By: Vanna karthik; Vel Tech University, Chennai, India
Abstract
The rise of Ransom Distributed Denial of Service (RDDoS) attacks has become a top security threat that affects businesses together with financial establishments and government institutions. Attacks based on RDDoS behave differently from typical ransomware by sending overwhelming traffic to networks to get funds instead of performing data encryption. The paper examines RDDoS attacks starting from their emergence and reveals their operational methods and organizational effects. This research introduces multiple mitigation methods that involve advanced DDoS protection in addition to incident response planning and necessary law enforcement participation. The research demonstrates that prevention measures need to be adopted as a fundamental defense strategy to stop RDDoS attacks through robust cybersecurity protocols.
Introduction
The cybersecurity threat environment has witnessed the rise of Ransom Distributed Denial of Service (RDDoS) attacks which present a substantial challenge to worldwide business operations. The distinctive feature of RDDoS attacks sets them apart from ransomware incidents because they use high traffic amounts to shut down online services before demanding ransom payments for restoration. The attacks signal danger because they succeed through massive malicious traffic targeted at network infrastructure without needing any network breaches.
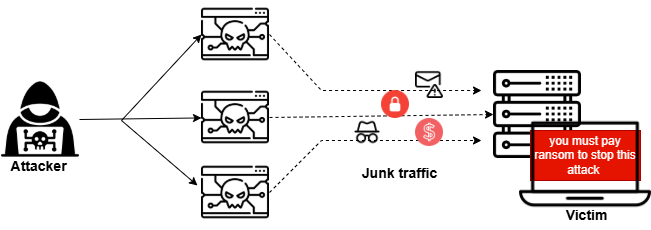
Understanding RDDoS attacks[1]
An RDDoS invasion tends to proceed in these consecutive stages.
1. Threat Notification functions as an initial stage where perpetrators warn targets about imminent large-scale DDoS attacks that can start after they refuse to pay ransom fees through cryptocurrency transactions.
2. Attackers frequently initiate small but strong DDoS attacks against their targets to prove their strength after warning the victim.
3. Attackers will prolong their attacks while they increase their efforts when ransom payments are not received. This type of attack campaign hurts business operations extensively for hours to days.
Recent trends in RDDoS attacks[2]
Sophisticated RDDoS attacks now use modern techniques which enhance their destructive capabilities during attacks. Key trends include:
Financial institutions as well as cloud service providers together with e-commerce platforms and government agencies comprise the main targets of these attacks since their online operations remain vital to their operations.
Attackers achieve broader attack effectiveness through their exploitation of vast compromised device networks that include IoT devices together with unprotected servers.
Criminals overcome traditional defenses by deploying three distinct advanced attack methods which include volumetric attacks and protocol-based attacks and application-layer attacks.
Some cybercriminals issue RDDoS threats to phony victim companies by making baseless ransom demands because they lack fundamental attack capabilities and are solely preying on businesses unprepared for such threats.
Case Studies of Notable RDDoS Attacks
Recent years have shown numerous prominent RDDoS attacks which have shown the serious consequences of this menace.
The financial institution experienced severe service disruptions and resulted in customer dissatisfaction after attackers hit with RDDoS attacks to demand Bitcoin payments[3].
Cloud service providers received ransom threats from hackers pretending to be established hacker organizations which compelled them to enhance their DDoS mitigation practices.
Lack of strong security defenses in smaller businesses created conditions for ransom payment to attackers which established an unsafe future attack strategy.
How to Protect Against RDDoS Attacks
Organizations need to take preventive security actions which effectively defend against DDOS attacks. Key protective measures include:
1. Implementing Strong DDoS Protection Measure
Organizations should integrate DDoS protection solutions from Cloudflare, AWS Shield, Akamai and Imperva which provide malicious traffic filtering and absorption services.
The network should use rate limiting and traffic filtering methods to stop attackers from attacking the network[3].
