times yet artificial intelligence (AI) has revolutionized these attacks to become more challenging to identify and more advanced. The phishing technique called spear phishing directs attacks at individual users through the utilization of custom information which bait victims to provide confidential information. AI technology provides capabilities for automatizing and improving these attacks which results in more credible and difficult to detect threats. AI tools are now more easily accessible which allows novice cybercriminals to execute effective spear phishing attacks. Modern security techniques alone prove insufficient to fight highly complex cyber-attacks which seem to be increasing in numbers. The author investigates how Artificial Intelligence systems contribute to spear phishing outbreaks while outlining the attackers’ methods and providing protection measures for organizations along with individual users against modern threats.
Introduction
Cybercriminals, through phishing attacks consistently keep cybersecurity stakeholders busy since they deceive victims with deceptive emails to obtain sensitive information. Spear phishing exists as the targeted version in which AI integration empowered cybercriminals to create messages that specifically match target recipients’ communication types[1]. The sector of spear phishing employs artificial intelligence to analyze big datasets through which attackers produce realistic social engineering messages which also aids in automating their large-scale attacks. These assaults have higher effectiveness due to AI’s capability to create natural human interactions in the messages. Digital connectivity between businesses and individuals boosts the danger of spear phishing which requires strong security protocols because these threats will persist in the future.
The Role of AI in Spear Phishing[2]
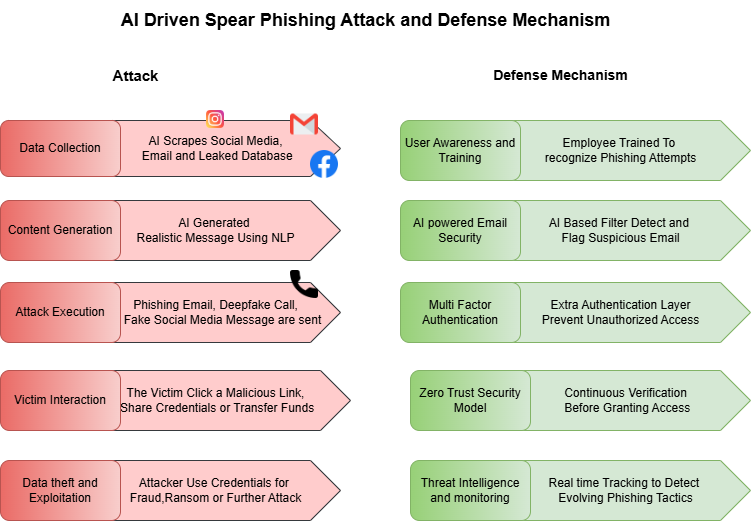
The abilities of cybercriminals to carry out spear phishing attacks have experienced major improvements because of AI technology. Spear phishing attackers benefit from algorithms of machine learning combined with natural language processing (NLP) to achieve their goals.
1.Personalized Attacks:
The data collected by AI from the victim’s social media accounts together with their work-related websites and leaked documents become the source material for creating specific messages that match the victim’s interests and responsibilities and the latest professional behaviors.
2. Crafting Seductive Content: The hackers, using AI-powered text generation applications, compile business emails modeled after the messages from trusted partners.
3. Automate Phishing Campaigns: By automating the attack management tasks, AI bots serve as digital messengers that can increase the attack success rate.
4. Avoid Detection: By modifying their language, some phishing emails can get past security filters and avoid detection by modern email security software.
Methods of AI-Assisted Spear Phishing
Cybercriminals use a variety of AI approaches to enhance secure spear phishing assaults in the following ways:
Deepfake Audio and Video: Cyber criminals boost phishing schemes by making AI-based videos or audio recordings of executives and colleagues which create more authentic phony communications[3].
Social Media Intelligence Gathering: The data AI collects automatically from LinkedIn alongside Facebook and Twitter enables its creation of believable messages[3].
The Advanced Version of Business Email Compromise (BEC) Runs Entirely on Automated Systems[4]. Technology produces authentic-seeming answers in real time which fools staff members of performing financial transfers or release secret company data.
