By: D. Singla
Basic of Voice over IP (VoIP)
Voice over IP (VoIP) is an innovation that permits voice, video, and sound to be sent as information bundles across an IP organization, regardless of whether private or public. VoIP advancement is rapidly standing out and interest in the space because of the advantages it might give. Cost decreases, wide media limits, phone and organization smallness, flexibility, and combination with different applications are, for the most part, benefits of VoIP for the two customers and correspondence specialists as demonstrated in Figure 1.
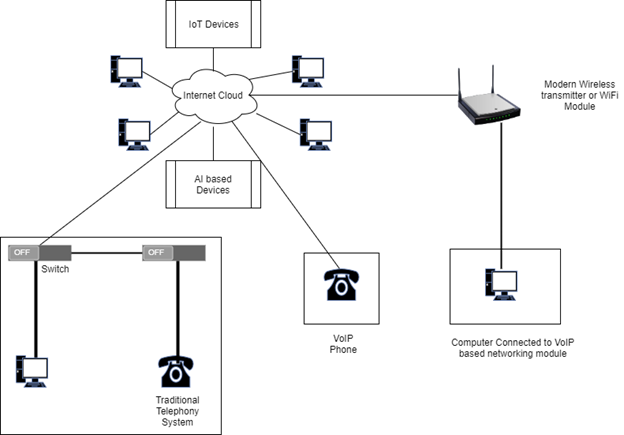
Voice over IP as Platform
At the point when we utilize an exemplary circuit-transmuted telephone to contact a partner’s office from yours, the call commences from the equipment around your work area, goes over one of a confined number of pathways on particular phone organizations, and emerges at a predetermined area-the circumventing telephone work area. VoIP calls are rudimentally pieces of information on the overall Internet. They are not bound to geological areas or explicit contraptions, because VoIP uses general guidelines, it can verbalize with any contrivance that upholds the Internet convention. It can peregrinate to an electronic mail inbox on a PC to a remote organization in any area of the planet similarly as promptly as it can to the telephone on that associate’s work area.
- The initial phase in building a VoIP stage is to introduce gadgets Converters, Programming, or Telephones, that workers see in their front office.
- VoIP programming and equipment design administer what capacities are offered, just as how VoIP gadgets speak with corporate IT frameworks [2].
- The initial phase in building a VoIP stage is to introduce front-office gadgets—the telephones, converters, or programming that workers visually perceive.
- The incipient VoIP programming and equipment design administer what capacities are offered, like how VoIP contrivances verbalize with corporate IT frameworks [2].
- Similarly, as static corporate Web destinations gave way to dynamic, intelligent, truly business-upgrading utilizations of the Internet 10 years prior, VoIP will fill in as an establishment for more essential correspondences that blend voice in with different information—supposed “united interchanges” [3].
- Consider VoIP’s potential as an essential instrument as far as three kinds of ability: Customization, Virtualization, and Intelligence.
Virtualization in Voice over IP
VoIP. With a couple of mouse clicks, it is likewise functional to make a help for a boundless number of telephones anyplace on the planet. This mix of compactness and versatility takes fixed and costly components of customary correspondences and makes them alterable and modest. It empowers organizations to set up minimal expense repetition to control hazards, and it gives organizations adaptable correspondences that can quickly respond to moving interests [4].
Customization in Voice over IP
The main advancements in conventional telephone network innovation (as shown in Figure 2), for example, guest ID and phone message, required a very long time to create and execute. New calling provisions or voice applications are easy to make and foster using VoIP. Albeit off-the-rack VoIP programming and gadgets offer a scope of functionalities, organizations are occupied with creating one-of-a-kind applications that might build up marking, further develop client care, and work on inner correspondences.

Intelligence
As these models show, organizations are now using VoIP’s customization and virtualization highlights, however, these are among the few that have advanced past straightforward expense cutting establishments. The best capability of VoIP will be acknowledged when organizations foster progressively modern frameworks to interface interchanges and business cycles and lift the efficiency of information laborers.
Some facts and myths about Voice over IP
- While the extraordinary greater part of individual organizations actually utilizes conventional telephones, around 10% of global telephone traffic presently streams over the Internet using voice over Internet convention, or VoIP [1].
- VoIP is more than essentially another innovation for making customary telephone discussions more reasonable.
- Its solidarity comes from the way that it changes over discourse into computerized information parcels that can be saved, blended, modified, copied, in with different information, and dispersed to almost any gadget that can associate with the Internet.
- Think of it as what could be compared to the World Wide Web (WWW).
- The term IP, or Internet convention, just alludes to the specialized rules that oversee how advanced information is encoded.
- Because of these mundane norms, VoIP might connect with other Internet-predicated information and frameworks progressively.
- Notwithstanding, think about this: Because VoIP changes over voice into Internet-accommodating information parcels, it can and will dislodge the firm, packaged telephone benefits that most organizations actually use.
- Also, because it will allow organizations to plan their own altered telephone applications, it will move control of telephone benefits from transporters who have customarily characterized (and controlled) them and toward the organizations that use them.
- VoIP will fill in as the binding system for such applications, empowering progressively custom-made, savvy, and vital voice conversations[5].
Conclusion
VoIP is coming. The key differentiation won’t be between the individuals who convey it and the people who don’t, or even between early adopters and loafers. Innovation will be a fight between the individuals who consider VoIP to be basically one more method for getting the normal, worn-out things done and other people who use it to totally rethink their organization.
References
- Article at: – https://hbr.org/2005/09/using-voip-to-compete.
- Vinokurov, D. & MacIntosh, R. W. (2005). Detection and mitigation of unwanted bulk calls (spam) in VoIP networks. US Patent No. US2005/ 0259667 A1. November 2005.
- VoIP Magazine Editorial Staff. (2005). ISS finds flaws in Cisco VoIP. Retrieved on December 20, 2007.
- William C.Hardy (2003). VoIP Service Quality Measuring and Evaluating Packet-Switched Voice. McGraw-Hill Networking.
- Y. Hanifan and Y. Bandung, “Designing VoIP security system for organizational network,” International Conference on ICT for Smart Society, 2013, pp. 1-5, doi: 10.1109/ICTSS.2013.6588074.
Cite this article as:
D. Singla (2021), Voice over IP (VoIP), Insights2Techinfo, pp.1
Also read:
- Smart Adoption of IoT in COVID-19 Pandemic paves new era of sustainable future world
- Moving Object Detection System: Wi-Vi
- Zero-Shot Temporal Activity Detection
- Virtual Personal Assistant
- CLASSIFICATION OF FUNGI MICROSCOPIC IMAGES – Leveraging the use of AI
- Humanoid Robots: The future of mankind