Stored anomaly detection technology provides identification of any unexpected traffic patterns which may signal an RDDoS attack.
2. Strengthening Incident Response Plans
The implementation of a detailed documented incident response plan should contain specific pre-defined measures to fight RDDoS attacks.
The organization should build an incident response team that receives cybersecurity incident response training as well as maintains service provider coordination abilities.
The organization should carry out frequent security drills which help maintain preparedness and fast response capabilities[4].
3. Educating Employees and Stakeholders[5]
The organization will instruct its IT personnel and all staff members about RDDoS attack recognition while also establishing security protocols.
The organization should notify shareholders and business partners about situations that could disrupt their operations while providing information about response plans to maintain trustworthy relationships.
4. Avoiding Ransom Payments
Financial ransom payments fail to guarantee the attack termination and tend to stimulate more attacks from hackers.
Report new cases of Distributed Denial of Service threats to appropriate law enforcement agencies along with cybersecurity organizations while implementing your existing defense strategies[4].
Conclusion
Businesses are increasingly in danger of financial loss and service interruptions due to RDDoS attacks, which constitute a serious and expanding cybersecurity concern. Organizations must proactively improve their cybersecurity frameworks as hackers continue to improve their attack methods. Effectively fighting RDDoS threats can be achieved by putting strong DDoS mitigation technologies into place, training stakeholders on cyberthreats, and encouraging cooperation with cybersecurity organizations. In order to identify and discourage cybercriminals engaged in RDDoS activities, future research should concentrate on creating AI-driven security systems and strengthening law enforcement activities.
References
- “What is Ransom DDoS (RDDoS) attack? Explanation ⚔️.” Accessed: Feb. 04, 2025. [Online]. Available: https://www.wallarm.com/what/ransom-ddos-rddos-attack
- “What is Ransom DDoS (RDDoS) | How it Works & Mitigation | Imperva,” Learning Center. Accessed: Feb. 04, 2025. [Online]. Available: https://www.imperva.com/learn/ddos/ransom-ddos-rddos/
- N. Ravichandran, T. Tewaraja, V. Rajasegaran, S. S. Kumar, S. K. L. Gunasekar, and S. R. Sindiramutty, “Comprehensive Review Analysis and Countermeasures for Cybersecurity Threats: DDoS, Ransomware, and Trojan Horse Attacks,” Sep. 20, 2024, Computer Science and Mathematics. doi: 10.20944/preprints202409.1369.v1.
- A. Farion-Melnyk, V. Rozheliuk, T. Slipchenko, S. Banakh, M. Farion, and O. Bilan, “Ransomware Attacks: Risks, Protection and Prevention Measures,” in 2021 11th International Conference on Advanced Computer Information Technologies (ACIT), Sep. 2021, pp. 473–478. doi: 10.1109/ACIT52158.2021.9548507.
- Siwar Qureshi, “Denial of Service (DoS) Attacks: Innovative Cybersecurity Solutions for Effective Attack Prevention,” 2024, Unpublished. doi: 10.13140/RG.2.2.24587.71200.
- Nguyen, G. N., Le Viet, N. H., Elhoseny, M., Shankar, K., Gupta, B. B., & Abd El-Latif, A. A. (2021). Secure blockchain enabled Cyber–physical systems in healthcare using deep belief network with ResNet model. Journal of parallel and distributed computing, 153, 150-160.
- Stergiou, C. L., Psannis, K. E., & Gupta, B. B. (2020). IoT-based big data secure management in the fog over a 6G wireless network. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 8(7), 5164-5171.
- Esposito, C., Ficco, M., & Gupta, B. B. (2021). Blockchain-based authentication and authorization for smart city applications. Information Processing & Management, 58(2), 102468.
- Reddy D.R.C. (2024) AI in Action: Securing Our Networks, Insights2Techinfo, pp.1
Cite As
Karthik V. (2025) The Rise of Ransom DDoS (RDDoS): A Growing Cybersecurity Threat, Insights2techinfo pp.1