Real-World Examples
Specific targeted phishing attacks known as spear phishing demonstrate their increasing danger through multiple public examples.
- A cybercriminal gang employed AI voice technology to create a fake CEO impersonation which led to employee compliance resulting in a $30 million money loss during the year 2015[5].
- Attackers took advantage of pandemic-related fears to construct AI-customized messages that seemed to originate from health authorities or work institutions[6].
Defense Strategies Against AI-Driven Spear Phishing Protection require
proactive cybersecurity defenses which organizations and users should implement because of growing AI threats.
1. Day-to-day cybersecurity training together with email phishing test programs enable the staff to understand how to identify and report security warnings in their emails.
2. The organizations should utilize AI-based tools in analyzing user behavior since these systems detect irregular email communications and send alerts.
3. MFA implementation creates protected access in that it creates several kinds of verification, preventing unwanted entry even when user credentials are compromised.
4. Every organization needs to use the Zero Trust Security Model by verifying user identities throughout system access while implementing strict access controls.
5. Real-time threat detection occurs through the service of monitoring and threat intelligence together with active system updates about spear phishing techniques.
Conclusion
The use of AI during spear phishing attacks has established them as a threat which security experts struggle to identify, and which has worsened in severity. Advancement in AI will drive attackers to discover fresh methods which exploit the technology for social engineering and cyber fraud. People and organizations need to maintain their guard up by investing in security functions with AI technology together with ongoing learning and sophisticated authentication systems to overcome sophisticated threats in their path. Rapid growth in AI-based cybercrime requires organizations to develop protected cybersecurity methods which adapt to new threats. Use of priority defense strategies with technological support together with awareness programs can help us confront AI spear phishing attacks and stop unauthorized access to sensitive information.
References
- OP Jindal University,Raigarh , Chhattisgarh and R. Tanti, “Study of Phishing Attack and their Prevention Techniques,” INTERANTIONAL J. Sci. Res. Eng. Manag., vol. 08, no. 10, pp. 1–8, Oct. 2024, doi: 10.55041/IJSREM38042.
- A. James, “AI and the Future of Spear Phishing,” Hut Six. Accessed: Feb. 11, 2025. [Online]. Available: https://www.hutsix.io/ai-and-the-future-of-spear-phishing
- S. J. Sohrawardi, Y. K. Wu, A. Hickerson, and M. Wright, “Dungeons & Deepfakes: Using scenario-based role-play to study journalists’ behavior towards using AI-based verification tools for video content,” in Proceedings of the CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Honolulu HI USA: ACM, May 2024, pp. 1–17. doi: 10.1145/3613904.3641973.
- A. Cidon, N. Korshun, M. Schweighauser, and A. Tsitkin, “High Precision Detection of Business Email Compromise”.
- trustpair_2438, “4 examples of spear phishing attacks,” Trustpair. Accessed: Feb. 11, 2025. [Online]. Available: https://trustpair.com/blog/4-examples-of-spear-phishing-attacks/
- R. Hoheisel, G. Van Capelleveen, D. K. Sarmah, and M. Junger, “The development of phishing during the COVID-19 pandemic: An analysis of over 1100 targeted domains,” Comput. Secur., vol. 128, p. 103158, May 2023, doi: 10.1016/j.cose.2023.103158.
- AI Safety and Security M Rahaman, P Pappachan, SM Orozco, S Bansal… – Challenges in Large Language Model Development …, 2024
- AlZu’bi, S., Shehab, M., Al-Ayyoub, M., Jararweh, Y., & Gupta, B. (2020). Parallel implementation for 3d medical volume fuzzy segmentation. Pattern Recognition Letters, 130, 312-318.
- Lu, J., Shen, J., Vijayakumar, P., & Gupta, B. B. (2021). Blockchain-based secure data storage protocol for sensors in the industrial internet of things. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 18(8), 5422-5431.
- Sravanthi B.S. (2024), Phishing Explained as A Comprehensive Guide to Different Types of Attacks from Email to Social Media Scams, Insights2Techinfo, pp.1
Cite As
Karthik V. (2025) Spear Phishing in the Age of AI : Personalized Attack on the Rise, Insights2techinfo pp.1